Abstract
Questions surrounding the kind of foreign direct investment that Pakistan attracts become important, especially with the unending debates that such investment can pose environmental challenges for the nation in particular and the world at large. While investment inflows are a prerequisite for economic growth, the environmental consequences are also vital for the quality of life of citizens. This study thus contributes to the debate on the trade-off between cross-border investment flows and environmental status in Pakistan, using annual time-series data spanning 1971–2018. The dynamic connection between foreign direct investment and ecological efficiency is scrutinized while controlling for the effects of environmental determinants—financial integration, economic growth, energy intensity and international trade—by employing dynamic autoregressive distributed lag simulations. The estimated elasticities as well as the counterfactual simulations show that even if ecological efficiency is used as the alternative measure of environmental performance within a dynamic framework, the pollution haven hypothesis still holds in Pakistan. Moroever, while economic growth, financial integration and international trade promote ecological efficiency, energy intensity condenses it. The robustness checks conducted using multivariate Quantle and Quantitle-on-Quantile Regressions also provide similar outcomes to that of the dynamic autoregressive distributed lag simulations.

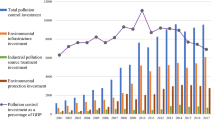
Source: Adopted from Musah et al. (2022) with some modifications







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The Ecological Efficiency was collected from https://www.footprintnetwork.org/ and World Development Indicators | DataBank (worldbank.org). per capital GDP, Net inflows of FDI, and Trade were collected from World Development Indicators | DataBank (worldbank.org).—Energy intensity was collected from Our World in Data and World Development Indicators | DataBank (worldbank.org). Financial integration was collected from Data—KOF Swiss Economic Institute | ETH Zurich.
Notes
Pollution haven hypothesis simply posits that foreign companies always seek to set up subsidiaries in developing countries because of the low cost of production and weak environmental regulations in these countries. This encourages highly intensive industries to (re)locate in these countries. However, pollution halo hypothesis is said to be valid when society promotes higher environmental standards, and as a result, discourages high pollution-intensive industries from operating in the countries.
References
Abbasi F, Riaz K (2016) CO2 emissions and financial development in an emerging economy: an augmented VAR approach. Energy Policy 90:102–114
Acheampong AO (2019) Modelling for insight: does financial development improve environmental quality? Energy Economics 83:156–179
Adebayo TS (2022) Impact of financial globalization on environmental degradation in the E7 countries: application of the hybrid nonparametric quantile causality approach. Problemy Ekorozwoju 17(2):1
Ahmad M, Wu Y (2022) Natural resources, technological progress, and ecological efficiency: Does financial deepening matter for G-20 economies? Resour Policy 77:102770
Ahmad M, Jabeen G, Irfan M, Işık C, Rehman A (2021) Do inward foreign direct investment and economic development improve local environmental quality: aggregation bias puzzle. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28(26):34676–34696
Ahmed K, Shahbaz M, Kyophilavong P (2016) Revisiting the emissions-energy-trade nexus: evidence from the newly industrializing countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(8):7676–7691
Alamrouni A, Aslanova F, Mati S, Maccido HS, Jibril AA, Usman AG, Abba SI (2022) Multi-regional modeling of cumulative COVID-19 cases ıntegrated with environmental forest knowledge estimation: a deep learning ensemble approach. Int J Environ Res Public Health 19(2):738
Alhassan A, Usman O, Ike GN, Sarkodie SA (2020) Impact assessment of trade on environmental performance: accounting for the role of government integrity and economic development in 79 countries. Heliyon 6(9):e05046
Alola AA, Özkan O, Usman O (2023a) Examining crude oil price outlook amidst substitute energy price and household energy expenditure in the USA: a novel nonparametric multivariate QQR approach. Energy Econ 120:106613
Alola AA, Özkan O, Usman O (2023b) Role of non-renewable energy efficiency and renewable energy in driving environmental sustainability in India: evidence from the load capacity factor hypothesis. Energies 16(6):2847
Antweiler W, Copeland BR, Taylor MS (2001) Is free trade good for the environment? Am Econ Rev 91(4):877–908
Azra A, Munir S, Abbas K, Khalid MH, Ul Haq I (2023) Empirical investigation of the impact of energy intensity and financial institutions efficiency on environmental degradation in Pakistan. Int J Energy Econ Policy 13(1):413–420
Balcilar M, Usman O, Ike GN (2023) Operational behaviours of multinational corporations, renewable energy transition, and environmental sustainability in Africa: Does the level of natural resource rents matter? Resour Policy 81:103344
Balsalobre-Lorente D, Gokmenoglu KK, Taspinar N, Cantos-Cantos JM (2019) An approach to the pollution haven and pollution halo hypotheses in MINT countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(22):23010–23026
Banga C, Deka A, Kilic H, Ozturen A, Ozdeser H (2022) The role of clean energy in the development of sustainable tourism: Does renewable energy use help mitigate environmental pollution? A panel data analysis. Environ Sci Pollut Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-022-19991-5
Bekhet HA, Othman NS (2017) Impact of urbanization growth on Malaysia CO2 emissions: evidence from the dynamic relationship. J Clean Prod 154:374–388
Chandrarin G, Sohag K, Cahyaningsih DS, Yuniawan D (2022) Will economic sophistication contribute to Indonesia’s emission target? A decomposed analysis. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 181:121758
Chen S, Zhang H, Wang S (2022) Trade openness, economic growth, and energy intensity in China. Technol Forecast Soc Chang 179:121608
Copeland BR, Taylor MS (1994) North-South trade and the environment. Q J Econ 109(3):755–787
Copeland BR, Taylor MS (2001) Trade and transboundary pollution 1. In: The economics of international trade and the environment. CRC Press, pp 119–142
Dickey DA, Fuller WA (1979) Distribution of the estimators for autoregressive time series with a unit root. J Am Stat Assoc 74(366):427–431
Dogan E, Turkekul B (2016) CO2 emissions, real output, energy consumption, trade, urbanization and financial development: testing the EKC hypothesis for the USA. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23(2):1203–1213
Essandoh OK, Islam M, Kakinaka M (2020) Linking international trade and foreign direct investment to CO2 emissions: Any differences between developed and developing countries? Sci Total Environ 712:136437
GFN. (2022). Global Footprint Network. https://www.footprintnetwork.org
Gokmenoglu KK, Rustamov B (2022) The role of the natural resource abundance in the short and long run: the case of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. Resour Policy 77:102699
Grossman G, Krueger A (1991) Environmental impacts of a North American free trade agreement. National Bureau of Economics Research Working Paper, No. 3194. NBER, Cambridge
Halicioglu F, Ketenci N (2018) Output, renewable and non-renewable energy production, and international trade: Evidence from EU-15 countries. Energy 159:995–1002
Hanif I (2018) Impact of economic growth, nonrenewable and renewable energy consumption, and urbanization on carbon emissions in Sub-Saharan Africa. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25(15):15057–15067
He P, Liang J, Qiu YL, Li Q, Xing B (2020) Increase in domestic electricity consumption from particulate air pollution. Nat Energy 5(12):985–995
Honma S (2015) Does international trade improve environmental efficiency? An application of a super slacks-based measure of efficiency. Journal of Economic Structures 4(1):1–12
Idris FM, Seraj M, Özdeşer H (2022) Renewable energy consumption, CO2 emissions and trade balance nexus in OECD countries: Evidence from ARDL bounds approach. Int J Energy Sect Manage. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJESM-02-2022-0009
Ike GN, Usman O, Alola AA, Sarkodie SA (2020) Environmental quality effects of income, energy prices and trade: the role of renewable energy consumption in G-7 countries. Sci Total Environ 721:137813
Iorember PT, Gbaka S, Jelilov G, Alymkulova N, Usman O (2022) Impact of international trade, energy consumption and income on environmental degradation in Africa’s OPEC member countries. Afr Dev Rev 34(2):175–187
Iorember PT, Terhemba G, Usman O, Işık A, Celik B (2021) The influence of renewable energy use, human capital, and trade on environmental quality in South Africa: Multiple structural breaks cointegration approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 28:13162–13174
Jin X, Li X, Feng Z, Wu J, Wu K (2020) Linking ecological efficiency and the economic agglomeration of China based on the ecological footprint and nighttime light data. Ecol Ind 111:106035
Jordan S, Philips AQ (2018) Cointegration testing and dynamic simulations of autoregressive distributed lag models. Stand Genomic Sci 18(4):902–923
Kahouli B, Nafla A, Trimeche H, Kahouli O (2022) Understanding how information and communication technologies enhance electric power consumption and break environmental damage to reach sustainable development. Energy Build 255:111662
Kripfganz S, Schneider DC (2020) Response surface regressions for critical value bounds and approximate p-values in equilibrium correction models 1. Oxford Bull Econ Stat 82(6):1456–1481
Kuznets S (1955) Economic growth and income inequality. Am Econ Rev 45(1):1–28
Le TH, Chang Y, Park D (2016) Trade openness and environmental quality: international evidence. Energy Policy 92:45–55
Ling CH, Ahmed K, Binti Muhamad R, Shahbaz M (2015) Decomposing the trade-environment nexus for Malaysia: What do the technique, scale, composition, and comparative advantage effects indicate? Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(24):20131–20142
Lv Z, Xu T (2019) Trade openness, urbanization and CO2 emissions: dynamic panel data analysis of middle-income countries. J Int Trade Econ Dev 28(3):317–330
Majeed MT, Ozturk I, Samreen I, Luni T (2022) Evaluating the asymmetric effects of nuclear energy on carbon emissions in Pakistan. Nucl Eng Technol 54(5):1664–1673
McFarlane A, Brown L, Campbell K, Das A (2022) Is the impact of financial development on energy consumption in Jamaica asymmetric? Int J Energy Sect Manage. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJESM-02-2022-0004
Mihci H, Cagatay S, Koska O (2005) The impact of environmental stringency on the foreign direct investments of the OECD countries. JEAPM 7(04):679–704
Murshed M, Elheddad M, Ahmed R, Bassim M, Than ET (2022) Foreign direct investments, renewable electricity output, and ecological footprints: Do financial globalization facilitate renewable energy transition and environmental welfare in Bangladesh? Asia-Pac Finan Markets 29(1):33–78
Musah M, Mensah IA, Alfred M, Mahmood H, Murshed M, Omari-Sasu AY, Boateng F, Nyeadi JD, Coffie CPK (2022) Reinvestigating the pollution haven hypothesis: the nexus between foreign direct investments and environmental quality in G-20 countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29:31330–31347
Namahoro JP, Wu Q, Zhou N, Xue S (2021) Impact of energy intensity, renewable energy, and economic growth on CO2 emissions: Evidence from Africa across regions and income levels. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 147:111233
Olasehinde-Williams G, Oshodi AF (2021) Global value chains and export growth in South Africa: Evidence from dynamic ARDL simulations. Transnational Corp Rev 1:1–13
Olasehinde-Williams G, Özkan O (2022) Is interest rate uncertainty a predictor of investment volatility? Evidence from the wild bootstrap likelihood ratio approach. Journal of Economics and Finance 46:507–521
OWD. (2022). Our World in Data. https://ourworldindata.org/grapher/per-capita-energy-use
Ozkan O, Coban MN, Iortile IB, Usman O (2023a) Reconsidering the environmental Kuznets curve, pollution haven, and pollution halo hypotheses with carbon efficiency in China: a dynamic ARDL simulations approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:68163–68176
Ozkan O, Haruna RA, Alola AA, Ghardallou W, Usman O (2023b) Investigating the nexus between economic complexity and energy-related environmental risks in the USA: empirical evidence from a novel multivariate quantile-on-quantile regression. Struct Chang Econ Dyn 65:382–392
Ozkan O, Khan N, Ahmed M (2023c) Impact of green technological innovations on environmental quality for Turkey: evidence from the novel dynamic ARDL simulation model. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:72207–72223
Ozkan O, Sharif A, Mey LS, Tiwari S (2023d) The dynamic role of green technological innovation, financial development and trade openness on urban environmental degradation in China: Fresh insights from carbon efficiency. Urban Climate 52:101679
Özkan O, Obekpa HO, Alola AA (2023) Examining the nexus of energy intensity, renewables, natural resources, and carbon intensity in India. Energy Environ. https://doi.org/10.1177/0958305X231169706
Özkan O, Olasehinde-Williams G, Olanipekun I (2022) Predicting stock returns and volatility in BRICS countries during a pandemic: evidence from the novel wild bootstrap likelihood ratio approach. Finance a Úvěr-Czech J Econ Financ 72:124–149
Pata UK, Erdogan S, Ozkan O (2023a) Is reducing fossil fuel intensity important for environmental management and ensuring ecological efficiency in China? J Environ Manag 329:117080
Pata UK, Olasehinde-Williams G, Ozkan O (2023b) Carbon efficiency in China: Should we be concerned about the shadow economy and urbanization? Geol J 58(10):3646–3658
Pesaran MH, Shin Y, Smith RJ (2001) Bounds testing approaches to the analysis of level relationships. J Appl Economet 16(3):289–326
Phillips PCB, Perron P (1988) Testing for a unit root in time series regression. Biometrika 75(2):335–346
Porter ME (1991) America’s green strategy. Sci Am 264:1
Rafindadi AA, Usman O (2019) Globalization, energy use, and environmental degradation in South Africa: startling empirical evidence from the Maki-cointegration test. J Environ Manage 244:265–275
Rafindadi AA, Muye IM, Kaita RA (2018) The effects of FDI and energy consumption on environmental pollution in predominantly resource-based economies of the GCC. Sustain Energy Technol Assess 25:126–137
Salari M, Javid RJ, Noghanibehambari H (2021) The nexus between CO2 emissions, energy consumption, and economic growth in the U.S. Econ Anal Policy 69:182–194
Shahbaz M, Chaudhary AR, Ozturk I (2017) Does urbanization cause increasing energy demand in Pakistan? Empirical evidence from STIRPAT model. Energy 122:83–93
Shahbaz M, Lean HH, Shabbir MS (2012) Environmental Kuznets curve hypothesis in Pakistan: cointegration and granger causality. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16(5):2947–2953
Shahbaz M, Nasreen S, Abbas F, Anis O (2015) Does foreign direct investment impede environmental quality in high-, middle-, and low-income countries? Energy Econ 51:275–287
Shahbaz M, Tiwari AK, Nasir M (2013) The effects of financial development, economic growth, coal consumption and trade openness on CO2 emissions in South Africa. Energy Policy 61:1452–1459
Shahzad SJH, Kumar RR, Zakaria M, Hurr M (2017) Carbon emission, energy consumption, trade openness and financial development in Pakistan: a revisit. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:185–192
Solarin SA, Al-Mulali U, Musah I, Ozturk I (2017) Investigating the pollution haven hypothesis in Ghana: an empirical investigation. Energy 124:706–719
Ssali MW, Du J, Mensah IA, Hongo DO (2019) Investigating the nexus among environmental pollution, economic growth, energy use, and foreign direct investment in 6 selected sub-Saharan African countries. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:11245–11260
Tamazian A, Chousa JP, Vadlamannati KC (2009) Does higher economic and financial development lead to environmental degradation: evidence from BRIC countries. Energy Policy 37(1):246–253
Tamazian A, Rao BB (2010) Do economic, financial and institutional developments matter for environmental degradation? Evid Transitional Econ Energy Econ 32(1):137–145
Taskin F, Zaim O (2001) The role of international trade on environmental efficiency: a DEA approach. Econ Model 18(1):1–17
Ulucak ZŞ, İlkay SÇ, Özcan B, Gedikli A (2020) Financial globalization and environmental degradation nexus: evidence from emerging economies. Resour Policy 67:101698
Usman O, Iorember PT, Ozturk I, Bekun FV (2022) Examining the interaction effect of control of corruption and income level on environmental quality in Africa. Sustainability 14(18):11391
Usman O, Akadiri SS, Adeshola I (2020) Role of renewable energy and globalization on ecological footprint in the USA: İmplications for environmental sustainability. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27(24):30681–30693
Wang B, Yan C, Iqbal N, Fareed Z, Arslan A (2022) Impact of human capital and financial globalization on environmental degradation in OBOR countries: critical role of national cultural orientations. Environ Sci Pollut Res 29(25):37327–37343
Wang Z, Bui Q, Zhang B, Nawarathna CLK, Mombeuil C (2021) The nexus between renewable energy consumption and human development in BRICS countries: the moderating role of public debt. Renew Energy 165(1):381–390
WDI (2022) World Development Indicators of the World Bank. https://databank.worldbank.org/source/world-development-indicators
World Bank (2016) The cost of air pollution: strengthening the economic case for action. The World Bank and Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation University of Washington, Seattle https://openknowledge.worldbank.org/handle/10986/25013. Accessed 18th August 2022
Yang L, Yang Y (2019) Evaluation of eco-efficiency in China from 1978 to 2016: based on a modified ecological footprint model. Sci Total Environ 662:581–590
Zhang W, Wang Z, Adebayo TS, Altuntaş M (2022) Asymmetric linkages between renewable energy consumption, financial integration, and ecological sustainability: moderating role of technology innovation and urbanization. Renew Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2022.08.021
Zugravu-Soilita N (2017) How does foreign direct investment affect pollution? Toward a better understanding of the direct and conditional effects. Environ Resource Econ 66(2):293–338
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Özkan, O., Olasehinde-Williams, G. & Usman, O. Foreign direct investment and ecological efficiency in Pakistan: a new perspective on the pollution haven hypothesis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05606-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05606-8