Abstract
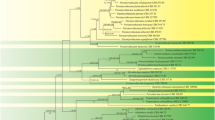
A new species of Stemphylium causing leaf and flower blight of Platycodon grandiflorus in Korea was determined on the basis of phylogenetic analysis and morphology. Phylogenetic analyses of internal transcribed spacer (ITS), glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (gpd), translation elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1α) and a combined dataset revealed that the fungus placed in a subclade distinct from the closely related Stemphylium species (S. lycopersici, S. xanthosomatis and S. subglobuliferum). The fungus morphologically differs from them by producing larger conidia and no brown pigment secreted on potato dextrose agar (PDA). Hence, the pathogenic fungus is proposed as Stemphylium platycodontis sp. nov.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berbee ML, Pirseyedi M, Hubbard S (1999) Cochliobolus phylogenetics and the origin of known, highly virulent pathogens, inferred from ITS and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene sequences. Mycologia 91:964–977
Câmara MPS, O’Neill NR, van Berkum P (2002) Phylogeny of Stemphylium spp. based on ITS and glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene sequences. Mycologia 94:660–672
Farr DF, Bills GF, Chamuris GP, Rossman AY (1989) Fungi on plants and plant products in the United States. APS Press, St. Paul, Minnesota, p 1252
Hosen MI, Ahmed AU, Zaman JJ, Ghosh S, Hossain KMK (2009) Cultural and physiological variation between isolates of Stemphylium botryosum the causal of Stemphylium blight disease of lentil (Lens culinaris). World J Agric Sci 5:94–98
Inderbitzin P, Mehta YR, Berbee ML (2009) Pleospora species with Stemphylium anamorphs: a four locus phylogeny resolves new lineages yet does not distinguish among species in the Pleospora herbarum clade. Mycologia 101:329–339
Kim BS, Yu SH, Cho HJ, Hwang HS (2004) Gray leaf spot in peppers caused by Stemphylium solani and S. lycopersici. Plant Pathol J 20:85–91
Leach CM, Aragaki M (1970) Effect of temperature on conidium characteristics of Ulocladium chartarum and Stemphylium floridanum. Mycologia 62:1071–1076
Park MS, Seo GS, Bae KS, Yu SH (2005) Characterization of Trichoderma spp. associated with green mold oyster mushroom by PCR-RFLP and sequence analysis of ITS regions of rDNA. Plant Pathol J 21:229–236
Pei YF, Wang Y, Geng Y, O’Neil NR, Zhang XG (2011) Three new species of Stemphylium from Sinkiang, China: their morphological and molecular characterization. Mycol Progress 10:163–173
Pei YF, Wang Y, Geng Y, Zhang XG (2009) Two new species of Stemphylium from Sinkiang, China. Mycotaxon 109:493–497
Pei YF, Wang Y, Geng Y, Zhang XG (2010) Three new species of Stemphylium from Sinkiang, China. Mycotaxon 111:167–173
Simmons EG (1967) Typification of Alternaria, Stemphylium, and Ulocladium. Mycologia 59:67–92
Simmons EG (1969) Perfect states of Stemphylium. Mycologia 61:1–26
Simmons EG, Roberts RG (1993) Alternaria themes and variations (73). Mycotaxon 48:109–140
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Tamura K, Peterson D, Peterson N, Stecher G, Nei M, Kumar S (2011) MEGA5: Molecular evolutionary genetics analysis using maximum likelihood, evolutionary distance, and maximum parsimony methods. Mol Biol Evol 28:2731–2739
Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The cluster X windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucl Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Wallroth FG (1833) Flora Cryptogamica Germaniae, pars. post. Nürnberg: J. L. Schrag. pp 923
Wang Y, Fu HB, O’Neill NR, Zhang XG (2009) Two new species of Stemphylium from Northwest China. Mycol Progress 8:301–304
Wang Y, Geng Y, Pei YF, Zhang XG (2010) Molecular and morphological description of two new species of Stemphylium from China and France. Mycologia 102:708–717
Wang Y, Zhang XG (2006) Tree new species of Stemphylium from China. Mycotaxon 96:77–81
Wang Y, Zhang XG (2009) Two new species of Stemphylium from Shandong, China. Nova Hedwigia 88:199–203
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: A guide to methods and applications. Academic Press San Diego, CA, USA, pp 315–322
Wiltshire SP (1938) The original and modern conceptions of Stemphylium. Trans Br Mycol Soc 21:211–239
Xue F, Zhang XG, Wang Y, Wang HZ (2005) Taxonomic studies of Stemphylium from China II: Stemphylium subglobuliferum sp. nov., and four new records. Mycosystema 24:322–329
Yu SH (2001) Korean Species of Alternaria and Stemphylium. National Institute of Agricultural Science and Technology Suwon, Korea, pp 170–171
Acknowledgments
The authors sincerely thank Dr. Walter Gams for the nomenclature of this species. This project was supported by a grant from the Regional Subgenebank Support Program of RDA and National Institute of Biological Resources, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Deng, J.X., Paul, N.C., Li, M.J. et al. Stemphylium platycodontis sp. nov., isolated from Platycodon grandiflorus in Korea. Mycol Progress 13, 477–482 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-013-0929-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-013-0929-z