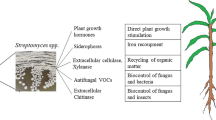
Abstract
Numerous factors contribute to the decline in crop yields, including plant diseases caused by bacteria, fungi, and viruses. The management of these diseases with chemical fertilizers is not a sustainable approach. This review briefly summarizes the role, mechanisms, advantages, and disadvantages of using Streptomyces species in plant disease management as an alternative method is needed to address the problems of using chemicals. One promising alternative is to use microbes to manage plant diseases. Streptomyces, a gram-positive saprophytic bacterium, is particularly effective at combating plant diseases. They produce bioactive-rich antimicrobial metabolites and enzymes that can kill or inhibit the growth of plant pathogens. Streptomyces species are widely distributed in nature but are especially abundant in the rhizosphere, the soil region surrounding plant roots. Streptomyces can be used as bioinoculants to protect plants from diseases. In addition to their disease-fighting abilities, they can promote plant growth in many ways. They produce plant growth-promoting substances, such as indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), cytokinin, and siderophores. They also suppress diseases through antibiosis, mycoparasitism, and nutrient competition. Streptomyces can also supply plants with essential minerals, i.e., iron, copper, phosphorus, and sulfur. Therefore, it concluded that Streptomyces species can be used as an alternative to chemicals to control plant diseases.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adhilakshmi M, Latha P, Paranidharan V, Balachandar D, Ganesamurthy K, Velazhahan R (2014) Biological control of stem rot of groundnut (Arachis hypogaea L.) caused by Sclerotium Rolfsii Sacc. With actinomycetes. Arch Phytopathol Plant Prot 47(3):298–311. https://doi.org/10.1080/03235408.2013.809224
Aggarwal N, Thind SK, Sharma S (2016) Role of secondary metabolites of actinomycetes in Crop Protection. In: Subramaniam G, Arumugam S, Rajendran V (eds) Plant Growth promoting Actinobacteria. Springer, Singapore, pp 99–121. DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-10-0707-1
Al Hamad BM, AlRaish SM, Ramadan GA, Alameri SSA, Al Senaani SS, AbuQamar SF, El-Tarabily KA (2021) Effectiveness of augmentative biological control of Streptomyces griseorubens UAE2 depends on 1-Aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase activity against Neoscytalidium Dimidiatum. J Fungi 7:885. https://doi.org/10.3390/jof7110885
Al Raish SM, Saeed EE, Alyafei DM, El-Tarabily KA, AbuQamar SF (2021) Evaluation of Streptomycete Actinobacterial isolates as biocontrol agents against royal poinciana stem canker Disease caused by the fungal pathogen Neoscytalidium Dimidiatum. Biol Control 164:104783. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2021.104783
Alwahshi KJ, Purayil GP, Saeed EE, Abufarajallah HA, Aldhaheri SJ, AbuQamar SF, El-Tarabily KA (2022) The 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase-producing Streptomyces violaceoruber UAE1 can provide protection from sudden decline syndrome on date palm. Front Plant Sci 13:904166. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.904166
Ambikapathy V, Babu S, Anbukumaran A, Shijila Rani A, Prakash PJMA (2022a) Isolation of actinobacteria from mangrove plants. In: Dharumadurai D (ed) Methods in actinobacteriology. Springer protocols handbooks. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1728-1_13
Ambikapathy V, Shijila Rani A, Anbukumaran A, Shanmugapriya R, Babu S (2022b) Solation of Actinobacteria from Earthworm cast. In: Dharumadurai D (ed) Methods in actinobacteriology. Springer protocols handbooks. Humana, New York, NY. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-0716-1728-1_8
Ashokvardhan T, Rajithasri A, Prathyusha P, Satyaprasad K (2014) Actinomycetes from Capsicum annuum L. Rhizosphere soil have the biocontrol potential against pathogenic fungi. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3(4):894–903
Atta HM (2015) Biochemical studies on antibiotic production from Streptomyces sp.: taxonomy, fermentation, isolation and biological properties. J Saudi Chem Soc 19(1):12–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jscs.2011.12.011
Baz M, Lahbabi D, Samri S, Val F, Hamelin G, Madore I, Bouarab K, Beaulieu C, Ennaji MM, Barakate M (2012) Control of potato soft rot caused by Pectobacterium carotovorum and Pectobacterium atrosepticum by Moroccan actinobacteria isolates. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:303–311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0820-5
Berdy J (2005) Bioactive microbial metabolites. J Antibiot 58(1):1–26. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2005.1
Bharathi R, Vivekananthan R, Harish S, Ramanathan A, Samiyappan R (2004) Rhizobacteria-based bio-formulations for the management of fruit rot Infection in chillies. Crop Prot 23(9):835–843. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2004.01.007
Bhardwaj A, Agrawal P (2014) A review fungal endophytes: as a store house of bioactive compound. World J Pharm Pharm Sci 3(9):228–237
Bouizgarne B, Lanoot B, Loqman S et al (2009) Streptomyces marokkonensis sp. nov., isolated from rhizosphere soil of Argania Spinosa L. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59(11):2857–2863. https://doi.org/10.1099/ijs.0.011387-0
Çakmakçi R, Dönmez F, Aydın A, Şahin F (2006) Growth promotion of plants by plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria under greenhouse and two different field soil conditions. Soil Biol Biochem 38(6):1482–1487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.09.019
Chaiharn M, Theantana T, Pathom-Aree W (2020) Evaluation of biocontrol activities of Streptomyces spp. against rice blast Disease fungi. Pathogens 9(2):126. https://doi.org/10.3390/pathogens9020126
Chen Y, Zhou D, Qi D, Gao Z, Xie J, Luo Y (2018) Growth promotion and Disease suppression ability of a Streptomyces sp. CB-75 from banana rhizosphere soil. Front Microbiol 8:2704. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.02704
Chen J, Xu L, Zhou Y, Han B (2021) Natural products from actinomycetes associated with marine organisms. Mar Drugs 19(11):629. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19110629
Cheng Q, Hu C, Jia W et al (2019) Selenium reduces the pathogenicity of Sclerotinia sclerotiorum by inhibiting sclerotial formation and germination. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109503. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.109503
Chouyia FE, Ventorino V, Pepe O (2022) Diversity, mechanisms and beneficial features of phosphate-solubilizing Streptomyces in sustainable agriculture: a review. Front Plant Sci 13:1035358. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.1035358
Danaei M, Baghizadeh A, Pourseyedi S, Amini J, Yaghoobi MM (2014) Biological control of plant fungal Diseases using volatile substances of Streptomyces griseus. Eur J Exp Biol 4(1):334–339
Devi SS, Rao KB (2017) Exploration of antimicrobial compounds from Streptomyces S9 against a phytopathogen, Corynespora Cassiicola. & Curtis) J Biopestic 10(1):1–9. https://doi.org/10.57182/jbiopestic.10.2.1-9. Berk
Donghua J, Qinying L, Yiming S, Hao J (2013) Antimicrobial compound from a novel Streptomyces termitum strain ATC-2 against Xanthomonas oryzae Pv. Oryzae. Res J Biotechnol 8(7):66–70
El-Saadony MT, Saad AM, Soliman MS, Salem HM, Ahmed AI, Mahmood M, El-Tahan AM, Ebrahim AAM, Abd El-Mageed TA, Negm SH, Selim S, Babalghith AO, Elrys AS, El-Tarabily KA, AbuQamar SF (2022) Plant growth-promoting microorganisms as biocontrol agents of plant Diseases: mechanisms, challenges, and future perspectives. Front Plant Sci 13:923880. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2022.923880
El-Tarabily KA (2003) An endophytic chitinase-producing isolate of Actinoplanes missouriensis, with potential for biological control of root rot of lupin caused by Plectosporium tabacinum. Aust J Bot 51:257–266. https://doi.org/10.1071/BT02107
El-Tarabily KA (2006) Rhizosphere-competent isolates of Streptomycete and non-streptomycete actinomycetes capable of producing cell-wall degrading enzymes to control Pythium aphanidermatum damping-off Disease of cucumber. Canad J Bot 84:211–222. https://doi.org/10.1139/b05-153
El-Tarabily KA (2008) Promotion of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) Plant growth by rhizosphere competent 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylic acid deaminase-producing Streptomycete actinomycetes. Plant soil 308:161–174. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9616-2
El-Tarabily KA, Sivasithamparam K (2006) Non-streptomycete actinomycetes as biocontrol agents of soil-borne fungal plant pathogens and as plant growth promoters. Soil Biol Biochem 38(7):1505–1520. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.12.017
El-Tarabily KA, Sykes ML, Kurtböke DI, Hardy GE, St J, Barbosa AM, Dekker RFH (1996) Synergistic effects of a cellulase-producing Micromonospora carbonacea and an antibiotic-producing Streptomyces violascens on the suppression of Phytophthora cinnamomi root-rot of Banksia Grandis. Canad J Bot 74:618–624. https://doi.org/10.1139/b96-078
El-Tarabily KA, Hardy GE, St J, Sivasithamparam K, Hussein AM, Kurtböke DI (1997) The potential for the biological control of cavity spot Disease of carrots caused by Pythium coloratum by Streptomycete and non-streptomycete actinomycetes in Western Australia. New Phytol 137:495–507. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1469-8137.1997.00856.x
El-Tarabily KA, Nassar AH, Hardy GE, St J, Sivasithamparam K (2009) Plant growth promotion and biological control of Pythium aphanidermatum, a pathogen of cucumber, by endophytic actinomycetes. J Appl Microbiol 106:13–26. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2008.03926.x
El-Tarabily KA, Hardy GE, St J, Sivasithamparam K (2010) Performance of three endophytic actinomycetes in relation to plant growth promotion and biological control of Pythium aphanidermatum, a pathogen of cucumber under commercial field production conditions in the United Arab Emirates. Eur J Plant Pathol 128:527–539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-010-9689-7
Elamvazhuthi P, Subramanian M (2013) Antagonistic activity of actinomycetes from Jeypore paddy soils against selective phytopathogenic fungi. J Mod Biol 2(3):66–72
Elnahal ASM, El-Saadony MT, Saad AM, Desoky EM, El-Tahan AM, Rady MM, AbuQamar SF, El-Tarabily KA (2022) The use of microbial inoculants for biological control, plant growth promotion, and sustainable agriculture: a review. Eur J Plant Pathol 162:759–792. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10658-021-02393-7
Ezeobiora CE, Igbokwe NH, Amin DH, Enwuru NV, Okpalanwa CF, Mendie UE (2022) Uncovering the biodiversity and biosynthetic potentials of rare actinomycetes. Future J Pharm Sci 8(1):1–19
Farda B, Djebaili R, Vaccarelli I, Del Gallo M, Pellegrini MJM (2022) Actinomycetes from caves: an overview of their diversity, biotechnological properties, and insights for their use in soil environments. 10(2):453. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10020453
Fernando WD, Ramarathnam R, Krishnamoorthy AS, Savchuk SC (2005) Identification and use of potential bacterial organic antifungal volatiles in biocontrol. Soil Biol Biochem 37(5):955–964. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2004.10.021
Gao Y, Ning Q, Yang Y et al (2021) Endophytic Streptomyces hygroscopicus OsiSh-2-mediated balancing between growth and disease resistance in host rice. mbio 12(4):10. https://doi.org/10.1128/mBio.01566-21
Glick BR (2012) Plant growth-promoting bacteria: mechanisms and applications. Scientifica 2012:1–15. https://doi.org/10.6064/2012/963401
Gopalakrishnan S, Ganeshkumar P (2013) Systematic reviews and meta-analysis: understanding the best evidence in primary healthcare. J Fam Med Prim Care Rev 2(1):9–14. https://doi.org/10.4103/2249-4863.109934
Gopalakrishnan S, Pande S, Sharma M, Humayun P, Kiran BK, Sandeep D, Rupela O (2011) Evaluation of actinomycete isolates obtained from herbal vermicompost for the biological control of Fusarium wilt of chickpea. Crop Prot 30(8):1070–1078. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2011.03.006
Goudjal Y, Toumatia O, Yekkour A, Sabaou N, Mathieu F, Zitouni A (2014) Biocontrol of Rhizoctonia solani damping-off and promotion of tomato plant growth by endophytic actinomycetes isolated from native plants of Algerian Sahara. Microbiol Res 169(1):59–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micres.2013.06.014
Gowdar S, Deepa H, Amaresh Y (2018) A brief review on biocontrol potential and PGPR traits of Streptomyces sp. for the management of plant Diseases. J Pharmacogn Phytochem 7(5):03–07
Gutleben J, Chaib De Mares M, Van Elsas JD, Smidt H, Overmann J, Sipkema D (2018) The multi-omics promise in context: from sequence to microbial isolate. Crit Rev Microbiol 44(2):212–229. https://doi.org/10.1080/1040841X.2017.1332003
Haggag WM, Mohamed H (2007) Biotechnological aspects of microorganisms used in plant biological control. Am Eurasian J Sust Agric Agric 1(1):7–12. https://doi.org/10.4172/scientificreports.277
Hamdali H, Hafidi M, Virolle MJ, Ouhdouch Y (2008) Rock phosphate-solubilizing actinomycetes: screening for plant growth-promoting activities. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 24:2565–2575. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-008-9817-0
Han JW, Kim DY, Lee YJ et al (2020) Transcription factor PdeR is involved in fungal development, metabolic change, and pathogenesis of gray mold Botrytis Cinerea. J Agric Food Chem 68(34):9171–9179. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jafc.0c02420
Harada S, Kishi T (1978) Isolation and characterization of mildiomycin, a new nucleoside antibiotic. J Antibiot 31(6):519–524. https://doi.org/10.7164/antibiotics.31.519
Harikrishnan H, Shanmugaiah V, Balasubramanian N (2014) Optimization for production of Indole acetic acid (IAA) by plant growth promoting Streptomyces Sp VSMGT1014 isolated from rice rhizosphere. Int J Curr Microbiol Appl Sci 3(8):158–171
Hassan A, El-Barawy A, El Mokhtar MN (2011) Evaluation of biological compounds of Streptomyces species for control of some fungal Diseases. J Am Sci 7(4):752–760
Hayakawa M (2008) Studies on the isolation and distribution of rare actinomycetes in soil. Actinomycetologica 22(1):12–19. https://doi.org/10.3209/saj.SAJ220103
Huang X, Ren J, Li P, Feng S, Dong P, Ren M (2021) Potential of microbial endophytes to enhance the resistance to postharvest Diseases of fruit and vegetables. J Sci Food Agri 101(5):1744–1757. https://doi.org/10.1002/jsfa.10829
Intra B, Mungsuntisuk I, Nihira T, Igarashi Y, Panbangred W (2011) Identification of actinomycetes from plant rhizospheric soils with inhibitory activity against Colletotrichum spp., the causative agent of anthracnose Disease. BMC Res Notes 4(1):1–9 •. https://doi.org/10.1186/1756-0500-4-98
Isono K, Nagatsu J, Kobinata K, Sasaki K, Suzuki S (1967) Studies on polyoxins, antifungal antibiotics: Part V. isolation and characterization of polyoxins C, D, E. F G H and I Agric Biol Chem 31(2):190–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/00021369.1967.10858788
Jaemsaeng R, Jantasuriyarat C, Thamchaipenet A (2018) Molecular interaction of 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate deaminase (ACCD)-producing endophytic Streptomyces sp. GMKU 336 towards salt-stress resistance of Oryza sativa L. Cv. KDML105. Sci Rep 8(1):1950. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-19799-9
Jagannathan SV, Manemann EM, Rowe SE, Callender MC, Soto W (2021) Marine actinomycetes, new sources of biotechnological products. Mar Drugs 19(7):365. https://doi.org/10.3390/md19070365
Jog R, Pandya M, Nareshkumar G, Rajkumar S (2014) Mechanism of phosphate solubilization and antifungal activity of Streptomyces spp. isolated from wheat roots and rhizosphere and their application in improving plant growth. Microbiology 160(4):778–788. https://doi.org/10.1099/mic.0.074146-0
Joo G-J (2005) Production of an anti-fungal substance for biological control of Phytophthora capsici causing phytophthora blight in red-peppers by Streptomyces halstedii. Biotechnol Lett 27:201–205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10529-004-7879-0
Junaid JM, Dar NA, Bhat TA, Bhat AH, Bhat MA (2013) Commercial biocontrol agents and their mechanism of action in the management of plant pathogens. Int J Modern Plant Animal Sci 1(2):39–57
Kanini GS, Katsifas EA, Savvides AL, Karagouni AD (2013) Streptomyces rochei ACTA1551, an indigenous Greek isolate studied as a potential biocontrol agent against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. lycopersici. BioMed Res Inte 2013:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1155/2013/387230
Khamna S, Yokota A, Peberdy JF, Lumyong S (2009) Antifungal activity of Streptomyces spp. isolated from rhizosphere of Thai medicinal plants. Int J Integr Biol 6(3):143–147
Kim BS, Hwang BK (2007) Microbial fungicides in the control of plant Diseases. J Phytopathol 155(11–12):641–653. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1439-0434.2007.01314.x
Kim YK, Xiao C (2011) Stability and fitness of pyraclostrobin-and boscalid-resistant phenotypes in field isolates of Botrytis Cinerea from apple. Phytopathology 101(11):1385–1391. https://doi.org/10.1094/PHYTO-04-11-0123
Kuffner M, Puschenreiter M, Wieshammer G, Gorfer M, Sessitsch A (2008) Rhizosphere bacteria affect growth and metal uptake of heavy metal accumulating willows. Plant Soil 304:35–44. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-007-9517-9
Kumar RR, Jadeja VJ (2016) Isolation of actinomycetes: a complete approach. Int J Curr Microbiol App Sci 5(5):606–618
Law JW-F, Ser H-L, Khan TM et al (2017) The potential of Streptomyces as Biocontrol agents against the rice blast fungus, Magnaporthe oryzae (Pyricularia Oryzae). Front Microbiol 8:3. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00003
Li G, Zheng X, Zhu Y, Long Y, Xia XJEM (2022) Bacillus symbiont drives alterations in intestinal microbiota and circulating metabolites of lepidopteran host. Environ Microbiol 24(9):4049–4064. https://doi.org/10.1111/1462-2920.15934
Liu Y, Shi J, Feng Y, Yang X, Li X, Shen Q (2013) Tobacco bacterial wilt can be biologically controlled by the application of antagonistic strains in combination with organic fertilizer. Biol Fertil Soils 49:447–464. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-012-0740-z
Lyu A, Liu H, Che H et al (2017) Reveromycins a and B from Streptomyces sp. 3–10: antifungal activity against plant pathogenic fungi in vitro and in a strawberry food model system. Front Microbiol 8:550. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2017.00550
Majhi S (2021) Applications of Yamaguchi method to esterification and macrolactonization in total synthesis of bioactive natural products. ChemistrySelect 6(17):4178–4206. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202100206
Malviya MK, Pandey A, Trivedi P, Gupta G, Kumar B (2009) Chitinolytic activity of cold tolerant antagonistic species of Streptomyces isolated from glacial sites of Indian Himalaya. Curr Microbiol 59:502–508. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00284-009-9466-z
Manasa M, Kambar Y, Pallavi S, Vivek M, Onkarappa R, TR PK (2013) Biocontrol potential of Streptomyces species against Fusarium oxysporum f. sp. zingiberi (causal agent of rhizome rot of ginger). J Adv Sci Res 4(04):1–3
Mingma R, Pathom-aree W, Trakulnaleamsai S, Thamchaipenet A, Duangmal K (2014) Isolation of rhizospheric and roots endophytic actinomycetes from Leguminosae plant and their activities to inhibit soybean pathogen, Xanthomonas campestris Pv. glycine. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 30:271–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-013-1451-9
Morales-Gonzalez M, Martinez BS, Ramirez-Rodriguez L, Gómez J, Diaz L (2018) Optimization of L-asparaginase activity of actinobacteria isolated from Guaviare river sediments in Colombia. Trop J Pharm Res 17(11):2199–2206. https://doi.org/10.4314/tjpr.v17i11.13
Nassar AH, El-Tarabily KA, Sivasithamparam K (2003) Growth promotion of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) by a polyamine-producing isolate of Streptomyces griseoluteus. Plant Growth Regul 40:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1024233303526
Nimaichand S, Tamrihao K, Yang L-L, Zhu WY, Zhang YG, Li L, Li WJ (2013) Streptomyces hundungensis sp. nov., a novel actinomycete with antifungal activity and plant growth promoting traits. J Antibiot 66(4):205–209. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2012.119
Nonthakaew N, Panbangred W, Songnuan W, Intra B (2022) Plant growth-promoting properties of Streptomyces spp. isolates and their impact on mung bean plantlets’ rhizosphere microbiome. Front Microbiol 13:967415. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2022.967415
Palaniyandi S, Yang S, Cheng J, Meng L, Suh JW (2011) Biological control of anthracnose (Colletotrichum gloeosporioides) in yam by Streptomyces sp. MJM5763. J Appl Microbiol 111(2):443–455. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2672.2011.05048.x
Patil HJ, Srivastava AK, Singh DP, Chaudhari BL, Arora DK (2011) Actinomycetes mediated biochemical responses in tomato (Solanum lycopersicum) enhances bioprotection against Rhizoctonia solani. Crop Prot 30(10):1269–1273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cropro.2011.04.008
Pattanapipitpaisal P, Kamlandharn R (2012) Screening of chitinolytic actinomycetes for biological control of Sclerotium rolfsii stem rot Disease of Chilli. Songklanakarin J Sci Technol 34(4):387–393
Peng F, Zhang M-Y, Hou S-Y, Chen J, Wu Y-Y, Zhang Y-X (2020) Insights into Streptomyces spp. isolated from the rhizospheric soil of Panax notoginseng: isolation, antimicrobial activity and biosynthetic potential for polyketides and non-ribosomal peptides. BMC Microbiol 20(1):1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12866-020-01832-5
Poomthongdee N, Duangmal K, Pathom-aree W (2015) Acidophilic actinomycetes from rhizosphere soil: diversity and properties beneficial to plants. J Antibiot 68(2):106–114. https://doi.org/10.1038/ja.2014.117
Prapagdee B, Kuekulvong C, Mongkolsuk S (2008) Antifungal potential of extracellular metabolites produced by Streptomyces hygroscopicus against phytopathogenic fungi. Int J Biol Sci 4(5):330. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijbs.4.330
Raaijmakers JM, Paulitz TC, Steinberg C, Alabouvette C, Moënne-Loccoz Y (2009) The rhizosphere: a playground and battlefield for soilborne pathogens and beneficial microorganisms. Plant Soil 321:341–361. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9568-6
Rasuk MC, Ferrer GM, Kurth D, Portero LR, Farías ME, Albarracín VH (2017) UV-Resistant actinobacteria from high‐altitude andean lakes: isolation, characterization and antagonistic activities. Photochem Photobiol 93(3):865–880. https://doi.org/10.1111/php.12759
Rey T, Dumas B (2017) Plenty is no Plague: Streptomyces symbiosis with crops. Trends Plant Sci 22(1):30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2016.10.008
Sabaratnam S, Traquair JA (2002) Formulation of a Streptomyces Biocontrol agent for the suppression of Rhizoctonia damping-off in tomato transplants. Biol Control 23(3):245–253. https://doi.org/10.1006/bcon.2001.1014
Salcedo-Porras N, Umaña-Diaz C, de Oliveira Barbosa Bitencourt R, Lowenberger C (2020) The role of bacterial symbionts in triatomines: an evolutionary perspective. Microorganisms 8(9):1438. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms8091438
Sangmanee P, Bhromsiri A, Akarapisan A (2009) The potential of endophytic actinomycetes,(Streptomyces sp.) for the biocontrol of powdery mildew Disease in sweet pea (Pisum sativum). As J Food Ag-Ind 93:e8
Savary S, Ficke A, Aubertot J-N, Hollier C (2012) Crop losses due to Diseases and their implications for global food production losses and food security. Food Secur 4(4):519–537. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12571-012-0200-5
Saxena S (2014) Microbial metabolites for development of ecofriendly agrochemicals. Allelopathy J 33(1):1–24
Schmidt R, Ulanova D, Wick LY, Bode HB, Garbeva P (2019) Microbe-driven chemical ecology: past, present and future. ISME J 13(11):2656–2663. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41396-019-0469-x
Selim MSM, Abdelhamid SA, Mohamed SS (2021) Secondary metabolites and biodiversity of actinomycetes. J Genet Eng Biotechnol 19(1):72. https://doi.org/10.1186/s43141-021-00156-9
Seratnahaei M, Eshraghi SS, Pakzad P, Ramazani AZ, Yaseri M (2022) Antimicrobial activities of the secondary metabolite extracted from a Nocardia strain. J Adv Biomed Sci 12(2):203–214. https://doi.org/10.18502/jabs.v12i2.9886
Sharma D, Mayilraj S, Manhas RK (2014) Streptomyces amritsarensis sp. nov., exhibiting broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity. Antonie Leeuwenhoek 105:943–949. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-014-0151-2
Shigaki T, Rees I, Nakhleh L, Hirschi K (2006) Identification of three distinct phylogenetic groups of CAX cation/proton antiporters. J Mol Evol 63:815–825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-006-0048-4
Shivabai C, Gutte S (2019) Isolation of actinomycetes from soil sample using different pretreatment methods and its comparative study. Int J Res Anal Rev 6(2):697–702
Siro G, Pipite A, Christi K, Srinivasan S, Subramani R (2022) Marine actinomycetes associated with stony corals: a potential hotspot for specialized metabolites. Microorganisms 10(7):1349. https://doi.org/10.3390/microorganisms10071349
Siupka P, Hansen FT, Schier A, Rocco S, Sørensen T, Piotrowska-Seget Z (2021) Antifungal activity and biosynthetic potential of new Streptomyces sp. MW-W600-10 strain isolated from coal mine water. Int J Mol Sci 22(14):7441. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms22147441
Solanki SK, Krivova NA, Haigh JD (2013) Solar irradiance variability and climate. Annu Rev Astron Astrophys 51:311–351. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-astro-082812-141007
Sonia M-T, Hafedh B, Abdennaceur H, Ali G (2011) Studies on the ecology of actinomycetes in an agricultural soil amended with organic residues: II. Assessment of enzymatic activities of Actinomycetales isolates. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 27:2251–2259. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-011-0688-4
Srividya S, Thapa A, Bhat DV, Golmei K, Dey N (2012) Streptomyces sp. 9p as effective biocontrol against Chilli soilborne fungal phytopathogens. Eur J Exp Biol 2(1):163–173
Subramani R, Sipkema D (2019) Marine rare actinomycetes: a promising source of structurally diverse and unique novel natural products. Mar Drugs 17(5):249. https://doi.org/10.3390/md17050249
Tahvonen R (1982) The suppressiveness of Finnish light coloured Sphagnum peat. Agric Food Sci 54(5):345–356. https://doi.org/10.23986/afsci.72115
Trejo-Estrada S, Paszczynski A, Crawford D (1998) Antibiotics and enzymes produced by the biocontrol agent Streptomyces violaceusniger YCED-9. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 21(1–2):81–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.jim.2900549
Vurukonda SSKP, Giovanardi D, Stefani E (2018) Plant growth promoting and biocontrol activity of Streptomyces spp. as endophytes. Int J Mol Sci 19(4):952. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19040952
Waksman SA, Henrici AT (1943) The nomenclature and classification of the actinomycetes. J Bacteriol 46(4):337–341. https://doi.org/10.1128/jb.46.4.337-341.1943
Wan M, Li G, Zhang J, Jiang D, Huang H-C (2008) Effect of volatile substances of Streptomyces platensis F-1 on control of plant fungal Diseases. Biol Control 46(3):552–559. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biocontrol.2008.05.015
Wang C, Wang Z, Qiao X, Li Z, Li F, Chen M, Cui H (2013) Antifungal activity of volatile organic compounds from Streptomyces alboflavus TD-1. FEMS Microbiol Lett 341(1):45–51. https://doi.org/10.1111/1574-6968.12088
Whitman W, Goodfellow M, Kampfer P, Busse HJ, Trujillo ME, Ludwig W, Suzuki KI (eds) (2012) Bergey’s manual of systematic bacteriology, vol 5: The Actinobacteria. Springer-Verlag New York
Wildermuth H (1970) Development and organization of the aerial mycelium in Streptomyces coelicolor. Microbiology 60(1):43–50. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-60-1-43
Wildermuth H, Hopwood D (1970) Septation during sporulation in. Streptomyces coelicolor Microbiology 60(1):51–59. https://doi.org/10.1099/00221287-60-1-51
Xiong Z-Q, Tu X-R, Wei S-J, Huang L, Li XH, Lu H, Tu GQ (2013) The mechanism of antifungal action of a new polyene macrolide antibiotic antifungalmycin 702 from Streptomyces padanus JAU4234 on the rice sheath blight pathogen Rhizoctonia Solani. PLoS ONE 8(8):e73884. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0073884
Yandigeri MS (2021) Role of actinomycetes in insect pest and plant Disease management. Biopestici Horticul Crops 17:152–172
Yandigeri MS, Malviya N, Solanki MK, Shrivastava P, Sivakumar G (2015) Chitinolytic Streptomyces vinaceusdrappus S5MW2 isolated from Chilika lake, India enhances plant growth and biocontrol efficacy through chitin supplementation against Rhizoctonia solani. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 31:1217–1225. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-015-1870-x
Yang M, Huang C, Xue Y, Li S, Lu L, Wang C (2018) Biofumigation with volatile organic compounds from Streptomyces alboflavus TD-1 and pure chemicals to control aspergillus ochraceus. Ann Appl Biol 173(3):313–322. https://doi.org/10.1111/aab.12465
Zhang Q, Yong D, Zhang Y et al (2016) Streptomyces rochei A-1 induces resistance and defense-related responses against Botryosphaeria Dothidea in apple fruit during storage. Postharvest Biol Technol 115:30–37. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.postharvbio.2015.12.013
Zhao S, Du C-M, Tian C-Y (2012) Suppression of Fusarium oxysporum and induced resistance of plants involved in the biocontrol of cucumber Fusarium wilt by Streptomyces bikiniensis HD-087. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 28:2919–2927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11274-012-1102-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflict of interest to declare that are relevant to this article.
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Al-Quwaie, D.A. The role of Streptomyces species in controlling plant diseases: a comprehensive review. Australasian Plant Pathol. 53, 1–14 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-023-00959-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-023-00959-z