Abstract
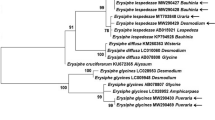
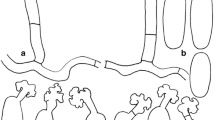
Podosphaera xanthii is presently considered as one of the powdery mildew fungi with the broadest host range. Confusion is caused by taxonomical and nomenclatural changes of the host plants and the fungal parasite. Based on the list of powdery mildews from Taiwan from 1998, an updated list of host plants of P. xanthii in this country is presented. New hosts from Taiwan are wild and horticultural herbs and woody plants collected between 2011 and 2020. Fifteen plant species were found to be the host of P. xanthii based on new collections of the anamorph and internal transcribed spacer (ITS) sequences. Among them, Cuphea carthagenensis, Cuphea hyssopifolia, Erigeron bellioides, Mazus pumilus, Phyllanthus tenellus, Salvia farinacea, and Sphagneticola trilobata were new hosts worldwide, whereas Bidens pilosa, Eclipta prostrata, Pouzolzia zeylanica, and Torenia fournieri were new hosts in Taiwan. Four further plant species were confirmed as known hosts (Emilia sonchifolia, Sesamum indicum, Trema orientalis, Zinnia elegans). Asteraceae contained most host species in Taiwan, which appeared proportional to the high species diversity in this plant family. The second highest host diversity in the Cucurbitaceae, however, was not proportional to plant diversity. Although the fungus is able to cause similar symptoms on a broad range of hosts, certain host species showed specific responses to infection. In some species, infection remains limited to old leaves, whereas in other species, only young leaves or mainly stems are infected.
















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amano KH (1986) Host range and geographical distribution of the powdery mildew fungi. Japan Scientific Society Press, Tokyo
Beales PA, Cook RTA (2008) A novel finding of Podosphaera causing powdery mildew on Cuphea rosea. Plant Pathology 57:778
Braun U (1987) A monograph of the Erysiphales (powdery mildews). Beihefte zur Nova Hedwigia 89:1–700
Braun U (2013) Proposals to conserve the teleomorph-typified name Blumeria against the anamorph-typified name Oidium and twenty-two teleomorph-typified powdery mildew species names against competing anamorph-typified names (Ascomycota: Erysiphaceae). Taxon 62:1328–1331
Braun U, Cook RTA (2012) The taxonomic manual of the Erysiphales (powdery mildews). CBS Biodiversity Series 11:1–707
Chao CT, Cheng CL, Wang CM (2019) Ipomoea lacunosa (Convolvulaceae: Ipomoea sect. Batatas): a newly naturalized species of Taiwan. Taiwan Journal of Forest Science 34:55–62
Cheng CW, Chen RS, Chang WH, Tsay JG (2006) The occurrence of powdery mildew on Physalis angulata caused by Podosphaera xanthii. Plant Protection Bulletin 48:41–51
Cho SE, Park JH, Shin HD, Hong SH (2013) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera xanthii on the invasive weed, Bidens pilosa, in Korea. Plant Disease 97:1254
Cho SE, Park JH, Kim BS, Han KS, Shin HD (2015) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera xanthii on Torenia fournieri in Korea. Plant Disease 99:1863–1864
Ellingham O (2016) Powdery mildew survey 2016. http://blogs.reading.ac.uk/crg/powdery-mildew-survey-2016
Farr DF, Rossman AY (2020) Fungal databases. U.S. National Fungus Collections, ARS, USDA from https://nt.ars-grin.gov/fungaldatabases/
Glawe DA (2008) The powdery mildews: a review of the world’s most familiar (yet poorly known) plant pathogens. Annual Review of Phytopathology 46:27–51
Hsieh C-F (2003) Composition, endemism and phytogeographical affinities of the Taiwan flora. Huang TC (Editor-in-Chief), Flora of Taiwan, 2nd ed., 6. Editorial Committee of the Flora of Taiwan, Dept. Bot., NTU, Taipei, pp. 1–14
Hsueh C-H, Yang Z-Y (2008) The scenic plants in Taiwan (1). United Distribution, Hsindian (in Chinese)
Hsueh C-H, Yang Z-Y (2014) The scenic plants in Taiwan (5). United Distribution, Hsindian (in Chinese)
Huang JH, Wang YH, Lo CT (2002) Development of leaf-disk method for screening melon varieties resistant to Sphaerotheca fuliginea race 1. Journal of Agricultural Research of China 51:49–56 (in Chinese with English abstract)
Jung M-J, Hsu T-C, Chung S-W, Peng C-I (2009) Three newly naturalized Asteraceae plants in Taiwan. Taiwania 54:76–81
Kirschner R (2015) New records of Pseudocercospora oenotherae and Synchytrium fulgens on the invasive coastal plant Oenothera laciniata in Taiwan. Plant Pathology and Quarantine 5:26–33
Kirschner R, Liu W-A (2014) Two new hosts of anamorphic Erysiphe quercicola: Cinnamomum camphora and Murraya paniculata. Mycoscience 55:190–195
Kuo K-C (1998) Checklist of Erysiphaceae in Taiwan. Fungal Sciences 13:39–59
Kuo K-C, Lee C-Y, Leu L-S (1991) Notes on the Erysiphaceae found in Taiwan (I). Transactions of the British Mycological Society ROC 6:13–44
Lebeda A, Křístová E, Rybka U, Havránek P (2001) Utricularia (Lentibulariaceae) – a new host plant genus of powdery mildew (Sphaerotheca sp.). Journal of Phytopathology 149:207–212
Liu W-A, Kirschner R (2015) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera xanthii on wild bitter gourd in Taiwan. Plant Disease 99:726
Lu T-C, Lin H-W, Wang J-C (2019) Two new species of Sedum (Crassulaceae) from Taiwan. Taiwania 64:426–431
Meeboon J, Hidayat I, Takamatsu S (2016) Notes on powdery mildews (Erysiphales) in Thailand I. Podosphaera sect. Sphaerotheca. Plant Pathology and Quarantine 6:142–174
Meeboon J, Takamatsu S (2020) Hosts of asexual morph of Erysiphe quercicola from Thailand. Tropical Plant Pathology 45:122–135
Pirondi A, Vela-Corcia D, Dondini L, Brunelli A, Perez-Garcia A, Collina M (2015) Genetic diversity analysis of the cucurbit powdery mildew fungus Podosphaera xanthii suggests a clonal population structure. Fungal Biology 119:791–801
Rodríguez-Alvarado G, Soto-Plancarte A, Fernández-Pavía SP, Betancourt-Resendes I, Braun U (2012) Identity of powdery mildew on Senna in Mexico. Plant Pathology and Quarantine 2:37–42
Sawada K (1919) Descriptive catalogue of the Formosan fungi I. Agricultural Experiment Station, Taipei (in Japanese)
Shen Y-M, Huang T-C, Liu H-L, Chao C-H (2015) First report of the powdery mildew Podosphaera xanthii on Gynura bicolor. Australasian Plant Disease Notes 10:1–3
Takamatsu S, Niinomi S, Harada M, Havrylenko M (2010) Molecular phylogenetic analyses reveal a close evolutionary relationship between Podosphaera (Erysiphales: Erysiphaceae) and its rosaceous hosts. Persoonia 24:38–48
Tsay J-G, Chen R-S, Wang H-L, Wang W-L, Weng B-C (2011) First report of powdery mildew caused by Erysiphe diffusa, Oidium neolycopersici, and Podosphaera xanthii on papaya in Taiwan. Plant Disease 95:1188
Wei I-C, Kirschner R (2017) Two fungicolous anamorphic species of Hypomyces s. lat. from Taiwan. Fungal Sciences 32:15–25
Wu S-H, Yang TYA, Teng Y-C, Chang C-Y, Yang K-C, Hsieh C-F (2010) Insights of the latest naturalized flora of Taiwan: change in the past eight years. Taiwania 55:139–159
Wu T-Y, Kirschner R (2017) A brief global review on the species of cucurbit powdery mildew fungi and new records in Taiwan. Mycologia Iranica 4:85–91
Wu T-Y, Kirschner R, Lu H-F (2019) First report of powdery mildew caused by Podosphaera xanthii on carnivorous plants outside Europe. Plant Disease 103:154
Yeh YW, Kirschner R, Lu HF (2018) First record of Erysiphe elevata on Plumeria rubra in Taiwan. Plant Disease 103:371
Yu J, Liang C, Xing H-H (2014) Identification of the pathogen in causing eggplant powdery mildew in Qingdao. Journal of Fungal Research 12:96–106
Acknowledgments
We thank Y.-H. Yeh for technical assistance for the DNA data.
Funding
Funding for this study was received from Cheng Hsin General Hospital (CHGH109-(N)34) and the Ministry of Science & Technology, Taiwan (NSC 102-2621-B-008-001-MY3 and MOST 108-2621-B-002-007).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation and data collection were performed by Yu-Wei Yeh, Ting-Ying Wu, Hsu-Lun Wen, and Roland Kirschner. Yu-Wei Yeh and Roland Kirschner together performed the data analysis and wrote the first draft of the manuscript. Herng-Woei Jair and Ming-Zhe Lee contributed to the data interpretation. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeh, YW., Wu, TY., Wen, HL. et al. Host plants of the powdery mildew fungus Podosphaera xanthii in Taiwan. Trop. plant pathol. 46, 44–61 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-020-00393-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40858-020-00393-2