CONYZA SCABRIDA HERBA - PlantZAfrica
CONYZA SCABRIDA HERBA - PlantZAfrica
CONYZA SCABRIDA HERBA - PlantZAfrica
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
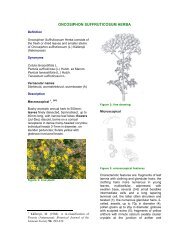
<strong>CONYZA</strong> <strong>SCABRIDA</strong> <strong>HERBA</strong>DefinitionConyza Scabrida Herba consists of the freshor dried leaves and smaller stems of Conyzascabrida DC (Asteraceae).SynonymsConyza ivifolia (L.) Less.Baccharis ivaefolia L.Vernacular namesoondbos, bakbos, paddabos (A)DescriptionMacroscopical 1Figure 2 – line drawingMicroscopicalfigure 1 – Live plantShrub to 1.2 metres high with pubescentstems; leaves borne on slender petioles upto 10mm long, up to 60 × 20mm, elliptic tolanceolate, 3-nerved from the base, marginssharply serrate, glabrous to pubescent;flowers borne in capitula less than 8mm indiameter, arranged in compact terminalcompound corymbs; outer ray florets female,inner disc forests hermaphrodite; fruit acompressed achene 1mm long; pappus ofwhitish scabrid bristles.1 Hilliard, O.M. (1977). Compositae in Natal: 86.University of Natal Press, Pietermaritzburg.Figure 3 – microscopical featuresCharacteristic features are: the thin-walledmulticellular clothing hairs of the leaf surfaceand margins, up to 240 microns long, oftenwith one cell collapsed, the apical celltapering sharply (1); the anomocytic stomataof both leaf surfaces (2); the epidermal cellsof the leaf lamina with striated cuticle,staining red with Sudan IV; the scattered
Methanol extract: (figure 6a)Retention times (mins): 18.16; 20.00; 20.55;24.54; 25.21DCM extract: (figure 6b)Retention times (mins): 2.26; 2.91Ethanol (70%) soluble extractive value: notless than 41.2% (range: 41.2 43.5%)Purity testsAssayNot yet availableMajor chemical constituentsThis herb is used as an external applicationto treat sores and inflammation and takeninternally for the relief of fever anddiarrhoea.Pharmacology/bioactivityLittle is known of the pharmacology of thisspecies. No in vitro antimicrobial activityagainst Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Candidaalbicans, Staphylococcus aureus orMycobacterium smegmatis was observed indisc assays of aqueous extracts conductedin our laboratories.ContraindicationsNone known.Adverse reactionsNone reported.PrecautionsNo special precautions.Figure 7 – chemical constituentsMicrochemical tests in our laboratoriesindicated the presence in this species ofcardiac glycosides, saponins and tanninsbut not alkaloids, cyanogens oranthraquinone derivatives. A number ofditerpene acids: conyscabraic acid,hautriwaic acid, nidoresedaic acid, printziaicacid and derivatives of these (figure 7) havebeen identified in the aerial parts of Conyzascabrida 2 .Dosage formsUsed mainly in the form of an aqueousinfusion, taken internally. The leaves may bemade into a poultice with vinegar andapplied locally.DosageEight tablespoonsful (±20g) of driedpowdered herb is infused until cold in onelitre (± 6 teacupfuls) of boiling water. Themixture is strained and taken in halfteacupful (90ml) doses three times daily.Copyright in this monograph resides with the authors, the SouthAfrican National Biodiversity Institute, the South African MedicalResearch Council and the University of the Western Cape. It maynot be reproduced in whole or in part without the written consent ofthe copyright holders.Medicinal uses2 Bohlmann, F., Grenz, M., Wegner, P. andJakupovic, J. (1983). Clerodendran derivativesand novel diterpenes from Conyza scabrida DC.Liebig’s Annals of Chemistry 11: 2008-2020.