Abstract
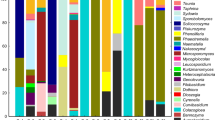
The present study was aimed at characterising species diversity of fungi inhabiting petroleum-contaminated soils of oil fields in a southern region of Iran. Two different techniques were used for fungal isolation including enrichment on atmospheres of phenolic hydrocarbons and crude oil as substrate. Phylogenetic analysis of the internal transcribed spacer of ribosomal DNA was used for taxonomic identification with additional information from the β-tubulin gene for selected taxa. Overall, 183 strains from 14 genera and five orders were obtained: Pleosporales (Alternaria, Curvularia, Stemphylium, Ulocladium), Chaetothyriales (Exophiala), Eurotiales (Aspergillus), Hypocreales (Acremonium, Emericellopsis, Sarocladium, Stachybotrys, Fusarium, Trichoderma, Beauveria), and Capnodiales (Cladosporium). The most frequently isolated strains belonged to the genera Alternaria, Exophiala and Aspergillus. The crude oil substrate was the most successful isolation method, and among the four hydrocarbon enrichments, toluene substrate yielded the highest number of strains. Enrichment on xylene and benzene also yielded herpotrichiellaceous and other filamentous fungi.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atlas RM (1992) Petroleum microbiology. Encyclopedia of Microbiology. Academic Press, Baltimore, pp 363–369
Atlas RM, Cerniglia CE (1995) Bioremediation of petroleum pollutants: diversity and environmental aspects of hydrocarbon biodegradation. Bioscience 45:332–338
Auria R, Frere G, Morales M, Acuna ME, Revah S (2000) Influence of mixing and water addition on the removal rate of toluene vapors in a biofilter. Biotechnol Bioeng 68:448–455
Brady NC, Weil RR (2001) The nature and properties of soils. Prentice-Hall, Englewood Cliffs
Cerniglia CE (1984) Microbial degradation of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Adv Appl Microbiol 30:31–71
Cerniglia CE, White GL, Heflich RH (1985) Fungal metabolism and detoxification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Arch Microbiol 143:105–110
Cerniglia CE, Sutherland JB, Crow SA (1992) Fungal metabolism of aromatic hydrocarbons. In: Winkelmann G (ed) Microbial degradation of natural products. VCH Press, Weinheim, pp 194–217
Chaudhry S, Luhach J, Sharma V, Sharma C (2012) Assessment of diesel degrading potential of fungal isolates from sludge contaminated soil of petroleum refinery, Haryana. Res J Microbiol 7:182–190
Chen M, Xu P, Zeng G, Yang C, Huang D, Zhang J (2015) Bioremediation of soils contaminated with polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons, petroleum, pesticides, chlorophenols and heavy metals by composting: applications, microbes and future research needs. Biotechnol Adv 33:745–755
Cox HHJ, Faber BW, Van Heiningen WNM, Radhoe H, Doddema HJ, Harder W (1996) Styrene metabolism in Exophiala jeanselmei and involvement of a cytochrome P-450-dependent styrene monooxygenase. Appl Environ Microbiol 62:1471–1474
Dawoodi V, Madani M, Tahmourespour A, Golshani Z (2015) The study of heterotrophic and crude oil-utilizing soil fungi in crude oil contaminated regions. J Bioremed Biodegrad 6:270
De Hoog GS (1997) Significance of fungal evolution for the understanding of their pathogenicity, illustrated with agents of phaeohyphomycosis. Mycoses 40:5–8
De Hoog GS (2014) Ecology and phylogeny of black yeast-like fungi: diversity in unexplored habitats. Fungal Divers 65:1–2
De Hoog GS, Haase G (1993) Nutritional physiology and selective isolation of Exophiala dermatitidis. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 64:17–26
De Hoog GS, Hermanides Nijhof EJ (1977) The black yeasts and allied hyphomycetes. Stud Mycol 15:1–222
Estevez E, Veiga MC, Kennes C (2005) Biodegradation of toluene by the new fungal isolates Paecilomyces variotii and Exophiala oligosperma. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 32:33–37
Fedorak PM, Westlake DW (1986) Fungal metabolism of n-alkylbenzenes. Appl Environ Microbiol 51:435–437
Flayyih I, AI-Jawhari HH (2014) Ability of some soil fungi in biodegradation of petroleum hydrocarbon. J Appl Environ Microbiol 2:46–52
Garcia Pena EI, Hernandez S, Favela Torres E, Auria R, Revah S (2001) Toluene biofiltration by the fungus Scedosporium apiospermum TB1. Biotechnol Bioeng 76:61–69
Gardes M, Bruns TD (1993) ITS primers with enhanced specificity for Basidiomycetes: application to the identification of mycorrhizae and rusts. Mol Ecol 2:113–118
Gorbushina AA, Whitehead K, Dornieden T, Niesse A, Schulte A, Hedges JI (2003) Black fungal colonies as units of survival: hyphal mycosporines synthesized by rock-dwelling microcolonial fungi. Can J Bot 81:131–138
Gorbushina AA, Kotlova ER, Sherstneva OA (2008) Cellular responses of microcolonial rock fungi to long-term desiccation and subsequent rehydration. Stud Mycol 61:91–97
Gunde Cimerman N, Zalar P, De Hoog GS, Plemenitas A (2000) Hypersaline water in salterns natural ecological niches for halophilic black yeasts. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 32:235–240
Hashem AR (2007) Bioremediation of petroleum contaminated soils in the Arabian Gulf region: a review. Kuwait J Sci 19:81–91
Hillis DM, Bull JJ (1993) An empirical test of bootstrapping as a method for assessing confidence in phylogenetic analysis. Syst Biol 42:182–192
Hohmann S, Mager WH (2003) Yeast stress responses. Springer, New York
Horre R, De Hoog GS (1999) Primary cerebral infections by melanized fungi: a review. Stud Mycol 43:176–193
Kim MJ, Lee H, Choi YS, Kim GH, Huh NY, Lee S, Lim YW, Lee SS, Kim JJ (2010) Diversity of fungi in creosote-treated crosstie wastes and their resistance to polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 97:377–387
Lee CC, Graig WK, Smith PJ (1974) Water-soluble hydrocarbons from crude oil. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 12:212–216
Maddison WP, Maddison DR (2011) Mesquite: a modular system for evolutionary analysis. Version 2.75. http://mesquiteproject.org
Mehlman MA (1992) Dangerous and cancer-causing properties of products and chemicals in the oil refining and petrochemical industry. VIII. Health effects of motor fuels: carcinogenicity of gasoline-scientific update. Environ Res 59:238–249
Middelhoven WJ (1993) Catabolism of benzene compounds by ascomycetous and basidiomycetous yeasts and yeast like fungi. A literature review and an experimental approach. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 63:125–144
Miller MA, Pfeiffer W, Schwartz T (2010) Creating the CIPRES Science Gateway for inference of large phylogenetic trees in Proceeding of Gateway Computing Environment Workshop (GCE), New Orleans, LA pp 1-8
Moye-Rowley WS (2003) Regulation of the transcriptional response to oxidative stress in fungi: similarities and differences. Eukaryot Cell 2:381–389
Muncnerova D, Augustin J (1994) Fungal metabolism and detoxification of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons: a review. Bioresour Technol 48:97–106
Obire O, Anyanwu EC, Okigbo RN (2008) Saprophytic and crude oil-degrading fungi from cow dung and poultry droppings as bioremediating agents. Int J Agric Technol 4:81–89
Onofri S, Zucconi L, Selbmann L, De Hoog GS, De Rios AL, Ruisi S, Grube M (2007) Fungal Association at the cold edge of life. In: Seckbach J (ed) Algae and cyanobacteria in extreme environments. Series cellular: origin life in extreme habitats and astrobiology. Springer, Berlin, pp 735–757
Paca J, Koutsky B, Maryska M, Halecky M (2001) Styrene degradation along the bed height of perlite biofilter. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 76:873–878
Palmer FE, Staley JT, Ryan B (1990) Ecophysiology of microcolonial fungi and lichens on rocks in Northeastern Oregon. New Phytol 116:613–620
Prenafeta Boldu FX, Kuhn A, Luykx DMAM, Anke H, Van Groenestijn JW, De Bont J (2001) Isolation and characterization of fungi growing on volatile aromatic hydrocarbons as their sole carbon and energy source. Mycol Res 105:477–484
Prenafeta Boldu FX, Summerbell RC, De Hoog GS (2006) Fungi growing on aromatic hydrocarbons: biotechnology’s unexpected encounter with biohazard? FEMS Microbiol Rev 30:109–130
Reyes-Cesar A, Absalon AE, Fernandez FJ, Gonzalez JM, Cortes-Espinosa DV (2014) Biodegradation of a mixture of PAHs by non-ligninolytic fungal strains isolated from crude oil-contaminated soil. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:999–1009
Ruibal C, Gueidan C, Selbmann L, Gorbushina AA, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Muggia L, Grube M, Isola CL, Schoch D, Staley JT, Lutzoni F, De Hoog GS (2009) Phylogeny of rock-inhabiting fungi related to Dothideomycetes. Stud Mycol 64:123–133
Satow MM, Attili Angelis D, De Hoog GS, Angelis DF, Vicente VA (2008) Selective factors involved in oil flotation isolation of black yeasts from the environment. Stud Mycol 61:157–163
Smits JP, van Sonsbeek HM, Rinzema A, Tramper J (1998) Solid-state fermentation- a mini review. Agro Food Ind High Tech 9:29–36
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Sterflinger K (1998) Temperature and NaCl-tolerance of rock-inhabiting meristematic fungi. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 74:271–281
Sudhadham M, Prakitsin S, Sivichai S, Chaiyarat R, Dorrestein GM, Menken SBJ, De Hoog GS (2008) The neurotropic black yeast Exophiala dermatitidis has a possible origin in the tropical rain forest. Stud Mycol 61:145–155
Swoboda-Colberg NG (1995) Chemical contamination of the environment: sources, types, and fate of synthetic organic chemicals. In: Young LY, Cerniglia CE (eds) Microbial transformations and degradation of toxic organic chemicals. Wiley-Liss, New York, pp 27–74
Van Hamme JD, Singh A, Ward OP (2003) Recent advances in petroleum microbiology. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev 67:503–549
Vicente VA, Angelis DA, Filho FQT, Pizzirani Kleiner AA (2001) Isolation of herpotrichiellaceous fungi from the environment. Braz J Microbiol 32:47–51
Vicente VA, Angelis DA, Pie MR, Queiros Telles F, Cruz LM, Najafzadeh MJ, De Hoog GS, Zhao J, Pizzirani Kleiner A (2008) Environmental isolation of black yeast-like fungi involved in human infection. Stud Mycol 61:136–144
Weber FJ, Hage KC, De Bont JAM (1995) Growth of the fungus Cladosporium sphaerospermum with toluene as the sole carbon and energy source. Appl Environ Microbiol 61:3562–3566
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfandm DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, New York, pp 315–322
Woertz JR, Kinney KA, McIntosh NDF, Szaniszlo PJ (2001) Removal of toluene in a vapour-phase bioreactor containing a strain of a dimorphic yeast Exophiala lecaniicorni. Biotechnol Bioeng 75:550–558
Wollenzien U, De Hoog GS, Krumbein WE, Uijthof JMJ (1997) Sarcinomyces petricola, a new microcolonial fungus from marble in the Mediterranean basin. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 71:281–288
Woo PCY, Ngan AHY, Tsang CCC, Ling IWH, Chan JFW, Leung S, Yuen K, Laua SKP (2013) Clinical spectrum of Exophiala infections and a novel Exophiala species, Exophiala hongkongensis. J Clin Microbiol 51:260–267
Zafra G, Absalon AE, Cuevas MC, Cortes Espinosa DV (2014) Isolation and selection of a highly tolerant microbial consortium with potential for PAH biodegradation from heavy crude oil contaminated soils. Water Air Soil Poll 225:1826
Zeng J, De Hoog GS (2008) Exophiala spinifera and its allies: diagnostics from morphology to DNA barcoding. Med Mycol 46:193–208
Zhao J, Zeng J, De Hoog GS, Attili Angelis D, Prenafeta Boldu FX (2010) Isolation and identification of black yeasts by enrichment on atmospheres of monoaromatic hydrocarbons. Microb Ecol 60:149–156
Acknowledgements
This work partially supported by an Ohio Agricultural Research and Development Center startup grant to Dr Jason C. Slot. We acknowledge the Research Deputy of the University of Tabriz, Iran. We are indebted to Dr Hannah T. Reynolds (Post-doctoral Research Associate at The Ohio State University) for technical assistance and critically reading the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mohammadian, E., Arzanlou, M. & Babai-Ahari, A. Diversity of culturable fungi inhabiting petroleum-contaminated soils in Southern Iran. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 110, 903–923 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0863-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-017-0863-1