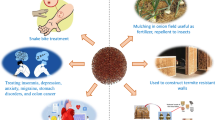
Abstract
Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) is a flowering plant in the grass family (Poaceae) characterized by a great genotypic and phenotypic diversity, making it a cereal species of major interest cultivated in warm climate worldwide. Fifth most cultivated cereal in the world and second in Africa, sorghum is the main cultivated species in the Sahelian zone. In 2020, its world and African estimated production were 58.7 and 27.5 million tonnes over an area of 40.3 and 27.3 million hectares, respectively. Primarily cultivated for its seeds, fodder, sugar and fiber, or for bioenergy production, sorghum is a staple food for millions of people. Its polymorphism gives it a versatile, multifunctional character and allows it to combine different food, energy and industrial uses. Mainly studied as a feedstock for the production of several chemicals and biofuels including bioethanol, biomethane, biohydrogen, biolipids, butyric and lactic acids, 1-butanol, acetone-butanol etc. and for electrical energy production in microbial fuel cells. The processes for exploiting the various components (starchy grains, lignocellulosic biomass and sweet juice extracted from the stem) of this plant generate a large quantity of by-products which are valued in many fields of application. Mainly as source of food and feed, biomolecules with therapeutic, nutraceutical and functional properties and for industrial or artisanal applications and biomaterials. The world population increasing combined with the decrease of biomass resources, due to the effects of climate change, imposed a reconsideration of the potential of the entire value chain of this crop. The present review focused on the biochemical composition of sorghum and its use as food but also as a source of valuable by-products.
Graphical Abstract







Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
Not applicable.
References
Ramatoulaye, F., Mady, C., Fallou, S.: Production and use sorghum: a literature review. J.Nutr. Health Food Sci. 4, 1–4 (2016)
Navnidhi, C., Burale, A., Claudia, M., Ravinder, K., Gurpreet, S., Anil, P.: Exploring the nutritional and phytochemical potential of sorghum in food processing for food security. Nutr. Food Sci. 05, 2018–2149 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1108/NFS-05-2018-0149
Kamara, A.Y., Ekeleme, F., Omoigui, L., Menkir, A., Chikoye, D., Dugje, I.Y.: Response of exotic sorghum (Sorghum bicolor [L.] moench) cultivars to planting date under natural infestation of striga hermonthica (del) benth. in the Sudan savanna zone of northeast Nigeria. Arch. Agron. Soil Sci. 57, 679–692 (2011)
Mwithiga, G., Sifuna, M.M.: Effect of moisture content on the physical properties of three varieties of sorghum seeds. J. Food Eng. 75, 480–486 (2006)
FAOSTAT.: Donnéesde l’alimentation et de l’agriculture. http://www.fao.org/faostat/fr/#home (2022). Accessed 28 July 2022
Nxele, X., Klein, A., Ndimba, B.K.: Drought and salinity stress alters ROS accumulation, water retention, and osmolyte content in sorghum plants. S. Afr. J. Bot. 108, 261–266 (2017)
Guo, Y.Y., Tian, S.S., Liu, S.S., Wang, W.Q., Sui, N.: Energy dissipation and antioxidant enzyme system protect photosystem II of sweet sorghum under drought stress. Photosynthetica 56, 861–872 (2018)
Badigannavar, A., Teme, N., de Oliveira, A.C., Li, G., Vaksmann, M., Viana, V.E., Sarsu, F.: Physiological, genetic and molecular basis of drought resilience in sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench]. Indian J. Plant. Physiol. 23, 670–688 (2018)
Thomas, H.L., Pot, D., Latrille, E., Trouche, G., Bonnal, L., Bastianelli, D., Carrère, H.: Sorghum biomethane potential varies with the genotype and the cultivation site. Waste Biomass Valoriz. (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-0099-3
Clarke, S.J., McLean, J., George-Jaeggli, B., McLean, G., de Voil, P., Eyre, J.X., Rodriguez, D.: Understanding the diversity in yield potential and stability among commercial sorghum hybrids can inform crop designs. Field Crops Res. 230, 84–97 (2019)
Saballos A.: Development and utilisation of sorghum as a bioenergy crop. Genet. Improvement Bioenergy Crops. 211–248 (2008)
Blummel, M., Rao, S.S., Palaniswami, S., Shah, L., Reddy, V.S.B.: Evaluation of sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) used for bio-ethanol production in the context of optimizing whole plant utilization. Anim. Nutr. Feed Technol. 9, 1–10 (2009)
Trappey, E.F., Khouryieh, H., Aramouni, F., Herald, T.: Effect of sorghum flour composition and particle size on quality properties of gluten-free bread. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 21, 188–202 (2015)
Althwab, S., Carr, T.P., Weller, C.L., Dweikat, I.M., Schlegel, V.: Advances in grain sorghum and its co-products as a human health promoting dietary system. Food Res. Int. 77, 349–359 (2015)
Anunciação, P.C., de Morais Cardoso, L., Gomes, J.V.P., Della Lucia, C.M., Carvalho, C.W.P., Galdeano, M.C., Pinheiro-Sant’Ana, H.M.: Comparing sorghum and wheat whole grain breakfast cereals: sensorial acceptance and bioactive compound content. Food Chem. 221, 984–989 (2017)
Dahlberg, J., Berenji, J., Sikora, V., Latkovic, D.: Assessing sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] germplasm for new traits: food, fuels & unique uses. Maydica 56, 86–92 (2012)
Nghiem, N.P., Montanti, J., Johnston, D.B.: Sorghum as a renewable feedstock for production of fuels and industrial chemicals. AIMS Bioeng. 3, 75–91 (2016)
Regassa, T.H., Wortmann, C.S.: Sweet sorghum as a bioenergy crop: literature review. Biomass Bioenergy 64, 348–355 (2014)
Szambelan, K., Nowak, J., Frankowski, J., Szwengiel, A., Jelen, H., Burczyk, H.: The comprehensive analysis of sorghum cultivated in Poland for energy purposes: separate hydrolysis and fermentation and simultaneous saccharification and fermentation methods and their impact on bioethanol effectiveness and volatile by-products from the grain and the energy potential of sorghum straw. Bioresour. Technol. 250, 750–757 (2018)
Dehaynin, N.: Utilisation du sorgho en alimentation animale. Ph. D. Thesis, médecine vétérinaire. Universite Claude-Bernard—lyon I, Lyon, p 108 (2007)
Hébert J.P., Griffon D.: Toutes les bières moussent-elles? 80 clés pour comprendre les bières. Quae, Versailles, p 223 (2010)
Xiong, Y., Zhang, P., Luo, J., Johnson, S., Fang, Z.: Effect of processing on the phenolic contents, antioxidant activity and volatile compounds of sorghum grain tea. J. Cereal Sci. 85, 6–14 (2019)
Dicko, M.H., Gruppen, H., Traoré, A.S., Voragen, A.G.J., van Berkel, W.J.H.: Sorghum grain as human food in Africa: relevance of content of starch and amylase activities. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 5, 384–395 (2006)
Medeiros, D., Vazquez-Araujo, L., Chambers, E., IV.: Sorghum: the forgotten grain. Food Technol. 65, 52–60 (2011)
Awika, J.M.: Sorghum: its unique nutritional and health-promoting attributes. In: Taylor, J.R.N., Awika, J.M. (eds.) Gluten free ancient grains, pp. 21–54. Woodhead Publishing, Cambridge (2017)
Pontieri, P., Del Giudice, L.: Sorghum: a novel and healthy food. Encycl. Food Health 33–43 (2016)
Taylor, J.R.N., Emmambux, M.N.: Gluten-free cereal products and beverages. In: Arendt, E.K., Bello, F.D. (eds.) Gluten Free Foods and Beverages from Millets, pp. 119–148. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2018)
Lopez, N., Tique, M., Perez, L.: Contribution to the study of sorghum [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] for human nutrition. Perspect. Hum. Nutr. 13, 33–44 (2011)
Shahidi, F., Peng, H.: Bioaccessibility and bioavailability of phenolic compounds. J. Food Bioactives 4, 11–68 (2018)
Kim, M., Day, D.F.: Composition of sugar cane, energy cane, and sweet sorghum suitable for ethanol production at Louisiana sugar mills. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 38, 803–807 (2011)
Nasidi, M., Agu, R., Deeni, Y., Walker, G.: Improved production of ethanol using bagasse from different sorghum cultivars. Biomass Bioenergy 72, 288–299 (2015)
John, M.J., Thomas, S.: Biofibres and biocomposites. Carbohydr. Polym. 71, 343–364 (2008)
Oo, A., Muntasir, N., Poon, K., Weersink, A., Thimmanagari, M.: Development of an Agricultural Biomaterial Industry in Ontario. Technical report, University of Guelph, No. 241708, p. 64 (2016)
Abe, M.M., Branciforti, M.C., Brienzo, M.: Biodegradation of hemicellulose-cellulose starch-based bioplastics and microbial polyesters. Recycling 6, 22 (2021)
Naidu, D.S., Hlangothi, S.P., John, M.J.: Bio-based products from xylan: a review. Carbohydr. Polym. 179, 28–41 (2018)
Machado, G., Leon, S., Santos, F., Lourega, R., Dullius, J., Mollmann, M.E., Eichler, P.: Literature review on furfural production from lignocellulosic biomass. Nat. Resour. 7, 115–129 (2016)
Schaffer, R.E., Gourley, L.M.: Sorghum as an energy source. In: House, L.R., Mughogho, L.K., Peack, J.M. (eds.) Sorghum in the Eighties, pp. 477–783. ICRISAT, Patancheru (1982)
Murray, S.C., Rooney, W.L., Hamblin, M.T., Mitchell, S.E., Kresovich, S.: Sweet sorghum genetic diversity and association mapping for brix and height. Plant Genome 2, 15 (2009)
Jacques, C., Jean-François, C., Alain, R., et Gilles, T.: Le sorgho. Agricultures tropicales en poche. Editions Quæ, CTA, Presses agronomiques de Gembloux, p. 245 (2013)
Sipos, B., Récey, J., Somorai, Z., Kádár, Z., Dienes, D., Réczey, K.: Sweet sorghum as feedstock for ethanol production: enzymatic hydrolysis of steam-pretreated bagasse. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 153, 151–162 (2009)
Kim, M., Han, K., Jeong, Y., Day, D.F.: Utilization of whole sweet sorghum containing juice, leaves, and bagasse for bio-ethanol production. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 21, 1075–1080 (2012)
Saidi, S., Gazull, L., Burnod, P., Fallot, A.: Atlas mondial du potentiel de mise en place de cultures dédiées à la production de biocarburants de seconde génération: un état des lieux pour 10 genres végétaux à fort potentiel lignocellulosique. Rapport, Cirad & Total, Montpellier, p. 63 (2010)
Whitfield, M.B., Chinn, M.S., Veal, M.W.: Processing of materials derived from sweet sorghum for biobased products. Rev. Ind. Crops Prod. 37, 362–375 (2012)
Clerget, B.: Le rôle du photopériodisme dans l’élaboration du rendement de trois variétés de sorgho cultivées en Afrique de l’Ouest. Ph. D. Theis. Ina-PG, p. 103 (2004)
Teetor, V.H., Duclos, D.V., Wittenberg, E.T., Young, K.M., Chawhuaymak, J., Riley, M.R., Ray, D.T.: Effects of planting date on sugar and ethanol yield of sweet sorghum grown in Arizona. Ind. Crops Prod. 34, 1293–1300 (2011)
Noura, S.: Amélioration de l’extraction des sucres de la biomasse du millet perlé sucré et du sorgho sucré pour une éventuelle production de bioéthanol. Mémoire, Maîtrise en sols et environnement. Université Laval, Québec, p. 2015 (2016)
Harland, J.R., De Wet, J.M.J.: A Simplified classification of cultivated sorghum. Crop Sci. Soc. Am. 12, 172–176 (1972)
Doggett, H.: Sorghum. London Harlow (GB), Longman Scientific Technical, (2ème edition), p. 512 (1988)
Wendorf, F., Close, A.E., Schild, R., Wasylikowa, K., Housley, R.A., Harlan, J.R., Krolik, H.: Saharan exploitation of plants 8000 years BP. Nature 359, 721–724 (1992)
Barro-kondombo, C.P.: Diversités agro-morphologique et génétique de variétés locales de sorgho (Sorghum bicolor [L.] Moench) du Burkina Faso. Eléments pour la valorisation des ressources génétiques locales. Ph. D. Theis, Sciences Biologiques Appliquées. Université de Ouagadougou, Burkina Fasso, p. 113 (2010)
Clara, W.M., Silvia, S., Kofi, A., Guangxing, W.: A regional comparison of factors affecting global sorghum production: the case of North America, Asia and Africa’s Sahel. Rev. Sustain. 11, 2135 (2019). https://doi.org/10.3390/su11072135
Balole, T.V., Legwaila, G.M.: Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench. Record from Protabase. Brink, M. & Belay, G. (Editors). PROTA (Plant Resources of Tropical Africa/Ressources végétales de l’Afrique tropicale), Wageningen (2006)
Boudries, N.: Caractérisation des amidons de sorgho et de mil perlé cultivés dans le Sahara algérien. Ph. D. Theis. Université de Liège—Gembloux Agro-Bio Tech, p. 225 (2017)
Schober, T.J., Bean, S.R.: Sorghum and maize. In: Arendt, E.K., Bello, F.D. (eds.) Gluten-Free Cereal Products and Beverages, pp. 101–118. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2008)
Eckhoff, S.R., Watson, S.A.: Corn and sorghum starch production. In: BeMiller, J., Whistler, R. (eds.) Starch: Chemistry and Technology, 3rd edn., pp. 373–439. Elsevier, Amsterdam (2009)
Pilar, E.H., Mónica, L., Chávez, G., Juan, A., Ascacio, V., Desiree, D., Medina, D., Antionio, F.N., Teresinha, S., Xóchitl, R.C., Leonardo, S.: Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) as a potential source of bioactive substances and their biological properties. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. Nutr. (2020). https://doi.org/10.1080/10408398.2020.1852389
Ayodeji, O.A.: African sorghum-based fermented foods: past, current and future prospects. Rev. Nutr. 12, 1111 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/nu12041111
Snowden, J.D.: The cultivated races of sorghum. London, Adlard, p. 274 (1936)
Deu, M., Sagnard, F., Chantereau, J., Calatayud, C., Hérault, D., Mariac, C., Pham, J.L., Vigouroux, Y., Kapran, I., Traoré, P.S., Mamadou, A., Gérard, B., Ndjeunga, J., Bezançon, G.: Niger-wide assessment of in situ sorghum genetic diversity with microsatellite markers. Theoret. Appl. Genet. 116, 903–916 (2008)
Chantereau, J., Deu, M., Pham, J.L., Kapran, I., Vigouroux, Y., Bezançon, G.: Evolution des diversités phénotypique et génétique des sorghos et mils cultivés au Niger de 1976 à 2003. Le Sélectionneur Français 61, 33–45 (2010)
Sagnard, F., Deu, M., Dembélé, D., Leblois, R., Touré, L., Diakité, M., Calatayud, C., Vaksmann, M., Bouchet, S., Mallé, Y., Togola, S., Traoré, P.C.S.: Genetic diversity, structure, gene flow and evolutionary relationships within the Sorghum bicolor wild–weedy–crop complex in a western African region. Theoret. Appl. Genet. 123, 1231–1246 (2011)
Ritter, K.B., Jordan, D.R., Chapman, S.C., Godwin, I.D., Mace, E.S., Mcintyre, C.L.: Identification of QTL for sugar related traits in a sweet x grain sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) recombinant inbred population. Mol. Breed. 22, 367–384 (2008)
Wang, L., Jiao, S., Jiang, Y., Yan, H., Su, D., Sun, G., Yan, X., Sun, L.: Genetic diversity in parent lines of sweet sorghum based on agronomical traits and SSR markers. Field Crop Res 149, 11–19 (2013)
Gutjahr, S.: Analyse des caractères d’intérêt morphogénétiques et biochimiques pour le développement de sorghos sucrés à double usage « grain-bioalcool ». Ph. D. Theis, Biologie Intégrative des Plantes (BIP). Université Montpellier II, Mont pellier, p 118 (2012)
Norman, M.J.T., Pearson, C.J., Searle, P.G.E.: Tropical Food Crops in their Environment, 2nd edn. University Press, Cambridge (1995)
Bellmer, D.D., Huhnke, R.L., Whiteley, R., Godsey, C.: The untapped potential of sweet sorghum as a bioenergy feedstock. Biofuels 1, 563–573 (2010)
Steduto, P., Katerji, N., Puertos-Molina, H., Unlu, M., Mastrorilli, M., Rana, G.: Water-use efficiency of sweet sorghum under water stress conditions. Gas exchange investigations at leaf and canopy scales. Field Crops Res. 54, 221–234 (1997)
Berenguer, M.J., Faci, J.M.: Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) yield compensation processes under different plant densities and variable water supply. Eur. J. Agron. 15, 43–55 (2001)
Almodares, A., Hadi, M.R.: Production of bioethanol from sweet sorghum: a review. Afr. J. Agric. Res. 4, 772–780 (2009)
Vasilakoglou, I., Dhima, K., Karagiannidis, N., Gatsis, T.: Sweet sorghum productivity for biofuels under increased soil salinity and reduced irrigation. Field Crop Res 120, 38–46 (2011)
Amaducci, S., Colauzzi, M., Battini, F., Fracasso, A., Perego, A.: Effect of irrigation and nitrogen fertilization on the production of biogas from maize and sorghum in a water limited environment. Eur. J. Agron. 76, 54–65 (2016)
Ameen, A., Yang, X., Chen, F., Tang, C., Du, F., Fahad, S., Xie, G.H.: Biomass yield and nutrient uptake of energy sorghum in response to nitrogen fertilizer rate on marginal land in a semi-arid region. BioEnergy Res. 10, 363–376 (2017)
Reddy, B.V.S., Ashok, Koumar A., Ramesh S.: Sweet sorghum: a water saving bio energy and crop. In: International conference on linkages between Energy and Water Management for agriculture in developing countries, January 29–30, 2007, IWMI, ICRISAT Campus, Hyderabad (2005)
Wu, X., Staggenborg, S., Propheter, J.L., Rooney, W.L., Yu, J., Wang, D.: Features of sweet sorghum juice and their performance in ethanol fermentation. Ind. Crops Prod. 31, 164–170 (2010)
Mahapatra, A.K., Latimore, M., Bellmer, D., Singh, B.P.: Utilization of sweet sorghum for ethanol production—a review. Paper presented at the 2011 ASABE Annual international Meeting, Louisville, Kentucky (2011)
Rao, P.S., Kumar, C.G., Reddy, B.V.S.: Sweet sorghum: from theory to practice. In: Rao, P.S., Kumar, C.G. (eds.) Characterization of Improved Sweet Sorghum Cultivars, pp. 1–15. Springer Briefs in Agriculture. Springer, New York (2013)
Basavaraj, G., Rao, P.P., Basu, K., Reddy, C.R., Kumar, A.A., Rao, P.S., Reddy, B.V.S.: Assessing viability of bio-ethanol production from sweet sorghum in India. Energy Policy 56, 501–508 (2013)
Yuan, J.S., Tiller, K.H., Al-Ahmad, H., Stewart, N.R., Stewart, C.N.J.: Plants to power: bioenergy to fuel the future, Review. Trends Plant Sci. 13, 421–429 (2008)
Temple, L., Levesque, A., Lamour, A., Charles, D., Braconnier, S.: Complémentarité des filières sorgho sucré et canne à sucre en Haïti : évaluation des conditions de développement sectoriel d’une innovation. Cah. Agric. 26, 55006 (2017)
Yevich, R., Logan, J.A.: An assessment of biofuel use and burning of agricultural waste in the developing world. Global Biogeochem. Cycles 17, 1–21 (2003)
Muhammad, N., Reginald, A., Yusuf, D., Graeme, W.: Utilisation of whole sorghum crop residues for bioethanol production. J. Inst. Brew. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1002/jib.324
Rooney, L., Waniska, R.: Sorghum food and industrial utilization. In: Smith et al. (ed.) Sorghum: Origin, History, Technology and Production, pp. 689–731. Wiley, New York (2000)
Zaldivar, J., Nielsen, J., Olsson, L.: Fuel ethanol production from lignocellulose: a challenge for metabolic engineering and process integration. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 56, 17–34 (2001)
Antonopoulou, G., Gavala, H.N., Skiadas, I.V., Angelopoulos, K., Lyberatos, G.: Biofuels generation from sweet sorghum: fermentative hydrogen productionand anaerobic digestion of the remaining biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 99, 110–119 (2008)
Bennett, A.S., Anex, R.P.: Production, transportation and milling costs of sweet sorghum as a feedstock for centralized bioethanol production in the upper Midwest. Bioresour. Technol. 100, 1595–1607 (2009)
Gutjahr, S., Clément-Vidal, A., Soutiras, A., Sonderegger, N., Braconnier, S., Dingkuhn, M., Luquet, D.: Grain, sugar and biomass accumulation in photoperiod-sensitive sorghums. II. Biochemical processes at internode level and interaction with phenology. Funct. Plant Biol. 40, 355–368 (2013)
Billa, E., Koullas, D.P., Monties, B., Koukios, E.G.: Stucture and compostion of sweet sorghum stalk components. Ind. Crops Prod. 6, 297–302 (1997)
Djomdi, Hamadou B., Klang M.J., Djoulde D.R., Christophe G., Michaud P.: Extraction performance of juice and bioethanol production from sweet sorghum (Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench). Glob. J. Eng. Sci. Res. Manag. 6, 57–66 (2019)
Forsan, C.F., Freitas, C., Masarin, F., Brienzo, M.: Xylooligosaccharide production from sugarcane bagasse and leaf using Aspergillus versicolor endoxylanase and diluted acid. Biomass Convers. Biorefin. 1–16 (2021)
Bidlack, J.: Molecular structure and component integration of secondary cell walls in plants. Proc. Oklahoma Acad. Sci. 72, 51–56 (1992)
Soha, R.A., Khalil, A.A., Abdelhafez, E.A.M.: Evaluation of bioethanol production from juice and bagasse of some sweet sorghum varieties. Ann. Agric. Sci. 60, 317–324 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.aoas.2015.10.005
Jolanta, B., Jakub, F., Aleksandra, W., Agnieszka, Ł: Bioethanol production from biomass of selected sorghum varieties cultivated as main and second crop. Energies 13, 6291 (2020). https://doi.org/10.3390/en13236291
Crépeau, M., Khelifi, M., Vanasse, A., Seguin, P., Trembly, G.F.: Compressive forces and harvest time effects on sugars and juice extracted from sweet pearl millet and sweet sorghum. Trans. ASABE 56, 1665–1671 (2013)
Crépeau M.: Optimisation de la récolte, de l’entreposage et du pressage du millet perlé sucré et du sorgho sucré cultivés au Québec pour la production de bioéthanol. Ph. D. Thesis, sols et environnement. Université Laval, Québec, p. 151 (2017)
Coble, C.G., Egg, R.P., Shmulevich, I.: Processing techniques for ethanol production from sweet sorghum. Biomass 6, 111–117 (1984)
Bellmer, D.D., Huhnke, R.L., Kundiyana. D.: Issues with in-field fermentation of sweet sorghum juice. 2008 ASABE annual international meeting. ASABE Paper No 084828. Providence, Rhode Island, 29 June–2 July, (2008)
Worley, J.W., Vaughan, D.H., Cundiff, J.S.: Energy analysis of ethanol production from sweet sorghum. Bioresour. Technol. 40, 263–273 (1992)
Rains, G.C., Cundiff, J.S., Welbaum, G.E.: Sweet sorghum for a piedmont ethanol industry. In: Janick, J., Simon, J.E. (eds.) New Crops, pp. 394–399. Wiley, New York (1993)
Mask, P.L., Morris, W.C.: Sweet sorghum culture and syrup production. ACES publication No AR-625. ACES, Alabama (1991)
Cosgrove, C.T., Huhnke, R.L., Bellmer, D.D.: Design of an improved laboratory-scale sweet sorghum press. ASABE publication No 095929. ASABE, Reno, Nevada (2009)
Gnansounou, E., Dauriat, A., Wyman, C.E.: Refining sweet sorghum to ethanol and sugar: economic trade-offs in the context of North China. Bioresour. Technol. 96, 985–1002 (2005)
Badalov, A.: Processing of sweet sorghum for bioethanol production. WIPO Publication Number, WO 2008/029163 (2008)
Crépeau, M., Khelifi, M., Vanasse, A.: Preliminary investigation into the pressing process of sweet pearl millet and sweet sorghum biomass for ethanol production. In: XVIIth World Congress of the International Commission of Agricultural and Biosystems Engineering (CIGR) (2010)
Jia, F., Chawhuaymak, J., Riley, M.R., Zimmt, W., Ogden, K.L.: Efficient extraction method to collect sugar from sweet sorghum. J. Biol. Eng. 7, 1–9 (2013)
Crank, J., McFarlane, N.R., Paterson, G.D., Pedley, J.B.: Diffusion Processes in Environmental Systems. Macmillan, London (1981)
Rein, P.W.: A comparison of cane diffusion and milling. In: Proceedings of the South African Sugar Technologists’ Association (1995)
El Belghiti, K., Vorobiev, E.: Mass transfer of sugar from beets enhanced by pulsed electric field. Food Bioprod. Process. 82, 226–230 (2004)
Toda, T.A., Sawada, M.M., Rodrigues, C.E.: Kinetics of soybean oil extraction using ethanol as solvent: experimental data and modeling. Food Bioprod. Process. 98, 1–10 (2016)
Grohmann, K., Baldwin, E., Buslig, B.: Production of ethanol from enzymatically hydrolyzed orange peel by the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 46, 315–327 (1994)
Cotlear, C.B.G.: Sugarcane juice extraction and preservation, and long-term lime pretreatment of bagasse. Doctoral dissertation, Texas A&M University (2004)
Rein, P.: Sugar Cane Engineering. Varlag Dr. Albert Bartens KG, Berlin (2007)
Serna-Saldívar, S.O., Chuck-Hernández, C., Pérez-Carrillo, E., Heredia-Olea, E.: Sorghum as a multifunctional crop for the production of fuel ethanol: current status and future trends. In: Lima MAP, Natalense APP Bioethanol (eds.), pp. 51–74. InTech (2012)
Daniel, E.E., Ajit, K.M., Mark, L.J., Danielle, D.B., Umakanta, J., Gerald, J.W., Archie, L.W.: Evaluation of three cultivars of sweet sorghum as feedstocks for ethanol production in the Southeast United States. Heliyon 3, e00490 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.heliyon.2017
Nebié, B.: Diversité génétique des sorghos à tige sucrée [Sorghum bicolor (L.) Moench] du Burkina Faso. Doctoral dissertation, University of Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso), p. 118 (2014)
Mabelebele, M., Siwela, M., Gous, R.M., Iji, P.A.: Chemical composition and nutritive value of South African sorghum varieties as feed for broiler chickens. S. Afr. J. Anim. Sci. 45, 206–213 (2015). https://doi.org/10.4314/sajas.v45i2.12
Beta, T., Corke, H., Taylor, J.R.N.: Starch properties of Barnard red, a South African red sorghum variety of significance in traditional African brewing. Starch 52, 467–470 (2000)
Topping, D.L.: Soluble fiber polysaccharides: effects on plasma cholesterol and colonic fermentation. Nutr. Rev. 49, 195–203 (1991)
Warrand, J.: Healthy polysaccharides the next chapter in food products. Food Technol. Biotechnol. 44, 355–370 (2006)
Kamath, V., Niketh, S., Chandrashekar, A., Rajini, P.S.: Chymotryptic hydrolysates of α-kafirin, the storage protein of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor) exhibited angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory activity. Food Chem. 100, 306–311 (2007)
Camargo-Filho, I., Cortez, D.A.G., Ueda-Nakamura, T., Nakamura, C.V., Dias-Filho, B.P.: Antiviral activity and mode of action of a peptide isolated from Sorghum bicolor. Phytomedicine 15, 202–208 (2008)
Lin, P., Wong, J.H., Ng, T.B., Ho, V.S., Xia, L.: A sorghum xylanase inhibitor-like protein with highly potent antifungal, antitumor and HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitory activities. Food Chem. 141, 2916–2922 (2013)
Cruz, R.A.O., López, J.L.C., Aguilar, G.A.G., García, H.A., Gorinstein, S., Romero, R.C., Sánchez, M.R.: Influence of sorghum karifin on serum lipid profile and antioxidant activity in hyperlipidemic rats (in vitro and in vivo studies). BioMed Res. Int. 164725 (2015)
Motlhaodi, T., Bryngelsson, T., Chite, S., Fatih, M., Ortiz, R., Geleta, M.: Nutritional variation in sorghum [Sorghum Bicolor (L.) Moench] accessions from Southern Africa revealed by protein and mineral composition. J. Cereal Sci. 83, 123–129 (2018)
De Morais, C.L., Montini, T.A., Pinheiro, S.S., PinheiroSant’Anaa, H.M., Martino, H.S.D., Moreira, A.V.B.: Effects of processing with dry heat and wet heat on the antioxidant profile of sorghum. Food Chem. 152, 210–217 (2014)
Rooney, L.W., Pflugfelder, R.L.: Factors affecting starch digestibility with special emphasis on sorghum and corn. J. Anim. Sci. 63, 1607–1623 (1986)
Cousin, B.W., Tanskley, T.D., Knabe, D.A., Zebrowska, Z.: Nutrient digestibility and performance of pigs fed sorghum varying in tannin concentration. J. Anim. Sci. 53, 1524–1537 (1981)
Ape, D.I., Nwogu, N.A., Uwakwe, E.I., Ikedinobi, C.S.: Comparative proximate analysis of maize and sorghum bought from Ogbete main market of Enugu state, Nigeria. Greener J. Agric. Sci. 6, 272–275 (2016)
Adebiyi, A.O., Adebiyi, A.P., Olaniyi, E.O.: Nutritional composition of Sorghum bicolor starch hydrolysed with amylase from Rhizopus sp. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 4, 1089–1094 (2005)
Udachan, I.S., Sahoo, A.K., Hend, G.M.: Extraction and characterization of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) starch. Int. Food Res. J. 19, 315–319 (2012)
Awadelkareem, A.M., Hassan, E.G., Fageer, A.S.M., Sulieman, A.M., Mustafa, A.M.I.: The nutritive value of two sorghum cultivar. Int. J. Food Nutr. Sci. 4, 1–7 (2015)
Jimoh, W.L.O., Abdullahi, M.S.: Proximate analysis of selected sorghum cultivars. Bayero. J. Pure Appl. Sci. 10, 285–288 (2017)
Abubakar, M., Doma, U.D., Kalla, D.J.U., Ngele, M.B., Augustine, C.L.D.: Effects of dietary replacement of maize with malted and unmalted sorghum on performance of weaner rabbits. Livest. Res. Rur. Dev. 18, 65 (2006)
Subramanian, V., Metta, V.C.: Sorghum grain for poultry feed. In: Chandrasher, A., Bandyopadhayi, R., Hall, A.J. (eds.) Technical and Institution Options for Sorghum Grain Mold Management. Proc. International Consultation. International Crop Research for the Semi Arid Tropics (ICRISAT). Patacheru 502–504, Andhra Pradesh, India, pp. 242–247 (2000)
Mohammed, Z.S., Mabudi, A.H., Murtala, Y., Jibrin, S., Sulaiman, S., Salihu, J.: Nutritional analysis of three commonly consumed varieties of sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L.) in Bauchi State, Nigeria. J. Appl. Sci. Environ. Manag. 23, 1329–1334 (2019)
Amélia, D.P.B.: Rendement en biomasse et en sucres et valeur nutritive du millet perlé sucré et du sorgho sucré en fonction de la date de récolte et du délai entre le hachage et le pressage du fourrage. Mémoire, Maîtrise en biologie végétale. Université Laval, Québec, p 114 (2012)
Tremblay, G.F., Lefebvre, D., Petit, H., Lafrenière, C.: La valeur nutritive des fourrages. In: G. Bélanger, L. Couture et G. Tremblay (eds.), Les plantes fourragères, pp. 189. Centre de Référence en Agriculture et Agroalimentaire du Québec (2005)
Black, J.R., Ely, L.O., McCullough, M.E., et Sudweeks, E.M.: Effects of stage of maturity and silage additives upon the yield of gross and digestible energy in sorghum silage. J. Anim. Sci. 50, 617–624 (1980)
Miron, J., Zuckerman, E., Sadeh, D., Adin, G., Nikbachat, M., Yosef, E., Ben-Ghedalia, D., Carmi, A., Kipnis, T., Solomon, R.: Yield composition and in vitro digestibility of new forage sorghum varieties and their ensilage characteristic. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 120, 17–32 (2005)
Corredor, D.Y., Salazar, J.M., Hohn, K.L., Bean, S., Bean, B., Wang, D.: Evaluation and characterization of forage sorghum as feedstock for fermentable sugar production. Appl. Biochem. Biotechnol. 158, 164–179 (2009)
Amer, S.M.M.: Evaluation of high water soluble carbohydrates annual forages for dairy cattle. Thesis. McGill University, pp. 32–87 (2011)
McCormick, M.E., Morris, D.R., Ackerson, B.A., Blouin, D.C.: Ratoon cropping forage sorghum for silage: yield, fermentation, and nutrition. Agron. J. 87, 952–957 (1995)
Di Marco, O.N., Ressia, M.A., Arias, S., Aello, M.S., Arzadún, M.: Digestibility of forage silages from grain, sweet and bmr sorghum types: comparison of in vivo, in situ and in vitro data. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol. 153, 161–168 (2009)
Venkata, S.C., Ramana, R.Y., Nagalakshmi, D., Jagadeeswara, R.S.: Evaluation of sweet (Sorghum bicolor (L.) moench) bagasse by chemical, in sacco and in vivo techniques in graded murrah buffalo bulls. J. Vet. Adv. 2, 418–423 (2012)
Negro, M.J., Solano, M.L., Ciria, P., Carrasco, J.: Composting of sweet sorghum bagasse with other wastes. Bioresour. Technol. 67, 89–92 (1999)
Rao, P.S., Umakanth, A.V., Reddy, B.V.S., Dweikat, I., Bhargava, S., Kumar, C.G., Braconnier, S., Patil, J.V.: Sweet Sorghum: genetics, breeding and commercialization. In: Singh, B.P. (ed.) Biofuel Crops: Production, Physiologyand Genetics, pp. 172–198. CABI, Fort Valley (2013)
Li, J., Li, S., Han, B., Yu, M., Li, G., Jiang, Y.: A novel cost-effective technology toconvert sucrose and homocelluloses in sweet sorghum stalks into ethanol. Biotechnol. Biofuels 6, 174 (2013)
Faraco, V.: Lignocellulose Conversion: Enzymatic and Microbial Tools for Bioethanol Production. Springer, Berlin (2013)
Du, R., Yan, J., Feng, Q., Li, P., Zhang, L., Chang, S., Li, S.: A novel wild-type Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain TSH1 in scaling-up of solid-state fermentation of ethanol from sweet sorghum stalks. PLoS ONE 9, e94480 (2014)
Phutela, U.G., Kaur, J.: Process optimization for ethanol production from sweet sorghum juice using saccharomyces cerevisiae strain NRRL Y-2034 by response surface methodology. Sugar Tech. 16, 411–421 (2014)
Appiah-Nkansah, N.B., Saul, K., Rooney, W., Wang, D.: Adding sweet sorghum juice into the current dry-grind ethanol process for improving ethanol yields and water efficiency. Int. J. Agric. Biol. Eng. 8, 97–103 (2015)
Stevens, G., Holou, R.A.: Sweet sorghum as a biofuel crop. In: Halford, N.G., Karp, A. (eds.) Energy Crops, pp. 56–76. The Royal Society of Chemistry, London (2010)
Rohowsky, B., Häßler, T., Gladis, A., Remmele, E., Schieder, D., Faulstich, M.: Feasibility of simultaneous saccharification and juice co-fermentation on hydrothermal pretreated sweet sorghum bagasse for ethanol production. Appl. Energy 102, 211–219 (2013)
Mood, S.H., Golfeshan, A.H., Tabatabaei, M., Jouzani, G.S., Najafi, G.H., Gholami, M., Ardjmand, M.: Lignocellulosic biomass to bioethanol, a comprehensive review with a focus on pretreatment. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 27, 77–93 (2013)
Wang, J.C., Dai, L., Tian, Y.S., Qin, S.P.: Analysis of the development status and trends of biomass energy industry in China. Trans. Chin. Soc. Agric. Eng. 23, 276–282 (2007)
Li, D.: Ethanol fuel from sweet sorghum desiderates development. J. Agric. Sci. Technol. Iran 4, 48–51 (2003)
Zhao, Y.L., Dolat, A., Steinberger, Y., Wang, X., Osman, A., Xie, G.H.: Biomass yield and changes in chemical composition of sweet sorghum cultivars grown for biofuel. Field Crop. Res. 111, 55–64 (2009)
Christakopoulos, P., Li, L.W., Kekos, D., Makris, B.J.: Direct conversion of sorghum carbohydrates to ethanol by a mixed microbial culture. Bioresour. Technol. 45, 89–92 (1993)
Lezinou, V., Christakopoulos, P., Li, L.W., Kekos, D., Macris, B.J.: Study of a single and mixed culture for the direct bio-conversion of sorghum carbohydrates to ethanol. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 43, 412–415 (1995)
Mamma, D., Koullas, D., Fountoukidis, G., Kekos, D., Makris, B.J., Koukios, E.: Bioethanol from sweet sorghum: simultaneous saccharification and fermentation of carbohydrates by a mixed microbial culture. Process Biochem. 31, 377–381 (1996)
Rajagopal, D., Zilberman, D.: Environmental, economic and policy aspects of biofuels. Found. Trends Microecon. 4, 353–468 (2008)
Hertel, T.W., Tyner, W.E.: Market-mediated environmental impacts of biofuels. Glob. Food Sec. 2, 131–137 (2013)
Claassen, P.A.M., van Lier, J.B., Contreras, A.M.L., van Niel, E.W.J., Sijtsma, L., Stams, A.J.M., de Vries, S.S., Weusthuis, R.A.: Utilisation of biomass for the supply of energy carriers. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 52, 741–755 (1999)
Agbor, V.B., Nazim, C., Richard, S., Alex, B., David, B.L.: Biomass pretreatment: fundamentals toward application. Biotechnol. Adv. 29, 675–685 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2011.05.005
Rabemanolontsoa, H., Saka, S.: Various pretreatments of lignocellulosics. Bioresour. Technol. 199, 83–91 (2016)
Sumitha, B.J., Kedar, S., Aruna, R., Vijayanand, S.M., Arun, G.: Comparative analysis of pretreatment methods on Sorghum (Sorghum durra) stalk agrowaste for holocellulose content. Prep. Biochem. Biotechnol. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1080/10826068.2018.1466148
Sambusiti, C., Ficara, E., Malpei, F., Steyer, J.P., Carrère, H.: Effect of sodium hydroxide pretreatment on physical, chemical characteristics and methane production of five varieties of sorghum. Energy 55, 449–456 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2013.04.025
Zhang, Z., Zhang, G., Li, W., Li, C., Xu, G.: Enhanced biogas production from sorghum stem by co-digestion with cow manure. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 41, 9153–9158 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.02.042
Kalamaras, S.D., Kotsopoulos, T.A.: Anaerobic co-digestion of cattle manure and alternative crops for the substitution of maize in South Europe. Bioresour. Technol. 172, 68–75 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.09.005
Kapdan, I.K., Kargi, F.: Bio-hydrogen production from waste materials. Enzym. Microbial. Technol. 38, 569–582 (2006)
Kumar, G., Periyasamy, S., Sen, B., Mudhoo, A., Davila-vazquez, G., Wang, G., Kim, S.H.: Research and development perspectives of lignocellulosebased biohydrogen production. Int. Biodeterior. Biodegrad. 119, 225–238 (2017)
Eric, T., Gwendoline, C., Eric, L., Christian, L.: Production de biohydrogène—Voie fermentaire sombre. Techniques de l’Ingénieur BIO 3(351), v2–v1 (2018)
Asada, Y., Miyake, J.: Photobiological hydrogen production. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 88(1), 1–6 (1999)
Morimoto, M.: Why is the anaerobic fermentation in the production of the biohydrogen attractive? In: The Proceedings of Conversion of Biomass into Bioenergy. Organized by New energy and Industrial Technology Development Organization (NEPO), Japan and Malaysian Palm oil Board (MPOP) (2002)
Atif, A.A.Y., Fakhru’l-Razi, A., Ngan, M.A., Morimoto, M., Iyuke, S.E., Veziroglou, N.T.: Fed batch production of hydrogen from palm oil mill effluent using anaerobic microflora. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 30, 1393–1397 (2005)
Nandi, R., Sengupta, R.: Microbial production of hydrogen: an overview. Crit. Rev. Microbiol. 24, 61–84 (1998)
Hawkes, F.R., Dinsdale, R., Hawkes, D.L., Hussy, I.: Sustainable fermentative hydrogen production: challenges for process optimisation. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 27, 1339–1347 (2002)
Ramachandran, R., Menon, R.K.: An overview of industrial uses of hydrogen. Int. J. Hydrog. Energy 23, 593–598 (1998)
Noike, T., Mizuno, O.: Hydrogen fermentation of organic municipal wastes. Water Sci. Technol. 42, 155–162 (2000)
Ajayan, P.M., Zhou, O.Z.: Applications of carbon nanotubes. Top. Appl. Phys. 80, 391–425 (2001)
Demirbas A.: Thermochemical conversion processes. In: Biofuels. Green Energy and Technology. Springer, London (2009)
Demirbas, A.: Combustion characteristics of different biomass fuels. Prog. Energy Combust. Sci. 30, 219–230 (2004)
Salas Fernandez, M.G., Becraft, P.W., Yin, Y., Lübberstedt, T.: From dwarves to giants? Plant height manipulation for biomass yield. Trends Plant Sci. 14, 454–461 (2009)
Carrillo, M.A., Staggenborg, S.A., Pineda, J.A.: Washing sorghum biomass with water to improve its quality for combustion. Fuel 116, 427–431 (2014)
Caputo, A.C., Palumbo, M., Pelagagge, P.M., Scacchia, F.: Economics of biomass energy utilization in combustion and gasification plants: effects of logistic variables. Biomass Bioenergy 28, 35–51 (2005)
Backreedy, R.I., Fletcher, L.M., Jones, J.M., Ma, L., Pourkashanian, M., Williams, A.: Co-firing pulverised coal and biomass: a modelling approach. Proc. Combust. Inst. 30, 2955–2964 (2005)
Serra, P., Colauzzi, M., Amaducci, S.: Biomass sorghum production risk assessment analysis: a case study on electricity production in the Po Valley. Biomass Bioenergy 96, 75–86 (2017)
Serra, P., Giuntoli, J., Agostini, A., Colauzzi, M., Amaducci, S.: Coupling sorghum biomass and wheat straw to minimise the environmental impact of bioenergy production. J. Clean. Prod. 154, 242–254 (2017)
Bridgwater, A.V., Carson, P., Coulson, M.: A comparison of fast and slow pyrolysis liquids from mallee. Int J Glob. Energy Issues 27, 204–216 (2007)
Font, R., Williams, P.T.: Pyrolysis of biomass with constant heating rate: influence of the operating conditions. Thermochim. Acta 250, 109–123 (1995)
Ansoumane, D.: Etude hydrodynamique et valorisation énergétique par transformation thermochimique de déchets de biomasse pour l’alimentation d’une briqueterie. thèse, doctorat en génie des procédés industriels. Universite Assane Seck de Ziguinchor (UASZ) et Universite de Technologie de Compiegne (UTC), p 193 (2017)
Stamenkovic, O.S., Kaliramesh, S., Vlada, B., Veljkovic, V.B., Bankovic-Ilic, I.B., Marija, B., Tasic, M.B., Ciampitti, I.A., Đalovic, I.G., Mitrovic, P.M., Sikora, V.S., Prasad, P.V.: Production of biofuels from sorghum. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 124, 109769 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2020.109769
Tumuluru, J., Sokhansanj, S., Wright, C., Hess, J., Boardman, R.: A review on biomass torrefaction process and product properties. INL/CON-11–22634. Idaho National Laboratory (2011)
Kotaiah, N.D., Monika, K., Prabhakar, S., Parthasarathy, R., Satyavathi, B.: Pyrolysis of sorghum bagasse biomass into bio-char and bio-oil products—a thorough physicochemical characterization. Therm. Anal. Calorim. 127, 1277–1289 (2017)
Filipovici, A., Tucu, D., Bialowiec, A., Bukowski, P., Crisan, G.C., Lica, S., Pulka, J.: Effect of temperature and heating rate on the char yield in sorghum and straw slow pyrolysis. Rev. Chim. 68, 576–580 (2017)
Yue, Y., Singh, H., Singh, B., Mani, S.: Torrefaction of sorghum biomass to improve fuel properties. Bioresour. Technol. 232, 372–379 (2017)
Cao, Y., Wang, Y., Riley, J.T., Pan, W.P.: A novel biomass air gasifcation process for producing tar-free higher heating value fuel gas. Fuel Process Technol. 87, 343–353 (2006)
Rapagna, S., Jand, N., Kiennemann, A., Foscolo, P.U.: Steam gasification of biomass in a fluidised-bed of olivine particles. Biomass Bioenergy 19, 187–197 (2000)
James, A.M., Zuan, W., Boyette, M.D., Wang, D.: The effect of air flow rate and biomass type on the performance of an updraft biomass gasifer. BioResource 10, 3615–3624 (2015)
Amin, S.: Review on biofuel oil and gas production processes from microalgae. Energy Convers Manag. 50, 1834–1840 (2009)
Qian, K., Kumar, A., Patil, K., Bellmer, D., Wang, D., Yuan, W., Huhnke, R.L.: Effects of biomass feedstocks and gasifcation conditions on the physiochemical properties of char. Energies 6, 3972–3986 (2013)
Elliott, C.D., Biller, P., Ross, B.A., Schmidt, J.A., Jones, B.S.: Hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass: developments from batch to continuous process. Bioresour. Technol. 178, 147–156 (2015)
Gollakota, A.R.K., Kishoreb, N., Gu, S.: A review on hydrothermal liquefaction of biomass. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81, 1378–1392 (2018)
Aljerf, L.: Fabrication et test d’un catalyseur d’acide sulfonique approprié pour la réaction de production des biocarburants. Afrique Sci. 11, 349–358 (2015)
Peterson, A.A., Vogel, F., Lachance, R.P., Froling, M., Antal, J.M.J., Tester, J.W.: Thermochemical biofuel production in hydrothermal media: a review of sub-and supercritical water technologies. Energy Environ. Sci. 1, 32–65 (2008)
Demirbas, A.: Competitive liquid biofuels from biomass. Appl. Energy 88, 17–28 (2011)
Huber, G.W., Chheda, J., Barrett, C., Dumesic, J.A.: Production of liquid alkanes by aqueous-phase processing of biomass-derived carbohydrates. Science 308, 1446–2079 (2005)
Bi, Z., Zhang, J., Peterson, E., Zhu, Z., Xia, C., Liang, Y., Wiltowski, T.: Biocrude from pretreated sorghum bagasse through catalytic hydrothermal liquefaction. Fuel 188, 112–120 (2017)
Chupin, L., De Ridder, D., Clément-Vidal, A., Soutiras, A., Gineau, E., Mouille, G., Arnoult, S., Brancourt-Hulmel, M., Pot, D., Vincent, L.: Influence of the radial stem composition on the thermal behaviour of miscanthus and sorghum genotypes. Carbohydr. Polym. 167, 12–19 (2017)
Hetényi, K., Gál, K., Németh, Á., Sevella, B.: Use of sweet sorghum juice for lactic acid fermentation: preliminary steps in a process optimization. J. Chem. Technol. Biotechnol. 85, 872–877 (2010)
Cheng, Y., Li, S., Huang, J., Zhang, Q., Wang, X.: Production of acetone and butanol by fermentation of sweet sorghum stalk juice. Trans. CSAE 24, 177–180 (2008)
Sjöblom, M., Matsakas, L., Krige, A., Rova, U., Christakopoulos, P.: Direct electricity generation from sweet sorghum stalks and anaerobic. Ind. Crops Prod. 108, 505–511 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.indcrop.2017.06.062
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank the French government which financed H.B.’s research mobility through its Eiffel scholarship program of excellence.
Funding
Author H.B. has received research support from Campus France (The French agency in charge of promoting French higher education abroad, managing scholarships from French and foreign governments and welcoming international students).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Literature search, and data analysis were performed by HB, and D. The first draft of the manuscript was written by HB and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interests
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bakari, H., Djomdi, Ruben, Z.F. et al. Sorghum (Sorghum bicolor L. Moench) and Its Main Parts (By-Products) as Promising Sustainable Sources of Value-Added Ingredients. Waste Biomass Valor 14, 1023–1044 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01992-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-022-01992-7