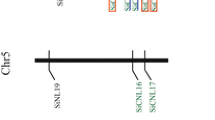
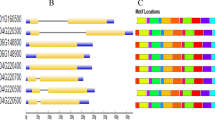
Abstract
Plants are constantly exposed to numerous biotic stresses; thus, they have evolved to defend themselves from their enemies such as pathogen or insect pests. Plant resistance (R) genes encoded by nucleotide binding site-leucine rich repeat (NBS-LRR) or LRR-containing transmembrane-receptor proteins play important roles in plant defense against various biotic stresses. In this paper, we report the identification of 308 R genes, including NBS-LRR, 175 genes encoding receptor-like kinases (RLKs) and 65 genes coding for receptor-like proteins (RLPs) in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] through genome-wide sequence analysis. Those genes were dispersed across all ten chromosomes of sorghum. Phylogenetic analysis of the newly identified NBS-LRR, RLP and RLK genes classified them into five, eleven, and six clades, respectively, of which region-specific subclades were established. Investigation of exon/intron organization demonstrates the variations in number and location of introns within the family, and the genes that evolved close to their originals share identical gene structures. Also, gene duplication was noted, including 142 pairs of duplicated genes in the NBS family, 12 RLK genes and one RLP gene, respectively. Chromosomal locations analysis of these newly-identified R genes and 17 published QTLs indicated two hot-spot regions referring resistance to at least two biotic stresses. Among those R genes, some of them showed significantly differential expression during the infestation by greenbug biotype I based on the expression profile. Particularly, three R genes were validated by quantitative real time PCR for their up-regulation in response to aphids. In summary, the results of this study contribute not only a valuable genetic resource for further functional characterization of those newly-identified R genes, but also provide insight into genetic improvement of sorghum for resistance to greenbug aphids.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ameline-Torregrosa C, Wang BB, O’Bleness MS, Deshpande S, Zhu H, Roe B, Young ND, Cannon SB (2008) Identification and characterization of nucleotide-binding site-leucine-rich repeat genes in the model plant Medicago truncatula. Plant Physiol 146:5–21. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.107.104588
Ananieva EA, Gillaspy GE, Ely A, Burnette RN, Erickson FL (2008) Interaction of the WD40 domain of a myoinositol polyphosphate 5-phosphatase with SnRK1 links inositol, sugar, and stress signaling. Plant Physiol 148:1868–1882. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.130575
Apotikar DB, Venkateswarlu D, Ghorade RB, Wadaskar RM, Patil JV, Kulwal PL (2011) Mapping of shoot fly tolerance loci in Sorghum using SSR markers. J Genet 90:59–66. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12041-011-0046-1
Belfanti E, Silfverberg-Dilworth E, Tartarini S, Patocchi A, Barbieri M, Zhu J, Vinatzer BA, Gianfranceschi L, Gessler C, Sansavini S (2004) The HcrVf2 gene from a wild apple confers scab resistance to a transgenic cultivated variety. PNAS 101:886–890. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0304808101
Dangl JL, Jones JD (2001) Plant pathogens and integrated defence responses to infection. Nature 411:826–833. https://doi.org/10.1038/35081161
DeYoung BJ, Innes RW (2006) Plant NBS-LRR proteins in pathogen sensing and host defense. Nat Immunol 7:1243–1249. https://doi.org/10.1038/ni1410
Foyer CH, Verrall SR, Hancock RD (2014) Systematic analysis of phloem-feeding insect-induced transcriptional reprogramming in Arabidopsis highlights common features and reveals distinct responses to specialist and generalist insects. J Exp Bot 66:495–512
Fritz-Laylin LK, Krishnamurthy N, Tör M, Sjölander KV, Jones JD (2005) Phylogenomic analysis of the receptor-like proteins of rice and Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 138:611–623. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.104.054452
Garcia A, Santamaria ME, Diaz I, Martinez M (2021) Disentangling transcriptional responses in plant defense against arthropod herbivores. Sci Rep 11:12996. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-92468-6
Gómez-Gómez L, Boller T (2000) FLS2: an LRR receptor–like kinase involved in the perception of the bacterial elicitor flagellin in Arabidopsis. Mol Cell 5:1003–1011. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1097-2765(00)80265-8
Huang Y (2006) Evaluating Sorghum germplasm for resistance to greenbug (Schizaphis graminum) biotype I. Int Sorghum Millet Newsl 47:72–74
Huang Y (2011) Improvement of crop protection against greenbug using the worldwide Sorghum germplasm collection and genomics-based approaches. Plant Genet Resour 9:317–320. https://doi.org/10.1017/s1479262111000633
Jones DA, Thomas CM, Hammond-Kosack KE, Balint-Kurti PJ, Jones JD (1994) Isolation of the tomato Cf-9 gene for resistance to Cladosporium fulvum by transposon tagging. Science 266:789–793. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.7973631
Karve R, Liu W, Willet SG, Torii KU, Shpak ED (2011) The presence of multiple introns is essential for ERECTA expression in Arabidopsis. RNA 17:1907–1921. https://doi.org/10.1261/rna.2825811
Kozik A, Kochetkova E, Michelmore R (2002) GenomePixelizer—a visualization program for comparative genomics within and between species. Bioinformatics 18:335–336. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/18.2.335
Krogh A, Larsson B, Von Heijne G, Sonnhammer EL (2001) Predicting transmembrane protein topology with a hidden Markov model: application to complete genomes. J Mol Biol 305:567–580. https://doi.org/10.1006/jmbi.2000.4315
Krzywinski M, Schein J, Birol I, Connors J, Gascoyne R, Horsman D, Jones SJ, Marra MA (2009) Circos: an information aesthetic for comparative genomics. Genome Res 19:1639–1645. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.092759.109
Larkan NJ, Lydiate DJ, Parkin IA, Nelson MN, Epp DJ, Cowling WA, Rimmer SR, Borhan MH (2013) The B rassica napus blackleg resistance gene LepR3 encodes a receptor-like protein triggered by the L eptosphaeria maculans effector AVRLM 1. New Phytol 197:595–605. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12043
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btm404
Leister RT, Katagiri F (2000) A resistance gene product of the nucleotide binding site—leucine rich repeats class can form a complex with bacterial avirulence proteins in vivo. Plant J 22:345–354. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-313x.2000.00744.x
Leister D, Kurth J, Laurie DA, Yano M, Sasaki T, Devos K, Graner A, Schulze-Lefert P (1998) Rapid reorganization of resistance gene homologues in cereal genomes. PNAS 95:370–375. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.1.370
Li H, Huang Y (2017) Expression of brown-midrib in a spontaneous sorghum mutant is linked to a 5′-UTR deletion in lignin biosynthesis gene SbCAD2. Scien Rep 7:11664. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-10119-1
Liu PL, Du L, Huang Y, Gao SM, Yu M (2017) Origin and diversification of leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase (LRR-RLK) genes in plants. BMC Evol Biol 17:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12862-017-0891-5
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2-ΔΔCT method. Methods 25:402–408. https://doi.org/10.1006/meth.2001.1262
Logemann E, Birkenbihl RP, Rawat V, Schneeberger K, Schmelzer E (2013) Somssich IE. Functional dissection of the PROPEP2 and PROPEP3 promoters reveals the importance of WRKY factors in mediating microbe-associated molecular pattern-induced expression. New Phytol 198:1165–1177. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.12233
Mace E, Tai S, Innes D, Godwin I, Hu W, Campbell B, Gilding E, Cruickshank A, Prentis P, Wang J, Jordan D (2014) The plasticity of NBS resistance genes in sorghum is driven by multiple evolutionary processes. BMC Plant Biol 14:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-014-0253-z
Man J, Gallagher JP, Bartlett M (2020) Structural evolution drives diversification of the large LRR-RLK gene family. New Phytol 226:1492–1505. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.16455
Meyers BC, Kozik A, Griego A, Kuang H, Michelmore RW (2003) Genome-wide analysis of NBS-LRR–encoding genes in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 15:809–834. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.009308
Mohan SM, Madhusudhana R, Mathur K, Howarth CJ, Srinivas G, Satish K, Reddy RN, Seetharama N (2009) Co-localization of quantitative trait loci for foliar disease resistance in sorghum. Plant Breed 128:532–535. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0523.2008.01610.x
Nagy ED, Lee TC, Ramakrishna W, Xu Z, Klein PE, SanMiguel P, Cheng CP, Li J, Devos KM, Schertz K, Dunkle L (2007) Fine mapping of the Pc locus of Sorghum bicolor, a gene controlling the reaction to a fungal pathogen and its host-selective toxin. Theor Appl Genet 114:961–970. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-006-0481-1
Niu L, Pan L, Zeng W, Lu Z, Cui G, Fan M, Xu Q, Wang Z, Li G (2018) Dynamic transcriptomes of resistant and susceptible peach lines after infestation by green peach aphids (Myzus persicae Sülzer) reveal defence responses controlled by the Rm3 locus. BMC Genomics 19:846
Noutoshi Y, Ito T, Seki M, Nakashita H, Yoshida S, Marco Y, Shirasu K, Shinozaki K (2005) A single amino acid insertion in the WRKY domain of the Arabidopsis TIR–NBS–LRR–WRKY-type disease resistance protein SLH1 (sensitive to low humidity 1) causes activation of defense responses and hypersensitive cell death. Plant J 43:873–888. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313x.2005.02500.x
Osuna-Cruz CM, Paytuvi-Gallart A, Di Donato A, Sundesha V, Andolfo G, Aiese Cigliano R, Sanseverino W, Ercolano MR (2018) PRGdb 3.0: a comprehensive platform for prediction and analysis of plant disease resistance genes. Nucleic Acids Res 46:D1197–D1201. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx1119
Park S, Shi A, Mou B (2020) Genome-wide identification and expression analysis of the CBF/DREB1 gene family in lettuce. Sci Rep 10:5733. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-62458-15
Paterson AH, Bowers JE, Bruggmann R, Dubchak I, Grimwood J, Gundlach H, Haberer G, Hellsten U, Mitros T, Poliakov A, Schmutz J (2009) The Sorghum bicolor genome and the diversification of grasses. Nature 457:551–556. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature07723
Periyannan S, Moore J, Ayliffe M, Bansal U, Wang X, Huang L, Deal K, Luo M, Kong X, Bariana H, Mago R (2013) The gene Sr33, an ortholog of barley Mla genes, encodes resistance to wheat stem rust race Ug99. Science 341:786–788. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1239028
Punnuri S, Huang Y (2017) Identification and confirmation of greenbug resistance loci in an advanced mapping population of Sorghum. J Agric Sci 155:1610–1622. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0021859617000685
Punnuri S, Huang Y, Steets J, Wu Y (2013) Developing new markers and QTL mapping for greenbug resistance in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Euphytica 191:191–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-012-0755-4
Reddy PS, Fakrudin B, Punnuri SM, Arun SS, Kuruvinashetti MS, Das IK, Seetharama N (2008) Molecular mapping of genomic regions harboring QTLs for stalk rot resistance in Sorghum. Euphytica 159:191–198. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10681-007-9472-9
Rossi M, Goggin FL, Milligan SB, Kaloshian I, Ullman DE, Williamson VM (1998) The nematode resistance gene Mi of tomato confers resistance against the potato aphid. PNAS 95:9750–9754. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.95.17.9750
Saintenac C, Zhang W, Salcedo A, Rouse MN, Trick HN, Akhunov E, Dubcovsky J (2013) Identification of wheat gene Sr35 that confers resistance to Ug99 stem rust race group. Science 341:783–786. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1239022
Satish K, Srinivas G, Madhusudhana R, Padmaja PG, Reddy RN, Mohan SM, Seetharama N (2009) Identification of quantitative trait loci for resistance to shoot fly in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Theor Appl Genet 119:1425–1439. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-009-1145-8
Tameling WI, Elzinga SD, Darmin PS, Vossen JH, Takken FL, Haring MA, Cornelissen BJ (2002) The tomato R gene products I-2 and MI-1 are functional ATP binding proteins with ATPase activity. Plant Cell 14:2929–2939. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.005793
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S (2007) MEGA4: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol 24:1596–1599. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msm092
Tamura Y, Hattori M, Yoshioka H, Yoshioka M, Takahashi A, Wu J, Sentoku N, Yasui H (2014) Map-based cloning and characterization of a brown planthopper resistance gene BPH26 from Oryza sativa L. ssp. indica cultivar ADR52. Sci Rep 4:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep05872
Tan S, Wu S (2012) Genome wide analysis of nucleotide-binding site disease resistance genes in Brachypodium distachyon. Comp Funct Genomics 2012:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/418208
Thomas CM, Jones DA, Parniske M, Harrison K, Balint-Kurti PJ, Hatzixanthis K, Jones JD (1997) Characterization of the tomato Cf-4 gene for resistance to Cladosporium fulvum identifies sequences that determine recognitional specificity in Cf-4 and Cf-9. Plant Cell 9:2209–2224. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.9.12.2209
Wan H, Yuan W, Bo K, Shen J, Pang X, Chen J (2013) Genome-wide analysis of NBS-encoding disease resistance genes in Cucumis sativus and phylogenetic study of NBS-encoding genes in Cucurbitaceae crops. BMC Genomics 14:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-14-109
Wang G, Ellendorff U, Kemp B, Mansfield JW, Forsyth A, Mitchell K, Bastas K, Liu CM, Woods-Tor A, Zipfel C, De Wit PJ (2008) A genome-wide functional investigation into the roles of receptor-like proteins in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 147:503–517. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.119487
Wang X, Tang H, Bowers JE, Paterson AH (2009) Comparative inference of illegitimate recombination between rice and sorghum duplicated genes produced by polyploidization. Genome Res 19:1026–1032. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.087288.108
Wang J, Hu T, Wang W, Hu H, Wei Q, Bao C (2019) Investigation of evolutionary and expressional relationships in the function of the leucine-rich repeat receptor-like protein kinase gene family (LRR-RLK) in the radish (Raphanus sativus L.). Sci Rep 9:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-43516-9
Wu Y, Huang Y (2008) Molecular mapping of QTLs for resistance to the greenbug Schizaphis graminum (Rondani) in Sorghum bicolor (Moench). Theor Appl Genet 117:117–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00122-008-0757-8
Wu YQ, Huang Y, Porter DR, Tauer CG, Hollaway L (2007) Identification of a major quantitative trait locus conditioning resistance to greenbug biotype E in sorghum PI 550610 using simple sequence repeat markers. J Econ Entomol 100:1672–1678. https://doi.org/10.1093/jee/100.5.1672
Yu J, Tehrim S, Zhang F, Tong C, Huang J, Cheng X, Dong C, Zhou Y, Qin R, Hua W, Liu S (2014) Genome-wide comparative analysis of NBS-encoding genes between Brassica species and Arabidopsis thaliana. BMC Genomics 15:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-15-3
Zhou T, Wang Y, Chen JQ, Araki H, Jing Z, Jiang K, Shen J, Tian D (2004) Genome-wide identification of NBS genes in japonica rice reveals significant expansion of divergent non-TIR NBS-LRR genes. Mol Genet Genomics 271:402–415. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00438-004-0990-z
Acknowledgements
We thank Ms. Angela L. Phillips for her excellent technical assistance. This research was supported by the funding from the United States Department of Agriculture—Agricultural Research Service, CRIS project number: 3072–21000–009–00D (YH). USDA is an equal opportunity provider and employer. Mention of trade names or commercial products in this publication is solely for the purpose of providing specific information and does not imply recommendation or endorsement by the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YH designed the research and supervised the entire study, HZ and JH performed genome analysis and all experiments, all authors contributed to interpretation of the data, discussion of the results and wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interests.
Additional information
Communicated by Dawei Xue.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, H., Huang, J. & Huang, Y. Identification and characterization of plant resistance genes (R genes) in sorghum and their involvement in plant defense against aphids. Plant Growth Regul 96, 443–461 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-022-00797-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10725-022-00797-x