Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the relationship between sleep quality as assessed using the Pittsburgh Sleep Quality Index (PSQI) and the index of diffusivity along the perivascular space (ALPS index), a possible indirect indicator of glymphatic system activity.
Materials and methods
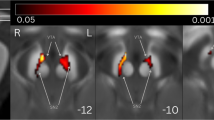
This study included the diffusion magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) data of 317 people with sleep disruption and 515 healthy controls (HCs) from the Human Connectome Project (WU-MINN HCP 1200). The ALPS index was calculated automatically based on diffusion tensor image analysis (DTI)-ALPS of diffusion MRI. The ALPS index of the sleep disruption and HC groups was compared using general linear model (GLM) analysis with covariates, such as age, sex, level of education, and intracranial volume. In addition, to confirm the relationship between sleep quality and the ALPS index in the sleep disruption group as well as evaluate the effect of each PSQI component on the ALPS index, correlation analyses between the ALPS indices and PSQI scores of all the components and between the ALPS index and each PSQI component was performed using GLM analysis with the abovementioned covariates, respectively.
Results
The ALPS index was significantly lower in the sleep disruption group than in the HC group (p = 0.001). Moreover, the ALPS indices showed significant negative correlations with the PSQI scores of all the components (false discovery rate [FDR]-corrected p < 0.001). Two significant negative correlations were also found between the ALPS index and PSQI component 2 (sleep latency, FDR-corrected p < 0.001) and 6 (the use of sleep medication, FDR-corrected p < 0.001).
Conclusion
Our findings suggest that glymphatic system impairment contributes to sleep disruption in young adults.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Moran M, Lynch CA, Walsh C, Coen R, Coakley D, Lawlor BA. Sleep disturbance in mild to moderate Alzheimer’s disease. Sleep Med. 2005;6:347–52.
Lysen TS, Darweesh SKL, Ikram MK, Luik AI, Ikram MA. Sleep and risk of parkinsonism and Parkinson’s disease: a population-based study. Brain. 2019;142:2013–22.
Boddy F, Rowan EN, Lett D, O’Brien JT, McKeith IG, Burn DJ. Subjectively reported sleep quality and excessive daytime somnolence in Parkinson’s disease with and without dementia, dementia with Lewy bodies and Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry. 2007;22:529–35.
Shi L, Chen S-J, Ma M-Y, Bao Y-P, Han Y, Wang Y-M, et al. Sleep disturbances increase the risk of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Sleep Med Rev. 2018;40:4–16.
Iliff JJ, Wang M, Liao Y, Plogg BA, Peng W, Gundersen GA, et al. A paravascular pathway facilitates CSF flow through the brain parenchyma and the clearance of interstitial solutes, including amyloid β. Sci Transl Med. 2012;4:147ra111.
Kress BT, Iliff JJ, Xia M, Wang M, Wei HS, Zeppenfeld D, et al. Impairment of paravascular clearance pathways in the aging brain. Ann Neurol. 2014;76:845–61.
Sundaram S, Hughes RL, Peterson E, Müller-Oehring EM, Brontë-Stewart HM, Poston KL, et al. Establishing a framework for neuropathological correlates and glymphatic system functioning in Parkinson’s disease. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2019;103:305–15.
Xie L, Kang H, Xu Q, Chen MJ, Liao Y, Thiyagarajan M, et al. Sleep drives metabolite clearance from the adult brain. Science. 2013;342:373–7.
Taoka T, Masutani Y, Kawai H, Nakane T, Matsuoka K, Yasuno F, et al. Evaluation of glymphatic system activity with the diffusion MR technique: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in Alzheimer’s disease cases. Jpn J Radiol. 2017;35:172–8.
Taoka T, Fukusumi A, Miyasaka T, Kawai H, Nakane T, Kichikawa K, et al. Structure of the medullary veins of the cerebral hemisphere and related disorders. Radiographics. 2017;37:281–97.
Bae YJ, Choi BS, Kim J-M, Choi J-H, Cho SJ, Kim JH. Altered glymphatic system in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2021;82:56–60.
Chen H-L, Chen P-C, Lu C-H, Tsai N-W, Yu C-C, Chou K-H, et al. Associations among cognitive functions, plasma DNA, and diffusion tensor image along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) in patients with Parkinson’s disease. Oxid Med Cell Longev. 2021;2021:4034509.
Steward CE, Venkatraman VK, Lui E, Malpas CB, Ellis KA, Cyarto EV, et al. Assessment of the DTI-ALPS parameter along the perivascular space in older adults at risk of dementia. J Neuroimaging. 2021;31:569–78.
Toh CH, Castillo M. Peritumoral brain edema volume in meningioma correlates with tumor fractional anisotropy but not apparent diffusion coefficient or cerebral blood volume. Neuroradiology. 2021;63:1263–70.
Yang G, Deng N, Liu Y, Gu Y, Yao X. Evaluation of glymphatic system using diffusion MR technique in T2DM cases. Front Hum Neurosci. 2020;14:300.
Yokota H, Vijayasarathi A, Cekic M, Hirata Y, Linetsky M, Ho M, et al. Diagnostic performance of glymphatic system evaluation using diffusion tensor imaging in idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus and mimickers. Curr Gerontol Geriatr Res. 2019;2019:5675014.
Zhang W, Zhou Y, Wang J, Gong X, Chen Z, Zhang X, et al. Glymphatic clearance function in patients with cerebral small vessel disease. Neuroimage. 2021;238: 118257.
Zhou W, Shen B, Shen W-Q, Chen H, Zheng Y-F, Fei J-J. Dysfunction of the glymphatic system might be related to iron deposition in the normal aging brain. Front Aging Neurosci. 2020;12: 559603.
Siow TY, Toh CH, Hsu J-L, Liu G-H, Lee S-H, Chen N-H, et al. Association of sleep, neuropsychological performance, and gray matter volume with glymphatic function in community-dwelling older adults. Neurology. 2022;98:e829–38.
Buysse DJ, Reynolds CF 3rd, Monk TH, Berman SR, Kupfer DJ. The pittsburgh sleep quality index: a new instrument for psychiatric practice and research. Psychiatry Res. 1989;28:193–213.
Van Essen DC, Smith SM, Barch DM, Behrens TEJ, Yacoub E, Ugurbil K, et al. The WU-minn human connectome project: an overview. Neuroimage. 2013;80:62–79.
Galea M, Woodward M. Mini-mental state examination (MMSE). Aust J Physiother. 2005;51:198.
Fischl B. FreeSurfer. Neuroimage. 2012;62:774–81.
Kochhann R, Varela JS, Lisboa CS de M, Chaves MLF. The Mini Mental State Examination: Review of cutoff points adjusted for schooling in a large Southern Brazilian sample. Dement Neuropsychol. 2010;4:35–41.
Glasser MF, Sotiropoulos SN, Wilson JA, Coalson TS, Fischl B, Andersson JL, et al. The minimal preprocessing pipelines for the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage. 2013;80:105–24.
Sotiropoulos SN, Jbabdi S, Xu J, Andersson JL, Moeller S, Auerbach EJ, et al. Advances in diffusion MRI acquisition and processing in the Human Connectome Project. Neuroimage. 2013;80:125–43.
Kamagata K, Andica C, Takabayashi K, Saito Y, Taoka T, Nozaki H, et al. Association of MRI indices of glymphatic system with amyloid deposition and cognition in mild cognitive impairment and Alzheimer disease. Neurology. Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the American Academy of Neurology; 2022;99:e2648–60.
Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. Asymptotic and resampling strategies for assessing and comparing indirect effects in multiple mediator models. Behav Res Methods. 2008;40:879–91.
Preacher KJ, Hayes AF. SPSS and SAS procedures for estimating indirect effects in simple mediation models. Behav Res Methods Instrum Comput. 2004;36:717–31.
Benveniste H. The Brain’s Waste-Removal System. Cerebrum. 2018;2018. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/30746031
O’Donnell J, Ding F, Nedergaard M. Distinct functional states of astrocytes during sleep and wakefulness: is norepinephrine the master regulator? Curr Sleep Med Rep. 2015;1:1–8.
Krueger JM, Frank MG, Wisor JP, Roy S. Sleep function: toward elucidating an enigma. Sleep Med Rev. 2016;28:46–54.
Hsiao W-C, Chang H-I, Hsu S-W, Lee C-C, Huang S-H, Cheng C-H, et al. Association of cognition and brain reserve in aging and glymphatic function using diffusion tensor image-along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS). Neuroscience. Elsevier BV; 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2023.04.004
Dai Z, Yang Z, Chen X, Zheng W, Zhuang Z, Liao Y, et al. The aging of glymphatic system in human brain and its correlation with brain charts and neuropsychological functioning. Cereb Cortex. Oxford University Press (OUP); 2023. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhad086
Zhou L, Nguyen TD, Li Y. Parenchymal CSF fraction and DTI‐ALPS in brain aging. Alzheimers Dement. Wiley; 2022;18. https://doi.org/10.1002/alz.069407
Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, Nakane T, Sakai M, Ichikawa K, et al. Diffusion-weighted image analysis along the perivascular space (DWI–ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid status: age dependence in normal subjects. Jpn J Radiol. 2022;40:894–902.
Muscogiuri G, Barrea L, Aprano S, Framondi L, Di Matteo R, Laudisio D, et al. Sleep quality in obesity: does adherence to the Mediterranean diet matter? Nutrients. MDPI AG; 2020;12:1364.
Iliescu EA, Coo H, McMurray MH, Meers CL, Quinn MM, Singer MA, et al. Quality of sleep and health-related quality of life in haemodialysis patients. Nephrol Dial Transpl Oxf Univ Press (OUP). 2003;18:126–32.
Sangalli L, Boggero IA. The impact of sleep components, quality and patterns on glymphatic system functioning in healthy adults: a systematic review. Sleep Med Elsevier BV. 2023;101:322–49.
Cole JC, Motivala SJ, Buysse DJ, Oxman MN, Levin MJ, Irwin MR. Validation of a 3-factor scoring model for the Pittsburgh sleep quality index in older adults. Sleep Oxford Univ Press (OUP). 2006;29:112–6.
Taoka T, Ito R, Nakamichi R, Kamagata K, Sakai M, Kawai H, et al. Reproducibility of diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS) for evaluating interstitial fluid diffusivity and glymphatic function: CHanges in Alps index on Multiple conditiON acquIsition eXperiment (CHAMONIX) study. Jpn J Radiol. 2022;40:147–58.
Maximov II, Alnaes D, Westlye LT. Towards an optimised processing pipeline for diffusion magnetic resonance imaging data: Effects of artefact corrections on diffusion metrics and their age associations in UK Biobank. Hum Brain Mapp. 2019;40:4146–62.
Kikuta J, Kamagata K, Takabayashi K, Taoka T, Yokota H, Andica C, et al. An investigation of water diffusivity changes along the perivascular space in elderly subjects with hypertension. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2022;43:48–55.
Acknowledgements
Data were provided (in part) by the Human Connectome Project, WU–Minn Consortium (Principal Investigators: David Van Essen and Kamil Ugurbil; 1U54MH091657) funded by the 16 NIH Institutes and Centers that support the NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research, and by the McDonnell Center for Systems Neuroscience at Washington University.
Funding
McDonnell Center for Systems Neuroscience; NIH Blueprint for Neuroscience Research, Grant/Award Number: 1U54MH091657. This study was partially supported by the Juntendo Research Branding Project, JSPS KAKENHI (Grant Nos. 20K16737, 21K07690, 21K12153, 21K15833, 22H04926, 23H02865), a Grant-in-Aid for Special Research in Subsidies for ordinary expenses of private schools from The Promotion and Mutual Aid Corporation for Private Schools of Japan, the Brain/MINDS Beyond program (Grant No. JP19dm0307101) of the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), and AMED under Grant Number JP21wm0425006. The Department of Innovative Biomedical Visualization (iBMV), Nagoya University Graduate School of Medicine, is financially supported by Canon Medical Systems Corporation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
YS, YH, and KK conceived the project. YS and YH developed the theory and conducted the experiments. KK and JK provided YS and YH with critical ideas and guidance for the experimental design. All authors contributed to the data interpretation and writing of the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Saito, Y., Hayakawa, Y., Kamagata, K. et al. Glymphatic system impairment in sleep disruption: diffusion tensor image analysis along the perivascular space (DTI-ALPS). Jpn J Radiol 41, 1335–1343 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-023-01463-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-023-01463-6