Abstract
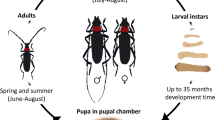
Holotrichia longipennis (Blanchard) is an extremely serious polyphagous pest in northwestern Himalayas. Both adults and grubs damage fruit, forest plants and field crops in mid and high hill areas. The adults of this species are defoliators and grubs are root feeders. Understanding the life history of H. longipennis is, therefore, essential for developing effective management strategies. H. longipennis populations were monitored and scouting for host plants was done during two consecutive years in 2011 and 2012. H. longipennis adults remain active from mid May - August and population buildup peaked during June in the north western Himalayas where they feed and damage location specific host plants. H. longipennis adults were recorded to damage 13 species of host plants from the region. Kheradhar, Palampur, Kullu, Dallash and Kwagdhar areas of north western Himalayas are the hotspots of H. longipennis. H. longipennis is univoltine and had annual life cycle with average duration of egg, larva, pre-pupa, and pupa was 13.1, 285.9, 13.2, and 9.5 days, respectively. H. longipennis completes one generation in 293–322 days in laboratory at 27 °C. Adult longevity averaged 25.3 days for males and 37.8 days for females. The grubs are exarate, scarabaeform and measured 32.9–34.2 mm (IIIrd instar) in length. The complete raster pattern H. longipennis grub and male and female genitalia of adults forms a basis for correct identification both at larval and adult stage. The species spends more than 90% of its life cycle under soil surface except for short periods for feeding and mating.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahrens, D. (2005). Illustrated key of phytophagous scarabs of the Chitwan region (Nepal): Including figures of adults of white grubs recorded in the IPM project entitled “Identification of whitegrub species of Nepal”. Project report NE36 (43636) Version 1.2.
Annonymous (2015). Encyclopedia of life. http://eol.org/pages/92486/names.
Arakaki, N., Sadoyama, Y., Kishita, M., Nagayama, A., Oyafuso, A., Ishimine, M., Ota, M., Akina, T., Fukaya, M., Hirai, Y., Yamamura, K., & Wakamura, S. (2004). Mating behavior of the scarab beetle Dasylepida ishigakiensis (Coleoptera:Scarabaeidae). Applied Entomology Zoology, 39(4), 669–674.
Beeson, C.F.C. (1941). The ecology and control of the forest insects in India and the neighbouring countries. Publications of forest Research, Division. Government of India. pp. 1007.
Bhagat, R. M., & Singh, V. (2006). Insect-pests associated with seabuckthorn (Hippophae rhamnoides L.) in Lahaul velley of Himachal Pradesh. Pest Management and Economic Zoology, 14(1/2), 191–193.
Bhattacharyya, B., Pujari, D., Bhuyan, U., Handique, G., Baurah, A. A. L. H., Dutta, S. K., & Tanaka, S. (2015). Seasonal life cycle and biology of Lepidiota mansueta (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae): a serious root‑feeding pest in India. Applied Entomology and Zoology. doi:10.1007/s13355-015-0349-4. Online Published in June 2015.
Chandel, R. S., Chander, R., & Verma, T. D. (1994a). Thurja orientalis L: a new host of scarabaeid beetles. Indian Journal of Plant Protection, 22(1), 134.
Chandel, R. S., Gupta, P. R., & Chander, R. (1994b). Diversity of scarabaeid beetles in mid hills of Himachal Pradesh. Himachal Journal of Agricultural Research, 20(1&2), 98–101.
Chandel, R. S., Gupta, P. R., & Chander, R. (1995). Behaviour and biology of the defoliating beetle, Brahmina coriacea (Hope) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in Himachal Pradesh. Journal of Soil Biology and Ecology, 15(1), 82–89.
Chandel, R. S., Kashyap, N. P., & Chandel, Y. S. (1996). White grubs survey on potato in Lahaul valley of Himachal Pradesh. Journal of Indian Potato Association, 23(3/4), 168–169.
Chandel, R. S., Gupta, P. R., & Thakur, J. R. (1997). Host preference and seasonal abundance of defoliating beetles infesting fruit trees in mid hills of Himachal Pradesh. Journal of Soil Biology and Ecology, 17(2), 140–146.
Chandra, K. (2005). Insecta: Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae. Zoological Survey of India Fauna, of Western Himalayas (Part 2). pp 141–155.
Chandra, K., & Gupta, D. (2012). Study of external male genitalia of ten species of Indian dung beetles (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Scarabaeinae). International Journal of Science and Nature, 31(3), 635–638.
Chandra, K., & Kumar, M. (1991). Studies on the female genitalia of Pleurostict scarabaeidae (Coleoptera: Insecta) of north west India. Journal of Hill Farming, 4(2), 57–65.
Cribb, B. W., Hull, C. D., Moore, C. J., Miller, L. J., & Yeates, D. K. (1998). Structure of raster in Melolonthine larvae. Annals of the Entomological Society of America, 91, 202–210.
Dixit, A. K., & Sharma, S. (2010). Potato in Garhwal region of Uttarakhand: some issues and suggestions. Potato Journal, 37(3–4), 157–163.
Fujiyama, S. (1983). The larval diapause of three scarabaeid beetles and its function in their life cycles. In V. K. Brown & I. Hodek (Eds.), Diapause and life cycle strategies in insects (pp. 55–66). The Hague: Dr. W. Junk.
Haq, A. (1962). Notes on the bionomics of Lachnosterna longipennis Bl. (Melolonthidae: Coleoptera). Indian Journal of Entomology, 24(3), 220–221.
Holloway, B. A. (1972). The systematic position of the genus Diphyllostoma Fall (Coleoptera: Scarabaeoidea). New Zealand Journal of Science, 13, 31–38.
Joshi, K. C. & Joshi, R. (1980). Insect pests of fruits trees in Kumaon hills. Indian Horticulture, 25(1), 21–24.
Khan, K. M., & Ghai, S. (1982). Taxonomic status of the genus Holotrichia Hope. (Melolonthini: Melolonthinae: Scarabaeidae) with description of five new species from India along with redescription of two poorly described species and a key to species. Indian Journal of Entomology, 23, 28–45.
Krell, F. T. (1996). Die Kopulationsorgane des Maika¨ fers Melolontha melolontha (Insecta: Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) – Ein Beitrag zur vergleichenden und funktionellen Anatomie.
Kumar, J., Sharma, S. D., Lal, R., & Deor, B. S. (2005). White grubs damaging maize and paddy crops in Kullu and Mandi districts of Himachal Pradesh. Pest Management and Ecological Zoology, 13(1), 15–20.
Litsinger J. A., Libetario E. M. & Barrion A. T. (2002) Population dynamics of white grubs in the upland rice and maize environment of Northern Mindanao, Philippines. International Journal of Pest Management, 48(3), 239–260.
Mehta, P. K., Chandel, R. S., & Mathur, Y. S. (2008). Phytophagous whitegrubs of Himachal Pradesh. Technical Bulletin: Depatment of Entomology (p. 13). Palampur: CSK HPKV.
Mehta, P. K., Chandel, R. S. & Mathur, Y. S. (2010). Status of whitegrubs in north western Himalaya. Journal of Insect Science, 23(1), 1–14.
Mishra, P. N. (2001). Scarab fauna of Himalayan region and their management. In G. Sharma, Y. S. Mathur, & R. B. L. Gupta (Eds.), Indian phytophagous scarabs and their management: Present status and future strategies (pp. 74–85). Jodhpur: Agrobios (India).
Mishra, P. N., & Singh, M. P. (1993). Field biology of white grubs, Holotrichia longipennis on potatoes in U.P. Hills. Journal of Indian Potato Association, 20(3), 249–251.
Mishra, P. N., & Singh, M. P. (1996). Studies on the white grubs (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) prevalent in Uttar Pradesh hills. Annals of Agricultural Research, 17(4), 411–413.
Misra, S. S. & Chandel, R.S. (2003). Potato whitegrubs in India. Technical Bulletin No. 60 (p 47). Shimla, India: CPRI.
Pathania, M. (2014). Studies on phytophagous whitegruibs of Himachal Pradesh. Ph. D. Thesis. Palampur (India). CSK HPKV, P. 268.
Pathania, M., & Chandel, R. S. (2016). Life history strategy and behavior of white grub, Brahmina coriacea (Hope) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Melolonthinae) an invasive pest of potato and apple agro-ecosystem in northwestern India. Oriental Insects. doi:10.1080/00305316.2016.1247756.
Pathania, M., Chandel, R. S., Verma, K. S., & Mehta, P. K. (2012). A survey study of potato white grubs in Himachal Pradesh. In: Proceeding of national seminar on Indian agriculture, remedies and road map, August 4–5, 2012 (pp. 60). Palampur: CSK HPKV.
Ritcher, P. O. (1966). White grubs and their allies. A study of North American Scarabaeoid Larvae. Oregon State Monographs. Studies in entomology. Corvallis: Oregon State University Press.
Sanmartin, I., & Martin-Piera, F. (2003). First phylogenetic analysis of the subfamily Pachydeminae (Coleoptera. Scarabaeoidea, Melolonthidae): the Palearctic Pachydeminae. Journal of Zoological Systematics and Evolutionary Research, 41, 2–46.
Saunders, D. S. (2002). Insect clocks (3rd ed.). Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Shah, N. K., & Shah, L. (1990). Bionomics of Holotrichia longipennis BL. (Coleoptera: Melolonthinae) in western Himalayas. Indian Journal of Forestry, 13(3), 234–237.
Sharma, P. L., Attari, B. S., & Aggarwal, S. C. (1969). Beetles causing damage to pome and stone fruits in Himachal Pradesh. Indian Journal of Entomology, 31(4), 377–379.
Sharma, G., Mathur, Y. S., & Gupta, R. B. L. (2001). Indian Phytophagous scarabs and their management. Present Status and Future Strategies. Jodhpur: Agrobios (India).
Sharma, P. L. & Bhalla, O. P. (1964). A survey study of insect pests of economic importance in Himachal Pradesh. Indian Journal of Entomology, 26, 318–331.
Singh, M. P., Bisht, R. S., & Mishra, P. N. (1999). Preference of host plants by white grub beetle, Holotrichia longipennis in Garhwal Himalaya. Indian Journal of Entomology, 61(1), 7–10.
Singh, S. S., Mishra, P. N., & Nainwal, N. C. (2002). Status and management of white grub (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in horticultural crops. Progressive Horticulture, 34(1), 6–16.
Singh, M. P., Bisth, R. S., & Mishra, P. N. (2003a). Distribution of white grub fauna in Garhwal hills of western Himalayas. Indian Journal of Entomology, 65(2), 217–221.
Singh, M. P., Mishra, P. N., & Bisth, R. S. (2003b). Nature and extent of damage of white grub Lachnosterna (Holotrichia) longipennis Blanch. Under various farming situations of Uttaranchal hills. Indian Journal of Entomology, 66(3), 277–280.
Sreedevi, K., Chandel, R. S., Pathania, M., & Stanley, J. (2014). Species distribution and larval diagnostic characters of white grub species, Holotrichia longipennis (Blanchard), H. sikkimensis (Brenske) and H. rosettae Frey. Current Biotica, 8(2), 151–156.
Sushil, S. N., Mohan, M., Selvakumar, G., & Bhatt, J. C. (2006). Relative abundance and host preference of white grubs (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae) in Kumaon hills of Indian Himalayas. Indian Journal of Agriculture Sciences, 76(5), 338–339.
Tanaka, S., Yukuhiro, F., & Wakamura, S. (2006). Sexual dimorphism in body dimensions and antennal sensilla in white grub beetle, Dasylepida ishigakiensis (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae). Applied Entomology Zoology, 41(3), 455–461.
Tanaka, S., Yukuhiro, F., Yasui, H., Fukaya, M., Akino, T., & Wakamura, S. (2008). Presence of larval and adult diapauses in a subtropical scarab beetle: graded thermal response for synchronized sexual maturation and reproduction. Physiological Entomology, 33, 334–345.
Tanner, V. M. (1927). The genitalia of female Coleoptera. Transactions of the American Entomological Society, 53, 3–50.
Tauber, M. J., Tauber, C. A., & Masaki, S. (1986). Seasonal adaptations of insects. Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Thakur, M. L. (2000). Nursery pests. In: Forest entomology (Ecology and Management) (pp. 98–123). Dehradun: Sai Publishers.
Thakur, Y., Sharma, A. K., Dhiman, K. R., & Chandla, V. K. (2008). Management of whitegrub, Brahmina coriacea (Hope) in potato (Solanam tuberosum) fields of Fagu (Shimla hills). In: II nd Congress on Insect Science, February 21–22 (pp. 232). Ludhiana: PAU.
Veeresh G. K. (1977). Studies on root grubs in Karnataka with special reference to bionomics and control of Holotrichia serrata F. (Coleoptera: Melolonthinae). UAS Monograph Series No. 2, Bangalore, P. 87.
Verma, A. N. (1975). Occurrence of white grubs in Haryana. Current Science, 44(1), 32–33.
Yadava, C. P. S. & Sharma, G. K. (1995). Indian white grubs and their management. Technical Bulletin No.2, Project Coordinating Centre AICRIP of whitegrub (p. 26). New Delhi: ICAR.
Acknowledgements
The first author would like to thank Department of Science and Technology, Government of India and All India Network Project on Whitegrubs and Other Soil Arthropods for providing financial support for this study. Thanks are due to technical and field staff of white grub laboratory of Department of Entomology, CSK HPKV, Palampur, namely Mr. Surinder Singh (TA), Mr. Rajesh Pathania (FA) and Mr. Anil Kumar (FH) for their sincere efforts in conducting surveys and collection and maintenance of insect culture.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pathania, M., Chandel, R.S., Verma, K.S. et al. Seasonal life cycle of Holotrichia longipennis (Blanchard ) (Coleoptera: Scarabaeidae: Melolonthinae): a serious foliage and root feeding pest in India. Phytoparasitica 44, 615–629 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-016-0557-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12600-016-0557-7