Abstract
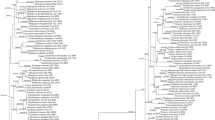
Polyporus sensu lato is understood to be a polyphyletic genus, including two narrowly defined genera (Favolus and Neofavolus), two subclades (Melanopus and Polyporellus), and some scattered species. In this study, Polyporus hapalopus is described and illustrated as a new species on the basis of morphological and molecular evidence. This species is characterized by laterally stipitate, imbricate and large basidiocarps (up to 40 cm diam.), grapefruit odor when fresh, angular pores with lacerate dissepiments, soft (when fresh) to tough (when dry) context, a dimitic hyphal system in context and stipe with variable wide skeleto-binding hyphae, a monomitic hyphal system in trama, and cylindrical basidiospores bearing one or two guttules. Phylogenetically, on the basis of the combined internal transcribed spacer and nuclear large subunit rDNA sequences, P. hapalopus is nested within the Polyporus sensu lato clade, but is separated from four previously established subclades and from other known species.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Buchanan PK, Ryvarden L (1998) New Zealand polypore fungi (Aphyllophorales): three new species and a new record. N Z J Bot 36:219–231
Cui BK, Yuan HS, Dai YC (2008) Wood-rotting fungi in eastern China 1. Polypores from Wuyi Mountains, Fujian Province. Sydowia 60:25–40
Dai YC (2010) Hymenochaetaceae (Basidiomycota) in China. Fungal Divers 45:131–343
Dai YC (2011) A revised checklist of corticioid and hydnoid fungi in China for 2010. Mycoscience 52:69–79
Dai YC (2012a) Two new polypores from tropical China, and renaming two species of Polyporus and Phellinus. Mycoscience 53:40–44
Dai YC (2012b) Polypore diversity in China with an annotated checklist of Chinese polypores. Mycoscience 53:49–80
Dai YC, Penttilä R (2006) Polypore diversity of Fenglin Nature Reserve, northeastern China. Ann Bot Fenn 43:81–96
Dai YC, Härköene M, Niemelä T (2003) Wood-inhabiting fungi in southern China 1. Polypores from Hunan Province. Ann Bot Fenn 40:381–393
Dai YC, Wei YL, Wang Z (2004) Wood-inhabiting fungi in southern China 2. Polypores from Sichuan Province. Ann Bot Fenn 41:319–329
Dai YC, Cui BK, Huang MY (2007a) Polypores from eastern Inner Mongolia, northeastern China. Nova Hedwigia 84:513–520
Dai YC, Cui BK, Yuan HS (2007b) Notes on polypores from Gansu and Qinghai Province, Northwest China. Cryptogam Mycol 28:177–187
Dai YC, Wei YL, Yuan HS, Huang MY, Penzina T (2007c) Polypores from Altay and Tian Mts. in Xinjiang, northwest China. Cryptogam Mycol 28:269–279
Dai YC, Yu CJ, Wang HC (2007d) Polypores from eastern Xizang (Tibet), western China. Ann Bot Fenn 44:135–145
Dai YC, Yuan HS, Wang HC, Yang F, Wei YL (2009) Polypores (Basidiomycota) from Qin Mts. in Shaanxi Province, Central China. Ann Bot Fenn 46:54–61
Dai YC, Xue HJ, Vlasák J, Rajchenberg M, Wang B, Zhou LW (2014) Phylogeny and global diversity of Polyporus group Melanopus (Polyporales, Basidiomycota). Fungal Divers. doi:10.1007/s13225-013-0248-3
Gilbertson RL, Ryvarden L (1987) North American polypores 2. Fungiflora, Oslo
Guindon S, Gascuel O (2003) A simple, fast and accurate method to estimate large phylogenies by maximum-likelihood. Syst Biol 52:696–704
Ko KS, Jung HS (2002) Phylogenetic evaluation of Polyporus s. str. based on molecular sequences. Mycotaxon 82:315–322
Krüger D, Petersen RH, Hughes KW (2006) Molecular phylogenies and mating study data in Polyporus with special emphasis on group “Melanopus” (Basidiomycota). Mycol Prog 5:185–206
Larkin MA, Blackshields G, Brown NP, Chenna R, McGettigan PA, McWilliam H, Valentin F, Wallace IM, Wilm A, Lopez R, Thompson JD, Gibson TJ, Higgins DG (2007) Clustal W and Clustal X version 2.0. Bioinformatics 23:2947–2948
Li J, Xiong HX, Dai YC (2008) Polypores from Shennongjia Nature Reserve in Hubei Province, Central China. Cryptogam Mycol 29:267–277
Núñez M, Ryvarden L (1995) Polyporus (Basidiomycotina) and related genera. Synopsis Fungorum 10:1–85
Pattengale ND, Alipour M, Bininda-Emonds ORP, Moret BME, Stamatakis A (2010) How many bootstrap replicates are necessary? J Comput Biol 17:337–354
Petersen JH (1996) Farvekort. The Danish Mycological Society’s colour-chart. Foreningen til Svampekundskabens Fremme, Greve
Posada D (2008) jModelTest: Phylogenetic model averaging. Mol Biol Evol 25:1253–1256
Ronquist F, Teslenko M, van der Mark P, Ayres D, Darling A, Hōhna S, Larget B, Liu L, Suchard MA, Huelsenbeck JP (2012) MrBayes 3.2: Efficient Bayesian phylogenetic inference and model choice across a large model space. Syst Biol 61:539–542
Silvestro D, Michalak I (2012) raxmlGUI: a graphical front-end for RAxML. Org Divers Evol 12:335–337
Sotome K, Hattori T, Kakishima M (2007) Polyporus phyllostachydis sp. nov. with notes on other rhizophilic species of Polyporus (Basidiomycota, Polyporaceae). Mycoscience 48:42–46
Sotome K, Hattori T, Ota Y, To-anun C, Salleh B, Kakishima M (2008) Phylogenetic relationships of Polyporus and morphologically allied genera. Mycologia 100:603–615
Sotome K, Hattori T, Ota Y, Kakishima M (2009) Second report of Polyporus longiporus and its phylogenetic position. Mycoscience 50:415–420
Sotome K, Hattori T, Ota Y (2011) Taxonomic study on a threatened polypore, Polyporus pseudobetulinus, and a morphologically similar species, P. subvarius. Mycoscience 52:319–326
Sotome K, Akagi Y, Lee SS, Ishikawa NK, Hattori T (2013) Taxonomic study of Favolus and Neofavolus gen. nov. segregated from Polyporus (Basidiomycota, Polyporales). Fungal Divers 58:245–266
Stamatakis A (2006) RAxML-VI-HPC: maximum likelihood-based phylogenetic analyses with thousands of taxa and mixed models. Bioinformatics 22:2688–2690
Wang B, Cui BK, Li HJ, Du P, Jia BS (2011) Wood-rotting fungi in eastern China 5. Polypore diversity in Jiangxi Province. Ann Bot Fenn 48:237–246
White TJ, Bruns T, Lee S, Taylor J (1990) Amplification and direct sequencing of fungal ribosomal RNA genes for phylogenetics. In: Innis MA, Gelfand DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 315–322
Xue HJ, Zhou LW (2012) Polyporus submelanopus sp. nov. (Polyporales, Basidiomycota) from Northwest China. Mycotaxon 122:433–441
Yuan HS, Dai YC (2008) Polypores from northern and central Yunnan Province, Southwestern China. Sydowia 60:147–159
Zheng HD, Liu PG (2005) Type studies on Albatrellus henanensis and A. jianfenglingensis. Mycotaxon 93:257–263
Zhou LW, Xue HJ (2012) Fomitiporia pentaphylacis and F. tenuitubus spp. nov. (Hymenochaetales, Basidiomycota) from Guangxi, southern China. Mycol Prog 11:907–913
Acknowledgments
We express our gratitude to Prof. Yu-Cheng Dai (IFP, China) for his guidance in the taxonomic study and also for his recommendations for improving the manuscript. L.W.Z. thanks Drs. Hai-Sheng Yuan (IFP, China), Shuang-Hui He (BJFC, China) and Wei Li (HMAS, China) for their company in the field trip. Dr. Hai-Sheng Yuan is also thanked for providing the in situ photo of Polyporus hapalopus and preparing the line drawing. The research was financed by National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project Nos. 31200015 & 30910103907) and the Youth Fund for Creative Research Groups, Institute of Applied Ecology, Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xue, HJ., Zhou, LW. Polyporus hapalopus sp. nov. (Polyporales, Basidiomycota) from China based on morphological and molecular data. Mycol Progress 13, 811–817 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-014-0964-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-014-0964-4