Abstract
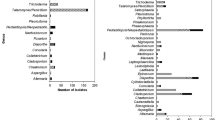
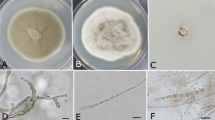
In spite of the self-cleaning property of its leaves called the lotus effect, leaves of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera) provide a habitat for an unknown fungal diversity. The aim of this study was to detect and identify fungi from leaves of N. nucifera, including ectophytic, parasitic and endophytic fungi, in Taiwan using different collection strategies, as well as morphological and diverse molecular markers established in the different systematic groups of fungi. Among ectophytic and parasitic fungi, a new species of Dissoconium and of Pseudocercospora are described, respectively. Phyllosticta nelumbonis Sawada is transferred to Diaporthe. Among plant parasitic fungi, Erysiphe takamatsui and Ps. nymphaeacea are recorded in Taiwan for the first time. Euryale is recorded as a new host genus for Ps. nymphaeacea. The basidiomycetous yeast Fereydounia khargensis is recorded for the first time from living plants and in East Asia. Endophytic fungi from lotus were studied for the first time. From 1002 plant segments, 476 endophytic isolates were produced in culture, comprising 33 typical terrestrial species mainly belonging to the genera Colletotrichum (mainly C. siamense), Diaporthe (D. tulliensis and D. ueckerae) and Fusarium (F. solani species 6, hitherto known from clinical samples), as well as to Xylariaceae, but no Ingoldian fungi. Most isolates were from leaf laminas (71%) compared to those from petioles (29%). From this observation, we conclude that the fungi of the aquatic lotus plant appear to have terrestrial origin and, after dispersal by wind and in spite of the lotus effect, may enter the plant from the lamina. Only three species isolated as endophytes were also found as ectophytic or parasitic fungi.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almeida TT, Orlandelli RC, Azevedo JL, Pamphile JA (2015) Molecular characterization of the endophytic fungal community associated with Eichhornia azurea(Kunth) and Eichhornia crassipes (Mart.) (Pontederiaceae) native to the upper Paraná River floodplain, Brazil. Genet Mol Res 14:4920–4931
Aoki T, O’Donnell K, Geiser DM (2014) Systematics of key phytopathogenic Fusarium species: current status and future challenges. J Gen Plant Pathol 80:189–201
Ariyawansa HA, Hawksworth DL, Hyde KD, Jones EG, Maharachchikumbura SS, Manamgoda DS, Thambugala KM, Udayanga D, Camporesi E, Daranagama A, Jayawardena R, Liu JK, McKenzie EH, Phookamsak R, Senanayake IC, Shivas RG, Tian Q, Xu JC (2014) Epitypification and neotypification: guidelines with appropriate and inappropriate examples. Fungal Divers 69:57–91
Arzanlou M, Groenewald JZ, Fullerton RA, Abeln EC, Carlier J, Zapater MF, Buddenhagen IW, Viljoen A, Crous PW (2008) Multiple gene genealogies and phenotypic characters differentiate several novel species of Mycosphaerella and related anamorphs on banana. Persoonia 20:19–37
Bai Q, Wang GP, Hong N, Guo YS, Fu M (2017) First report of Diaporthe tulliensis and Diaporthe actinidiae causing kiwifruit stem canker in Hubei and Anhui provinces, China. Plant Dis 101:508
Barthlott W, Neinhuis C (1997) Purity of the sacred lotus, or escape from contamination in biological surfaces. Planta 202:1–8
Bills GF, Platas G, Overy DP, Collado J, Fillola A, Jiménez MR, Martín J, González del Val A, Vicente F, Tormo JR, Peláez F, Calati K, Harris G, Parish G, Xu D, Roemer T (2009) Discovery of the parnafungins, antifungal metabolites that inhibit mRNA polyadenylation, from the Fusarium larvarum complex and other hypocrealean fungi. Mycologia 101:449–472
Braun U, Cook RTA (2012) Taxonomic manual of the Erysiphales (powdery mildews). CBS Biodiversity Series no. 11. CBS-KNAW Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Braun U, Delhey R, Dianese JC, Hosagoudar VB (2006) Miscellaneous notes on biotrophic micromycetes. Schlechtendalia 14:85–97
Chang C-Q, Cheng Y-H, Xiang M-M, Jiang Z-D, Chi P-K(2005) New species of Phomopsis on woody plants in Fujian province. Mycosystema 24:6–11
Chi PK (1994) Fungal diseases of cultivated medicinal plants in Guangdong province. Guangdong Keji Chubanshe, Guangdong (in Chinese)
Cooke MC (1888) New British fungi. Grevillea 16(79):77–81
Crous PW (2002) Taxonomy and pathology of Cylindrocladium (Calonectria) and allied genera. American Phytopathological Society Press, St. Paul, Minnesota
Crous PW, Shivas RG (2011) Fungal planet description sheets 92:132–133
Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Mansilla JP, Hunter GC, Wingfield MJ (2004) Phylogenetic reassessment of Mycosphaerella spp. and their anamorphs occurring on Eucalyptus. Stud Mycol 50:195–214
Crous PW, Summerell BA, Carnegie AJ, Mohammed C, Himaman W, Groenewald JZ (2007) Foliicolous Mycosphaerella spp. and their anamorphs on Corymbia andEucalyptus. Fungal Divers 26:143–185
Crous PW, Summerell BA, Mostert L, Groenewald JZ (2008) Host specificity and speciation of Mycosphaerella and Teratosphaeria species associated with leaf spots of Proteaceae. Persoonia 20:59–86
Cui RQ, Sun XT (2012) First report of Curvularia lunata causing leaf spot on lotus in China. Plant Dis 96:1068
Damm U, Cannon PF, Woudenberg JHC, Crous PW (2012) The Colletotrichum acutatum species complex. Stud Mycol 73:37–113
de Hoog GS, van Oorschot CAN, Hijwegen T (1983) Taxonomy of the Dactylaria complex. II. Dissoconium gen. nov. and Cordana Preuss. Proc K Ned Akad Wet C 86:197–206
De Hoog GS, Hijwegen T, Batenburg-van der Vegte WH (1991) A new species of Dissoconium. Mycol Res 95:679–682
de Oliveira RJV, Bezerra JL, Lima TEF, da Silva GA, Cavalcanti MAQ (2016)Phaeosphaeria nodulispora, a new endophytic coelomycete isolated from tropical palm (Cocos nucifera) in Brazil. Nova Hedwigia 103:185–192
Delaye L, García-Guzmán G, Heil M (2013) Endophytes versus biotrophic and necrotrophic pathogens—are fungal lifestyles evolutionarily stable traits? Fungal Divers 60:125–135
Du Z, Fan X-L, Hyde KD, Yang Q, Liang YM, Tian CM (2016) Phylogeny and morphology reveal two new species of Diaporthe from Betula spp. in China. Phytotaxa 269(2):90–102
Farr DF, Rossman AY (2017) Fungal Databases, U.S. National Fungus Collections, Systematic Mycology and Microbiology Laboratory, ARS, USDA. https://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases/
Forbes P (2005) The Gecko’s foot: bio-inspiration: engineering new materials and devices from nature. WW Norton, New York
Gao Y, Liu F, Cai L (2016) Unravelling Diaporthe species associated with Camellia. Syst Biodivers 14:102–117
Ge Q, Chen Y, Xu T (2009) Flora Fungorum Sinicorum. Vol. 38. Pestalotiopsis. Science Press, Beijing
Gomes RR, Glienke C, Videira SIR, Lombard L, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2013)Diaporthe: a genus of endophytic, saprobic and plant pathogenic fungi. Persoonia 31:1–41
Groenewald JZ, Nakashima C, Nishikawa J, Shin H-D, Park J-H, Jama AN, Groenewald M, Braun U, Crous PW (2013) Species concepts in Cercospora: spotting the weeds among the roses. Stud Mycol 75:115–170
Guo YL, Liu XL, Hsieh WH (1998) Flora Fungorum Sinicorum. Vol. 9. Pseudocercospora. Science Press, Beijing
Guo YL, Liu XL, Hsieh WH (2005) Flora Fungorum Sinicorum. Vol. 24. Cercospora. Science Press, Beijing
Hennings PC (1899) Die in den Gewächshäusern des Berliner Botanischen Gartens beobachteten Pilze. Borntraeger, 1898. Verh Bot Ver Prov Brandenb 40:109–177
Hsueh C-H, Yang Z-Y(2016) The scenic plants in Taiwan (6). United Distribution, Hsindian (in Chinese)
Ibrahim M, Schlegel M, Sieber TN (2016)Venturia orni sp. nov., a species distinct from Venturia fraxini, living in the leaves of Fraxinus ornus. Mycol Prog 15(29):1–12
Ingold CT (1975) An illustrated guide to aquatic and water-borne hyphomycetes. Freshwater Biological Association, Scientific Publication No. 30, Windermere, UK
Katumoto K (2010) List of fungi recorded in Japan. The Kanto Branch of the Mycological Society of Japan, Tokyo
Kirschner R (2010) First record of Erysiphe magnifica on lotus, a host outside the Magnoliales. Mycol Prog 9:417–424
Kirschner R (2014) A new species and new records of cercosporoid fungi from ornamental plants in Taiwan. Mycol Prog 13:483–491
Kirschner R (2017) Fungi on the leaf—a contribution towards a review of phyllosphere microbiology from the mycological perspective. In: Biodiversity and ecology of fungi, lichens and mosses—Kerner von Marilaun workshop 2015 in memory of Josef Poelt. P Blanz (Ed.) Biosystematics and Ecology Series, Commission for Interdisciplinary Ecological Studies, Austrian Academy of Sciences 31:426–441 (in press)
Kruse J, Kummer V, Thiel H (2014) Bemerkenswerte Funde phytoparasitischer Kleinpilze (3). Z Mykol 80:593–626
Kuhnert E, Sir EB, Lambert C, Hyde KD, Hladki AI, Romero AI, Rohde M, Stadler M (2016) Phylogenetic and chemotaxonomic resolution of the genus Annulohypoxylon(Xylariaceae) including four new species. Fungal Divers (in press). doi:10.1007/s13225-016-0377-6
Kurtzman CP, Fell JW, Boekhout T (2011) The yeasts: a taxonomic study, 5th edn. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam
Lawson SP, Christian N, Abbot P (2014) Comparative analysis of the biodiversity of fungal endophytes in insect-induced galls and surrounding foliar tissue. Fungal Divers 66:89–97
Li HY, Zhao CA, Liu CJ, Xu XF (2010) Endophytic fungi diversity of aquatic/riparian plants and their antifungal activity in vitro. J Microbiol 48:1–6
Li HY, Sun GY, Zhai XR, Batzer JC, Mayfield DA, Crous PW, Groenewald JZ, Gleason ML (2012) Dissoconiaceae associated with sooty blotch and flyspeck on fruits in China and the United States. Persoonia 28:113–125
Li J, Li H, Zheng L, Yan SL, Wang QZ (2016) First report of lotus root disease caused by Fusarium tricinctum in China. Plant Dis 100(8):1784
Lledó S, Rodrigo S, Poblaciones MJ, Santamaria O (2015) Biomass yield, mineral content, and nutritive value of Poa pratensis as affected by non-clavicipitaceous fungal endophytes. Mycol Prog 14:67
Matsushima T (1975) Icones microfungorum a Matsushima lectorum. Published by the author, Kobe, Japan, 209 pp, 415 pl
McNeill J, Barrie FR, Buck WR, Demoulin V, Greuter W, Hawksworth DL, Herendeen PS, Knapp S, Marhold K, Prado J, Prud’homme van Reine WF, Smith GF, Wiersema JH, Turland NJ (2012) International code of nomenclature for algae, fungi and plants (Melbourne code) adopted by the eighteenth international botanical congress Melbourne, Australia, July 2011. Regnum Vegetabile 154:1–240
Meeboon J (2009) Diversity and phylogeny of true cercosporoid fungi from northern Thailand. Chiang Mai University, Thailand, Chiang Mai
Meeboon J, Takamatsu S (2015)Erysiphe takamatsui, a powdery mildew of lotus: rediscovery of teleomorph after 40 years, morphology and phylogeny. Mycoscience 56(2):159–167
Mehl HL, Epstein L (2007)Fusarium solani species complex isolates conspecific with Fusarium solani f. sp. cucurbitae race 2 from naturally infected human and plant tissue and environmental sources are equally virulent on plants, grow at 37°C and are interfertile. Environ Microbiol 9:2189–2199
Nakashima C, Motohashi K, Chen CY, Groenewald JZ, Crous PW (2016) Species diversity of Pseudocercospora from far East Asia. Mycol Prog 15(10–11):1093–1117
Nasr S, Soudi MR, Fazeli SAS, Nguyen HDT, Lutz M, Piątek M (2014) Expanding evolutionary diversity in the Ustilaginomycotina: Fereydouniaceae fam. nov. and Fereydounia gen. nov., the first urocystidalean yeast lineage. Mycol Prog 13:1217–1226
Nisikado Y, Watanabe K (1953) On the rhizome rot of lotus, Nelumbo nucifera Gaertn., caused by a new Fusarium, F. bulbigenum Wr. nelumbicolum Nis. et Wat. Ber Ohara Inst Landw Forsch Kurashiki 10:1–8, 2 plates
Nisikado Y, Watanabe K (1955) On a lotus anthracnose new to Japan. Ber Ohara Inst Landw Forsch Kurashiki 10:117–124, 2 plates
O’Donnell K, Sutton DA, Fothergill A, McCarthy D, Rinaldi MG, Brandt ME, Zhang N, Geiser DM (2008) Molecular phylogenetic diversity, multilocus haplotype nomenclature, and in vitro antifungal resistance within the Fusarium solani species complex. J Clin Microbiol 46:2477–2490. doi:10.1128/JCM.02371-07
Park J-H, Hong S-B, Kim B-S, Kim J-Y, Shin H-D(2015)Pseudocercospora leaf spot caused by Pseudocercospora nymphaeacea on Nymphaea tetragona. Trop Plant Pathol 40:401–404
Petrini O, Fisher PJ, Petrini LE (1992) Fungal endophytes of bracken (Pteridium aquilinum), with some reflections on their use in biological control. Sydowia 44:282–293
Pugh GJF, Mulder JL (1971) Mycoflora associated with Typha latifolia. Trans Br Mycol Soc 57:273–282
Punithalingam E (1975) Some new species and combinations in Phomopsis. Trans Br Mycol Soc 64:427–435
Raviraja NS, Sridhar KR, Bärlocher F (1996) Endophytic aquatic hyphomycetes of roots of plantation crops and ferns from India. Sydowia 48(1):152–160
Rodriguez RJ, Henson J, Van Volkenburgh E, Hoy M, Wright L, Beckwith F, Kim YO, Redman RS (2008) Stress tolerance in plants via habitat-adapted symbiosis. ISME J 2:404–416
Saccardo PA (1892) Supplementum Universale, Pars II. Discomyceteae-Hyphomyceteae. Sylloge Fungorum 10:1–964
Saccardo PA, Sydow P (1902) Supplementum Universale, Pars V. Sylloge Fungorum. 16:1–1291
Sati SC, Pargaein N, Belwal M (2009) Diversity of aquatic hyphomycetes as root endophytes on pteridophytic plants in Kumaun Himalaya. J Am Sci 5(4):179–182
Sawada K (1959) Descriptive catalogue of Taiwan (Formosan) fungi. Part XI. Spec Publ Coll Agric Taiwan Univ 8:1–268
Schroers HJ, Samuels GJ, Zhang N, Short DP, Juba J, Geiser DM (2016) Epitypification of Fusisporium (Fusarium) solani and its assignment to a common phylogenetic species in the Fusarium solani species complex. Mycologia 108:806–819
Selosse MA, Vohník M, Chauvet E (2008) Out of the rivers: are some aquatic hyphomycetes plant endophytes? New Phytol 178:3–7
Shivas RG, Tan YP, Vawdrey LL (2015) Fungal Planet 387:300–301
Short DP, O’Donnell K, Zhang N, Juba JH, Geiser DM (2011) Widespread occurrence of diverse human pathogenic types of the fungus Fusarium detected in plumbing drains. J Clin Microbiol 49:4264–4272
Siemaszko W (1923) Fungi caucasici novi vel minus cogniti. II. Diagnoses specierum novarum ex Abchazia Adzariaque provenientium. Acta Soc Bot Pol 1:19–28
Simmons EG (2007)Alternaria: an identification manual. CBS Fungal Biodiversity Centre, Utrecht, The Netherlands
Simpson MG (2010) Plant systematics, 2nd edn. Academic Press/Elsevier, San Diego, USA
Stadler M (2011) Importance of secondary metabolites in the Xylariaceae as parameters for assessment of their taxonomy, phylogeny, and functional biodiversity. Curr Res Environ Appl Mycol 1(2):75–133
Su L, Deng H, Niu Y-C(2016)Phialemoniopsis endophytica sp. nov., a new species of endophytic fungi from Luffa cylindrica in Henan, China. Mycol Prog 15:48
Takahashi M, Ohuchi A, Alicbusan RV (1965) Ecologic and taxonomic studies on Pythium as pathogenic soil fungi. VI. Some species of Pythium causing rhizome rot of Hindu lotus. Ann Phytopath Soc Japan 30:186–191
Tamura K, Stecher G, Peterson D, Filipski A, Kumar S (2013) MEGA6: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis version 6.0. Mol Biol Evol 30:2725–2729
Tap RM, Ramli NY, Sabaratnam P, Hashim R, Bakri AR, Bee LB, Ginsapu SJ, Ahmad R, Razak MF, Ahmad N (2016) First two cases of fungal infections associated with multi-drug resistant yeast, Fereydounia khargensis. Mycopathologia 181:531–537
Tateno O, Hirose D, Osono T, Takeda H (2015) Beech cupules share endophytic fungi with leaves and twigs. Mycoscience 56:252–256
Tharp BC (1917) Texas parasitic fungi. New species and amended descriptions. Mycologia 9:105–124
Thirumalachar MJ, Mishra JN (1953) Contribution to the study of fungi of Bihar, India—I. Sydowia 7(1–4):79–83
Udayanga D, Castlebury LA, Rossman AY, Chukeatirote E, Hyde KD (2015) The Diaporthe sojae species complex: phylogenetic re-assessment of pathogens associated with soybean, cucurbits and other field crops. Fungal Biology 119:383–497
van der Aa HA, Vanev S (2002) A revision of the species described in Phyllosticta. Centraalbureau voor Schimmelcultures, Utrecht, The Netherlands
von Arx JA (1970) A revision of the fungi classified as Gloeosporium. Bibl Mycol 24:1–203
Weir BS, Johnston PR, Damm U (2012) The Colletotrichum gloeosporioides species complex. Stud Mycol 73:115–180
Yang J-W, Yeh Y-H, Kirschner R (2016) A new endophytic species of Neostagonospora(Pleosporales) from the coastal grass Spinifex littoreus in Taiwan. Botany 94:593–598
Yeh Y-H, Kirschner R (2014)Sarocladium spinificis, a new endophytic species from the coastal grass Spinifex littoreus in Taiwan. Bot Stud 55:1–6
Yin X, Li XZ, Yin JJ, Wu X (2016) First report of Phytopythium helicoides causing rhizome rot of Asian lotus in China. Plant Dis 100(2):532–533
Zhang T-Y, Gao M-X(2000) Taxonomic studies of Alternaria from China V. New taxa and new records on Malvaceae, Nymphaeaceae and Rosaceae. Mycosystema 19:454–458
Zhao Z (2010) New data and new issues for the study of origin of rice agriculture in China. Archaeol Anthropol Sci 2:99–105
Acknowledgements
We thank Wei-An Liu for providing a sample and ITS sequence of Erysiphe takamatsui at National Central University (NCU, Taiwan) and other students at NCU for technical help in the lab, particularly Yu-Hung Yeh for dealing with sequencing of the protein genes. Dr. Chih-Hsiung Chen and Siou-Zhen Chen kindly provided assistance in collecting specimens in the Botanical Garden at Taichung, and Prof. Chee-Jen Chen collected and sent samples from Tainan, Prof. Dr. Wen-Feng Hsiao and colleagues are thanked for the opportunity to collect specimens at National Chiayi University, the Taipei City Government and Taipei Botanical Garden for collection permit, and the owners of tourist lotus ponds at Guanyin District (Taoyuan) for the opportunity to take samples. Dr. Takayuki Aoki and Dr. Yu-Ming Ju provided valuable hints for the identification of Fusarium species and Xylariaceae, respectively. We thank the curators of BPI and PPMH for the loan of specimens. Prof. Dr. Chenglin Hou (Capital Normal University, Beijing) helped us with the literature from mainland China. The study was supported by the Ministry of Science and Technology (former National Science Council) of Taiwan (NSC100-2621-B-008-001-MY3, NSC102-2621-B-008-001-MY3 and MOST 102-2621-B-008-001-MY3).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Section Editor: Marc Stadler
This article is part of the “Special Issue on ascomycete systematics in honour of Richard P. Korf who died in August 2016”.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, KL., Kirschner, R. Fungi from leaves of lotus (Nelumbo nucifera). Mycol Progress 17, 275–293 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-017-1324-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-017-1324-y