Inhibition of prolyl oligopeptidase by flavonoids isolated from the roots of Allexis obanensis (Baker f.) Melch
BIOMED Natural and Applied Science,1(2):39-44
- Author(s): Olivier Ndogo Eteme, Ernestine Nkwengoua Tchouboun Zondegoumba, Soh Desire, Oladimeji Taiwo Babatunde, and Barthelemy Nyasse
- September 5, 2021
- eISSN - 2789-178X
- Keywords - Allexis obanensis; Flavonoids; Prolyl oligopeptidase; Inhibition
Abstract
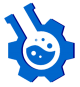
Background: Prolyl oligopeptidase is a cytosolic serine peptidase that hydrolyzes peptides containing proline at the carboxy terminus of proline residues. It has been associated with several neurodegenerative diseases. Therefore, it is a target in the management of these disease conditions. Methods: Allexis obanensis was taken through cold extraction, subjected to column chromatography and flavonoids isolated via high-performance liquid chromatographic technique. The flavonoids obtained were investigated for their in vitro prolyl oligopeptidase inhibitory activity. Results: The flavonoids isolated include: 4.4”’- dimethoxylophirone A [1] and 7-hydroxy-3-(3-hydroxy-4 méthoxyphenyl)-5-méthoxy-4H chromen-4-one [2]. They inhibited prolyl oligopeptidase at low IC50 concentrations of 7.201±3.021 µM and 6.223±2.002 µM respectively. Conclusion: The results obtained from this study proves the potential of these flavonoids as prolyl oligopeptidase inhibitors, by inference, their potentiality in the management of neuropsychiatric disorders.
Corresponding Author(s)
Olivier Ndogo Eteme; leptit.neo@gmail.com
Citations
Eteme, O.N., Zondegoumba, E.N.T., Desire, S., Babatunde, O.T., and Nyasse, B. (2021). Inhibition of prolyl oligopeptidase by flavonoids isolated from the roots of Allexis obanensis (Baker f.) Melch. BIOMED Natural and Applied Science,1(2):39-44, https://doi.org/10.53858/bnas01023944