Abstract
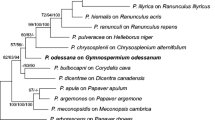
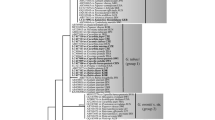
On the family Brassicaceae, the causal agent responsible for downy mildew disease was originally regarded as a single species, Peronospora parasitica (now under Hyaloperonospora), but it was recently reconsidered to consist of many distinct species. In this study, 11 specimens of Peronospora drabae and P. norvegica parasitic on the genus Draba were investigated morphologically and molecularly. Pronounced differences in conidial sizes (P. drabae: 14–20 × 12.5–15.5 μm; P. norvegica: 20–29 × 15.5–22 μm) and 7.8% sequence distance between their ITS1-5.8S-ITS2 rDNA sequences confirmed their status as distinct species. Based on ITS phylogeny and morphology (monopodially branching conidiophores, flexuous to sigmoid ultimate branchlets, hyaline conidia and lobate haustoria), the two species unequivocally belong to the genus Hyaloperonospora and not to Peronospora to which they were previously assigned. Therefore, two new combinations, Hyaloperonospora drabae and H. norvegica, are proposed. The two taxa are illustrated and compared using the type specimen for H. norvegica and authentic specimens for H. drabae, which is lectotypified.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Persoon CH. Observationes mycologicae. Vol. 1. Leipzig: P.P. Wolf; 1796.
Gäumann E. Über die Formen der Peronospora parasitica (Pers.) Fries. Ein Beitrag zur Speziesfrage bei den parasitischen Pilzen. Beih Bot Centralb. 1918;34(1):395–533.
Gäumann E. Beiträge zu einer Monographie der Gattung Peronospora Corda. Beitr Kryptogamenfl Schweiz. 1923;5(4):1–360.
Gustavsson A. Studies on nordic peronosporas. I. Taxonomic revision. Opera Bot. 1959;3(1):1–271.
Yerkes WD, Shaw CG. Taxonomy of the Peronospora species on Cruciferae and Chenopodiaceae. Phytopathology. 1959;49:499–507.
Constantinescu O, Fatehi J. Peronospora-like fungi (Chromista, Peronosporales) parasitic on Brassicaceae and related hosts. Nova Hedwigia. 2002;74:291–338.
Riethmüller A, Voglmayr H, Göker M, Weiß M, Oberwinkler F. Phylogenetic relationships of the downy mildews (Peronosporales) and related groups based on nuclear large subunit ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycologia. 2002;94:834–49.
Choi YJ, Hong SB, Shin HD. Diversity of Hyaloperonospora parasitica complex from core brassicaceous hosts based on ITS rDNA sequence. Mycol Res. 2003;107:1313–21.
Voglmayr H. Phylogenetic relationships of Peronospora and related genera based on nuclear ribosomal ITS sequences. Mycol Res. 2003;107:1132–42.
Göker M, Voglmayr H, Riethmüller A, Weiß M, Oberwinkler F. Taxonomic aspects of Peronosporaceae inferred from Bayesian molecular phylogenetics. Can J Bot. 2003;81:672–83.
Göker M, Riethmüller A, Voglmayr H, Weiss M, Oberwinkler F. Phylogeny of Hyaloperonospora based on nuclear ribosomal internal transcribed spacer sequences. Mycol Prog. 2004;3:83–94.
Göker M, Voglmayr H, García–Blázquez G, Oberwinkler F. Species delimitation in downy mildews: the case of Hyaloperonospora in the light of nuclear ribosomal ITS and LSU sequences. Mycol Res. 2009;113:308–25.
Shin HD, Choi YJ. A first check-list of Peronosporaceae from Korea. Mycotaxon. 2003;86:249–67.
Shin HD, Choi YJ. Peronosporaceae of Korea. Suwon, Korea: National Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology; 2006.
Holmgren PK, Holmgren NH. 1998. Index Herbariorum. New York Botanical Garden. http://sciweb.nybg.org/science2/indexHerbariorum.asp.
Lee SB, Taylor JW. Isolation of DNA from fungal mycelia and single spores. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ, editors. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. San Diego: Academic Press; 1990. p. 282–7.
Cooke DEL, Drenth A, Duncan JM, Wagels G, Brasier M. A molecular phylogeny of Phytophthora and related Oomycetes. Fungal Genet Biol. 2000;30:17–32.
Moncalvo JM, Wang HH, Hseu RS. Phylogenetic relationships in Ganoderma inferred from the internal transcribed spacer and 25S ribosomal DNA sequences. Mycologia. 1995;87:223–38.
Voglmayr H, Constantinescu O. Revision and reclassification of three Plasmopara species based on morphological and molecular phylogenetic data. Mycol Res. 2008;112:487–501.
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor JW. Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ, editors. PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. San Diego: Academic Press; 1990. p. 315–22.
Voglmayr H, Jaklitsch W. Prosthecium species with Stegonsporium anamorphs on Acer. Mycol Res. 2008;112:885–905.
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG. The Clustal X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 1997;24:4876–82.
Stamatakis E. RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2006;22:2688–90.
Tamura K, Dudley J, Nei M, Kumar S. MEGA4: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis (MEGA) software version 4.0. Mol Biol Evol. 2007;24:1596–9.
Felsenstein J. Confidence limits on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution. 1985;39:783–91.
Ronquist F, Huelsenbeck JP. MRBAYES 3: Bayesian phylogenetic inference under mixed models. Bioinformatics. 2003;19:1572–4.
Göker M, Voglmayr H, Riethmüller A, Oberwinkler F. How do obligate parasites evolve? A multi-gene phylogenetic analysis of downy mildews. Fungal Genet Biol. 2007;44:105–22.
Thines M. Evaluation of characters available from herbarium vouchers for the phylogeny of the downy mildew genera (Chromista, Peronosporales), with focus on scanning electron microscopy. Mycotaxon. 2006;97:195–218.
Hamilton AJ, Cunnington JH. Calculating minimum sample sizes for taxonomic measurements: examples using Gäumann’s Peronospora spore data. Mycotaxon. 2006;95:189–94.
Choi YJ, Constantinescu O, Shin HD. A new downy-mildew of the Rosaceae: Peronospora oblatispora sp. nov. (Chromista, Peronosporales). Nova Hedwigia. 2007;85:93–101.
Choi YJ, Hong SB, Shin HD. Re-consideration of Peronospora farinosa infecting Spinacia oleracea as distinct species, Peronospora effusa. Mycol Res. 2007;111:381–91.
Choi YJ, Denchev CM, Shin HD. Morphological and molecular analyses support the existence of host-specific Peronospora species infecting Chenopodium. Mycopathologia. 2008;168:155–64.
Choi YJ, Shin HD, Thines M. Two novel Peronospora species are associated with recent reports of downy mildew on sages. Mycol Res. 2009;113:1340–50.
Kochman J, Majewski T. Grzyby (Mycota). Tom IV. Glonowce (Phycomycetes), Wroslikowe (Peronosporales). Państwowe Wydawnictwo Naukowe: Warzawa; 1970.
Ul’yanishchev VI, Osipian LL, Kanchaveli LA, Akhundov TM. Peronosporovye griby (Peronosporaceous Fungi). In: Ul’yanishchev VI, editor. Opredelitel’ gribov zakavkaz’ya: Erevan University, Erevan; 1985.
Staneviciené S. Peronosporales. In: Mazelaitis J, Staneviciené S, editors. Lietavos Grybai. I. Gleivunai (Myxomycota), Peronosporieciai (Peronosporales) 1. Vilnius: Mokslo ir enciklopediju leidykla; 1995. p. 85–291.
Novotelnova NS, Pystina KA. Ordo Peronosporales (Fam. Pythiaceae, Phytophthoraceae, Peronosporaceae, Cystopaceae). In: Gorlenko MV, editor. Cryptogamic flora of URSS, vol, 11, Fungi (3). Leningrad: Nauka; 1985.
Rouppert K. Przyczynek do znajomości grzybów Galicyi i Bukowiny. Kosmos, Lwów. 1911;36:936–44.
Voglmayr H, Fatehi J, Constantinescu O. Revision of Plasmopara (Chromista, Peronosporales) parasitic on Geraniaceae. Mycol Res. 2006;110:633–45.
Thines M, Choi YJ, Kemen E, Ploch S, Holub EB, Shin HD, Jones JDG. A new species of Albugo parasitic to Arabidopsis thaliana reveals new evolutionary patterns in white blister rusts (Albuginaceae). Persoonia. 2009;22:123–8.
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to the herbarium curators of the U.S. National Fungus Collections (BPI), the Royal Botanic Gardens Kew (K), the Botanical Museum Oslo (O), the Naturhistorisches Museum Wien (W) and the Universität Wien (WU) for providing the Peronospora specimens. Financial support via a research grant from the Korea University to H. D. S. in 2007 and a EU SYNTHESYS grant (GB-TAF-4625) to H. V. for a research stay at the Royal Botanic Gardens Kew are gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, YJ., Shin, HD. & Voglmayr, H. Reclassification of Two Peronospora Species Parasitic on Draba in Hyaloperonospora Based on Morphological and Molecular Phylogenetic Data. Mycopathologia 171, 151–159 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-010-9340-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11046-010-9340-3