Abstract
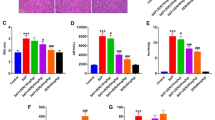
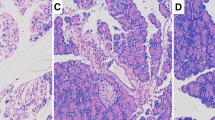
We investigated the effects of Baicalin and Octreotide on the levels of endotoxin and TNF-α in blood and the effects of apoptotic changes in multiple organs of SAP rats, and explored the underlying therapeutic mechanisms of Baicalin and Octreotide. In this study, 135 SAP rats were randomly divided into model control, Baicalin treated and Octreotide treated group (n = 45), respectively, the same number of normal rats were included in sham-operated group (n = 45). The above-mentioned groups were further subdivided into 3, 6 and 12 h subgroups, respectively (15 rats in each subgroup). At 3, 6 and 12 h after operation, the mortality rate of rats, endotoxin and TNF-α levels in blood as well as the pathological severity scores, expression levels of Bax protein and apoptosis indexes in multiple organs were determined. Compared to model control group (1),both drugs can relieve the pathological injuries of multiple organs and decrease significantly the levels of endotoxin and TNF-α in blood and the mortality rate of rats in treated groups (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01); (2) the expression of Bax protein was upregulated in pancreas, lung, intestinal mucosa (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01) but downregulated in spleen and lymph nodes (P < 0.001 and P < 0.05, respectively) in Baicalin treated group; The apoptosis indexes significantly increased in pancreas, intestinal mucosa, lymph nodes and spleen (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). (3) the expression of Bax protein was upregulated in pancreas and lung but downregulated in spleen and lymph nodes (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01) in Octreotide treated group; The apoptosis indexes significantly increased in lymph nodes and spleen in Octreotide treated group (P < 0.05 or P < 0.01). Baicalin and Octreotide share a similar therapeutic efficacy in the treatment of SAP via a mechanism that is associated with inhibiting the levels of TNF-α in blood and induce apoptosis in multiple organs.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al Mofleh, I. A. 2008. Severe acute pancreatitis: pathogenetic aspects and prognostic factors. World J. Gastroenterol. 14(5):675–684 Review. PMID: 18205255. doi:10.3748/wjg.14.675.
Ioannidis, O., A. Lavrentieva, and D. Botsios. 2008. Nutrition support in acute pancreatitis. JOP J. Pancreas. 9(4):375–390 Review. PMID: 18648127.
Christophi, C., I. Millar, M. Nikfarjam, V. Muralidharan, and C. Malcontenti-Wilson. 2007. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy for severe acute pancreatitis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 22(11):2042–2046 PMID: 17914992. doi:10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.03380.x.
Panek, J., J. Zasada, and M. Poniczek. 2007. Microcirculatory disturbance in the course of acute pancreatitis. Prz. Lek. 64(6):435–437 Review. Polish.
Schneider, L., M. Pietschmann, W. Hartwig, S. S. Marcos, T. Hackert, M. M. Gebhard, W. Uhl, M. W. Büchler, and J. Werner. 2006. Inosine reduces microcirculatory disturbance and inflammatory organ injury in experimental acute pancreatitis in rats. Am. J. Surg. 191(4):510–514 PMID: 16531145. doi:10.1016/j.amjsurg.2005.09.009.
Zhang, X. P., Q. Lin, and Y. F. Zhou. 2007. Progress of study on the relationship between mediators of inflammation and apoptosis in acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 52(5):1199–1205 Review. PMID: 17372825. doi:10.1007/s10620-006-9388-6.
Chan, Y. C., and P. S. Leung. 2007. Acute pancreatitis: animal models and recent advances in basic research. Pancreas. 34(1):1–14 PMID:17198179. doi:10.1097/01.mpa.0000246658.38375.04.
Dimagno, M. J., and E. P. Dimagno. 2007. New advances in acute pancreatitis. Curr. Opin. Gastroenterol. 23(5):494–501 PMID:17762554.
Zhang, X. P., L. Chen, Q. F. Hu, H. Tian, R. J. Xu, Z. W. Wang, K. Y. Wang, Q. H. Cheng, W. Yan, Y. Li, Q. Y. Li, Q. He, and F. Wang. 2007. Effects of large dose of Dexamethasone on inflammatory mediators and pancreatic cell apoptosis of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(41):5506–5511 PMID: 17907297.
Zhang, X. P., L. Zhang, L. J. Chen, Q. H. Cheng, J. M. Wang, W. Cai, H. P. Shen, and J. Cai. 2007. Influence of Dexamethasone on inflammatory mediators and NF-kappaB expression in multiple organs of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(4):548–556 PMID: 17278220. doi:10.3748/wjg.13.6385.
Nikou, G. C., T. P. Amaoutis, E. J. Giamarellos-Bourboulis, O. Samolada, I. Vafiadis-Zouboulis, N. Katsilambros, and C. Arvanitakis. 2001. The significance of the dosage adjustment of Octreotide in the treatment of acute pancreatitis of moderate severity. Hepatogastroenterology. 48(42):1754–1757 PMID:11813617.
Bagnenko, S. F., N. V. Rukhliada, A. D. Tolstoi, V. R. Gol'tsov, and V. E. Nazarov. 2002. Comparative characteristics of Octreotide and famotidine in the treatment of acute pancreatitis. Vestn. Khir. Im. I. I. Grek. 161(6):26–29 PMID:12638487.
Zhang, X., H. Tian, and Q. Cheng. 2003. The current situation in pharmacological study on Baicalin. Chin. Pharmacol. Bull. 19(11):1212–1215.
Liu, L. L., L. K. Gong, H. Wang, Y. Xiao, X. F. Wu, Y. H. Zhang, X. Xue, X. M. Qi, and J. Ren. 2008. Baicalin inhibits macrophage activation by lipopolysaccharide and protects mice from endotoxin shock. Biochem. Pharmacol. 75:914–922 PMID:18191816. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2007.10.009.
Zhu, Y. 1993. The study on baicalin in China. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi. 13(9):567–569 in Chinese. PMID: 8111218.
Zhang, X. P., L. Zhang, P. Yang, R. P. Zhang, and Q. H. Cheng. 2007. Protective effects of Baicalin and Octreotide on multiple organ injury in severe acute pancreatitis. Dig. Dis. Sci. 53(2):581–591 [PMID:17549629].
Zhang, X. P., L. Zhang, J. X. He, R. P. Zhang, Q. H. Cheng, Y. F. Zhou, and B. Lu. 2007. Experimental study of therapeutic efficacy of Baicalin in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(5):717–724 PMID:17278194.
Zhang, X. P., H. Tian, Y. H. Lai, L. Chen, L. Zhang, Q. H. Cheng, W. Yan, Y. Li, Q. Y. Li, Q. He, and F. Wang. 2007. Protecting effects and mechanism of Baicalin and Octreotide on renal injury of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(38):5079–5089 PMID: 17876873.
Xiping, Z., T. Hua, C. Hanqing, C. Li, W. Zhiwei, W. Keyi, Y. Wei, L. Yun, L. Qingyu, H. Qing, and W. Fei. 2007. The protecting effects and mechanisms of Baicalin and Octreotide on heart injury in rats with SAP. Mediat. Inflamm. 2007:19469 [PMID:18274634].
Zhang, X. P., H. M. Xu, Y. Y. Jiang, S. Yu, Y. Cai, B. Lu, Q. Xie, and T. F. Ju. 2008. Influence of dexamethasone on mesenteric lymph node of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 14(22):3511–3517 PMID:18567079. doi:10.3748/wjg.14.3511.
Liu, H., W. Li, X. Wang, J. Li, and W. Yu. 2008. Early gut mucosal dysfunction in patients with acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 36(2):192–196 PMID: 18376312. doi:10.1097/MPA.0b013e31815a399f.
Pastor, C. M., J. Pugin, B. Kwak, M. Chanson, F. Mach, A. Hadengue, and J. L. Frossard. 2004. Role of Toll-like receptor 4 on pancreatic and pulmonary injury in a mice model of acute pancreatitis associated with endotoxemia. Crit. Care Med. 32(8):1759–1763 PMID: 15286555. doi:10.1097/01.CCM.0000133020.47243.8E.
Zhang, X. P., J. Zhang, Q. L. Song, and H. Q. Chen. 2007. Mechanism of acute pancreatitis complicated with injury of intestinal mucosa barrier. J. Zhejiang Univ. Sci. B. 8(12):888–895 PMID: 18257123. doi:10.1631/jzus.2007.B0888.
Alsfasser, G., B. Antoniu, S. P. Thayer, A. L. Warshaw, and C. Fernández-del Castillo. 2005. Degradation and inactivation of plasma tumor necrosis factor-alpha by pancreatic proteases in experimental acute pancreatitis. Pancreatology. 5(1):37–43 PMID:15775698. doi:10.1159/000084489.
Dianliang, Z., L. Jieshou, J. Zhiwei, and Y. Baojun. 2003. Association of plasma levels of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha and its soluble receptors, two polymorphisms of the TNF gene, with acute severe pancreatitis and early septic shock due to it. Pancreas. 26(4):339–343 PMID: 12717265. doi:10.1097/00006676-200305000-00005.
Wang, X., B. Wang, K. Wu, M. Xu, and Z. Gong. 2002. Growth hormone downregulated the excessive apoptosis of ileal intestinal epithelial cells in rats during the early course of acute necrotizing pancreatitis. Pancreas. 25(2):205–209 PMID: 12142747. doi:10.1097/00006676-200208000-00016.
Leindler, L., E. Morschl, F. László, Y. Mándi, T. Takács, K. Jármai, and G. Farkas. 2004. Importance of cytokines, nitric oxide, and apoptosis in the pathological process of necrotizing pancreatitis in rats. Pancreas. 29(2):157–161 PMID: 15257108. doi:10.1097/00006676-200408000-00011.
Yuan, Y. Z., Z. H. Gong, K. X. Lou, S. P. Tu, Z. K. Zhai, and J. Y. Xu. 2000. Involvement of apoptosis of alveolar epithelial cells in acute pancreatitis-associated lung injury. World J. Gastroenterol. 6(6):920–924 No abstract available.
Takeyama, Y. 2005. Significance of apoptotic cell death in systemic complications with severe acute pancreatitis. J Gastroenterol. 40(1):1–10 PMID:15692783. doi:10.1007/s00535-004-1505-8.
Zhao, M., D. B. Xue, B. Zheng, W. H. Zhang, S. H. Pan, and B. Sun. 2007. Induction of apoptosis by artemisinin relieving the severity of inflammation in caerulein-induced acute pancreatitis. World J. Gastroenterol. 13(42):5612–5617 PMID: 17948936.
Takase, K., Y. Takeyama, J. Nishikawa, T. Ueda, Y. Hori, M. Yamamoto, and Y. Kuroda. 1999. Apoptotic cell death of renal tubules in experimental severe acute pancreatitis. Surgery. 125(4):411–420 PMID:10216532.
Nakajima, T., T. Ueda, Y. Takeyama, T. Yasuda, M. Shinzeki, H. Sawa, and Y. Kuroda. 2007. Protective effects of vascular endothelial growth factor on intestinal epithelial apoptosis and bacterial translocation in experimental severe acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 34(4):410–416 PMID: 17446839. doi:10.1097/mpa.0b013e3180335c64.
Chen, H. M., J. T. Hsu, J. C. Chen, C. J. Ng, D. F. Chiu, and M. F. Chen. 2005. Delayed neutrophil apoptosis attenuated by melatonin in human acute pancreatitis. Pancreas. 31(4):360–364 PMID:16258371. doi:10.1097/01.mpa.0000180905.05494.9a.
Kataoka, K., H. Yasuda, and J. Sakagami. 2004. Role of apoptosis in severe acute pancreatitis. Nippon Rinsho. 62(11):2021–2026 Review. Japanese.
Liu, X. M., J. Xu, and Z. F. Wang. 2005. Pathogenesis of acute lung injury in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 4(4):614–617 PMID: 16286275.
Muñoz-Casares, F. C., F. J. Padillo, J. Briceño, J. A. Collado, J. R. Muñoz-Castañeda, R. Ortega, A. Cruz, I. Túnez, P. Montilla, C. Pera, and J. Muntané. 2006. Melatonin reduces apoptosis and necrosis induced by ischemia/reperfusion injury of the pancreas. J. Pineal Res. 40(3):195–203 PMID: 16499554. doi:10.1111/j.1600-079X.2005.00291.x.
Hauck, L., G. Hansmann, R. Dietz, and R. von Harsdorf. 2002. Inhibition of hypoxia-induced apoptosis by modulation of retinoblastoma protein-dependent signaling in cardiomyocytes. Circ. Res. 91:782–789 PMID:12411392. doi:10.1161/01.RES.0000041030.98642.41.
von Harsdorf, R., P. F. Li, and R. Dietz. 1999. Signaling pathways in reactive oxygen species-induced cardiomyocyte apoptosis. Circulation. 99:2934–2941 PMID:10359739.
Stangl, V., G. Baumann, K. Stangl, and S. B. Felix. 2002. Negative inotropic mediators released from the heart after myocardial ischaemia-reperfusion. Cardiovasc. Res. 53:12–30 PMID:11744010. doi:10.1016/S0008-6363(01)00420-5.
Fang, H., Y. B. Feng, and Y. Fang. 2005. Mechanism by which activation of α1-adrenoceptor before ischemia controls myocardial apoptosis. Chin. J. Pathophysiol. 21:714–717 in Chinese.
Yasuda, H., K. Kataoka, H. Ichimura, M. Mitsuyoshi, T. Iida, M. Kita, and J. Imanishi. 1999. Cytokine expression and induction of acinar cell apoptosis after pancreatic duct ligation in mice. J. Interferon Cytokine Res. 19(6):637–644 PMID:10433365. doi:10.1089/107999099313785.
Gu, J. C., Y. Wang, Z. T. Zhang, J. G. Xue, J. S. Li, and Y. Z. Zhou. 2005. Effects of human interleukin 10 gene transfer on the expression of Bcl-2 Bax and apoptosis of hepatocyte in rats with acute hemorrhagic necrotizing pancreatitis. Chin. Med. J. (Engl). 118(19):1658–1660 PMID: 16232353.
Gomez, G., H. M. Lee, Q. He, E. W. Englander, T. Uchida, and G. H. Greeley Jr. 2001. Acute pancreatitis signals activation of apoptosis-associated and survival genes in mice. Exp. Biol. Med. (Maywood). 226(7):692–700 PMID: 11444106.
Yuan, Y., Z. Gong, K. Lou, S. Tu, Z. Di, and J. Xu. 2001. Effects and mechanisms of somatostatin analogs on apoptosis of pancreatic acinar cells in acute pancreatitis in mice. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 16(6):683–688 PMID: 11422623. doi:10.1046/j.1440-1746.2001.02499.x.
Hirota, M., H. Sugita, K. Maeda, A. Ichibara, and M. Ogawa. 2004. Concept of SIRS and severe acute pancreatitis. Nippon Rinsho. 62:2128–2136 PMID:15552899.
Zhang, X. P., H. Tian, D. J. Wu, G. H. Feng, L. Chen, J. Zhang, R. J. Xu, Y. Cai, T. F. Ju, and Q. Xie. 2009. Pathological changes in multiple organs of rats with severe acute pancreatitis treated by Baicalin and Octreotide. Hepatobiliary Pancreat. Dis. Int. 8(1):85–92 PMID: 19208522.
Xiping, Z., Z. Jie, X. Qin, F. Guanghua, C. Yang, J. Tongfa, and X. Qi. 2009. Influence of Baicalin and Octreotide on NF-kappaB and P-Selectin expression in liver and kidney of rats with severe acute pancreatitis. Inflammation. 32(1):1–11 PMID: 19030975. doi:10.1007/s10753-008-9096-9.
Zhang, X. P., H. Tian, H. Q. Chen, L. Chen, B. Y. Yu, and J. Ma. 2009. Effects of Baicalin and Octreotide on inflammatory mediators and pancreatic acinar cell apoptosis in rats with severe acute pancreatitis. JRMS. 14(1):19–27.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
We claimed that this paper was original and would not have any financial interest in a company or its competitor, and that all authors meet criteria for authorship. We abided the ethics in this animal experiment study. The ethics committee approval of our hospital was secured for the animal study reported, and all rats have not been abused and executive mercy killing when the observing time in this study was over. As a corresponding author, Zhang Xiping takes the equal task to Tian Hua in this study. The levels of TNF-α and Endotoxin can be used as important markers for assessing the severity of multiple organ injury in SAP, so we repeated the data in our manuscript although they have been published in other journals.
Supported by technological foundation project of Traditional Chinese Medicine Science of Zhejiang province (NO.2003C130; NO.2004C142), foundation project for medical science and technology of Zhejiang province (No.2003B134), grave foundation project for technological and development of Hangzhou (NO.2003123B19), intensive foundation project for technology of Hangzhou (NO.2004Z006), foundation project for medical science and technology of Hangzhou (No.2003A004) and foundation project for technology of Hangzhou (No.2005224).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hua, T., Xiping, Z., Chengjun, W. et al. Effects of Baicalin and Octreotide on the Serum TNF-α Level and Apoptosis in Multiple Organs of Rats with Severe Acute Pancreatitis. Inflammation 32, 191–201 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-009-9120-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-009-9120-8