Abstract
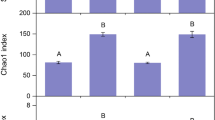
Ectomycorrhizal fungal community composition and changes are crucial for evaluating ecological restoration. This study was conducted to reveal significant differences in the community structure and composition of soil ectomycorrhizal fungi in different tree afforestation species in the Three-North Shelter Forest Program area of Liaoning. In this experiment, high-throughput sequencing was used to investigate the correlation between soil ectomycorrhizal fungal community characteristics and silvicultural species, including Populus × canadensis, Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica, and Pinus tabuliformis, the main silvicultural species in the Three-North Shelter Forest Program in western Liaoning, China. Among them, Populus × canadensis had the highest soil pH, DOC, available N, and available P, while having the lowest C/N ratio and total C, according to the results. Ascomycota, Mortierellomycota, and Basidiomycota were the three most prevalent phyla in the soil ectomycorrhizal fungal communities between plantations, which also showed significant differences. The diversity of the soil ectomycorrhizal fungal communities was significantly impacted by the physicochemical characteristics of the soil in the various plantations. Under the same climatic conditions, the soil characteristics of different tree species after afforestation showed significant differences, especially between coniferous and broad-leaved species. The significant differences in the composition and structure of soil ectomycorrhizal fungal communities after afforestation greatly illustrate the correlation between soil microbial community characteristics and tree species.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Augusto L, Ranger J, Binkley D, Rothe A (2002) Impact of several common tree species of European temperate forests on soil fertility. Ann Forest Sci 59:233–253. https://doi.org/10.1051/forest:2002020
Bansal S, Hallsby G, Lofvenius MO, Nilsson MC (2013) Synergistic, additive and antagonistic impacts of drought and herbivory on Pinus sylvestris: leaf, tissue and whole-plant responses and recovery. Tree Physiol 33:451–463. https://doi.org/10.1093/treephys/tpt019
Bao SD (2000) Soil and agricultural chemistry analysis. China Agriculture Press, Beijing, pp 263–270
Bokulich NA, Kaehler BD, Ram RJ, Matthew D, Evan B, Rob K, Huttley GA, Caporaso JG (2018) Optimizing taxonomic classification of marker-gene amplicon sequences with QIIME 2’s q2-feature-classifier plugin. Microbiome 6:90. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40168-018-0470-z
Bollmann-Giolai A, Malone JG, Arora S (2022) Diversity, detection and exploitation: linking soil fungi and plant disease. Curr Opin Microbiol 70:102199. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2022.102199
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet C, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F, Bai Y, Bisanz JE, Bittinger K, Brejnrod A, Brislawn CJ, Brown CT et al (2019) Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME2. Nat Biotechnol 37:852–857. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41587-019-0209-9
Boscaro V, Fokin S, Schrallhammer M, Schweikert M, Petroni G (2013) Revised systematics of Holospora-like bacteria and characterization of “Candidatus Gortzia infectiva”, a novel macronuclear symbiont of Paramecium jenningsi. Microb Ecol 65:255–267. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00248-012-0110-2
Burton J, Chen C, Xu Z, Ghadiri H (2010) Soil microbial biomass activity and community composition in adjacent native and plantation forests of subtropical Australia. J Soil Sediment 10:1267–1277. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-010-0238-y
Callahan BJ, Mcmurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJ, Holmes SP (2016) DADA2: high-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat Methods 13:581–583. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3869
Cao S, Suo X, Xia C (2020) Payoff from afforestation under the Three-North Shelter Forest Program. J Clean Prod 256:120461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120461
Chatterjee A, Vance GF, Pendall E, Stahl PD (2008) Timber harvesting alters soil carbon mineralization and microbial community structure in coniferous forests. Soil Biol Biochem 40:1901–1907. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2008.03.018
Chaudhary D, Gautam R, Ghosh A, Chikara J, Jha B (2015) Effect of nitrogen management on soil microbial community and enzymatic activities in Jatropha curcas L. plantation. Clean (Weinh) 43:1058–1065. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201400357
Chen YL, Dell B, Malajczuk N (2006) Effect of scleroderma spore density and age on mycorrhiza formation and growth of containerized Eucalyptus globulus and E. urophylla seedlings. New For 31:453–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-005-0880-1
Degrune F, Dufrêne M, Colinet G, Massart S, Taminiau B, Bodson B, Marie-Pierre H, Daube GC, Vandenbol M (2015) A novel sub-phylum method discriminates better the impact of crop management on soil microbial community. Agron Sustain Dev 35:1157–1166. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13593-015-0291-4
Deng JJ, Zhang Y, Yin Y, Zhu WX, Zhou YB (2019) Comparison of soil bacterial community and functional characteristics following afforestation in the semi-arid areas. PeerJ 7:e7141. https://doi.org/10.7717/peerj.7141
Deng Q, Mcmahon DE, Xiang Y, Yu C, Jackson RB, Hui D (2017) A global meta-analysis of soil phosphorus dynamics after afforestation. New Phytol 10:1988–1995. https://doi.org/10.1111/nph.14119
Deng JJ, Zhu WX, Zhang Y, Yin Y, Zhou YB (2020) Soil fungal community structure and functional characteristics of different plantations in the sandy area of northwestern Liaoning. Forestry Science Research 033:44–54. https://doi.org/10.13275/j.cnki.lykxyj.2020.01.006
Dinesh R, Chaudhuri SG (2013) Soil biochemical/microbial indices as ecological indicators of land use change in mangrove forests. Ecol Indic 32:253–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2013.03.035
Don A, Kalbitz K (2005) Amounts and degradability of dissolved organic carbon from foliar litter at different decomposition stages. Soil Biol Biochem 37:2171–2179. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2005.03.019
Emtery O (1989) Chemical and physical analysis of inorganic nutrients in plant, soil, water and air. Swedish University of Aricultural Sciences, department of forest site research, Umeå, p 181
Erland S, Taylor A (2002) Diversity of ectomycorrhizal fungal communities in relation to the abiotic environment. Mycorrhizal Ecol 157:163–200. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-38364-2_7
Fadrosh DW, Ma B, Gajer P, Sengamalay N, Ott S, Brotman RM, Ravel J (2014) An improved dual-indexing approach for multiplexed 16s rRNA gene sequencing on the Illumina MiSeq platform. Microbiome 2:6–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/2049-2618-2-6
Fierer N, Jackson RB (2006) The diversity and biogeography of soil bacterial communities. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:626–631. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0507535103
Gao H, Huang Y (2020) Impacts of the Three-North Shelter Forest Program on the main soil nutrients in Northern Shaanxi China: a meta-analysis. Forest Ecol Manag 458:117808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2019.117808
Gao Y, Qiu GY, Shimizu H, Tobe K, Sun B, Wang J (2002) A 10-year study on techniques for vegetation restoration in a decertified Salt Lake area. J Arid Environ 524:483–497. https://doi.org/10.1006/jare.2002.1013
Gong MQ, Chen YL, Zhong CL (1997) Research and application of mycorrhiza. China Forestry Press, Beijing, pp 84–88
Gu Z, Hübschmann D (2022) Make interactive complex heatmaps in R. Bioinformatics 38:1460–1462. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btab806
Guo M, Ding G, Gao G, Zhang Y (2020) Community composition of ectomycorrhizal fungi associated with Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations of various ages in the Horqin Sandy Land. Ecol Indic 110:105860. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2019.105860
Heijden MGAVD, Bardgett RD, Straalen NMV (2010) The unseen majority: soil microbes as drivers of plant diversity and productivity in terrestrial ecosystems. Ecol Lett 11:296–310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1461-0248.2007.01139.x
Herrmann L, Lesueur D, Davison J, Jairus T, Robain H, Vasar M, Wiriyakitnateekul W (2016) Diversity of root-associated arbuscular mycorrhizal fungal communities in a rubber tree plantation chronosequence in Northeast Thailand. Mycorrhiza 26:863–877. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00572-016-0720-5
Hou W, Lian B, Dong H, Jiang H, Wu X (2012) Distinguishing ectomycorrhizal and saprophytic fungi using carbon and nitrogen isotopic compositions. Geosci Front 3:351–356. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2011.12.005
Jahed RR (2014) The effect of natural and planted forest stands on soil fertility in the Hyrcanian region Iran. Biodivers J Biol Divers 15:206–214. https://doi.org/10.13057/biodiv/d150213
Jia GM, Jing C, Wang C, Wang G (2005) Microbial biomass and nutrients in soil at the different stages of secondary forest succession in Ziwulin northwest China. Forest Ecol Manag 217:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foreco.2005.05.055
Jim CY (1998) Physical and chemical properties of a Hong Kong roadside soil in relation to urban tree growth. Urban Ecosyst 2:171–181. https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1009585700191
Kalbitz K, Schwesig D, Schmerwitz J, Kaiser K, Haumaier L, Glaser B, Ellerbrockd R, Leinwebere P (2003) Changes in properties of soil-derived dissolved organic matter induced by biodegradation. Soil Biol Biochem 35:1129–1142. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0038-0717(03)00165-2
Karl R, Helaina JIB, Colin DC, Jim AH, Claire W (2009) Selecting biological indicators for monitoring soils: a framework for balancing scientific and technical opinion to assist policy development. Ecol Indic 9:1212–1221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2009.02.009
Karliński L, Rudawska M, Leski T (2013) The influence of host genotype and soil conditions on ectomycorrhizal community of poplar clones. Eur J Soil Biol 58:51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2013.05.007
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma K, Miyata T (2002) Mafft: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Res 30:3059–3066. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkf436
Kolář T, Kusbach A, Čermák P, Štěrba T, Batkhuu E, Rybníček M (2020) Climate and wildfire effects on radial growth of Pinus sylvestris in the Khan Khentii Mountains, north-central Mongolia. J Arid Environ 182:104223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2020.104223
Kutszegi G, Siller I, Dima B, Takács K, Merényi Z, Varga T, Turcsányi G, Bidló A, Péter D (2015) Drivers of macrofungal species composition in temperate forests west Hungary: functional groups compared. Fungal Ecol 17:69–83. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2015.05.009
Lan G, Wu Z, Yang C, Sun R, Zhang X (2020) Tropical rainforest conversion into rubber plantations results in changes in soil fungal composition, but underling mechanisms of community assembly remain unchanged. Geoderma 375:114505. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2020.114505
Li D, Xu D, Wang Z, Ding X, Song A (2018) Ecological compensation for desertification control: a review. J Geogr Sci 28:367–384. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11442-018-1478-9
Li H, Huang J, Yuan L (2013) Influence of aluminum and manganese on the growth nutrient uptake and the efflux by ectomycorrhizal fungi. Huan Jing Ke Xue 34:315–320. https://doi.org/10.13227/j.hjkx.2013.01.009
Li J (2018) Spatiotemporal distribution of precipitation recycling across the arid regions of Asia and Africa. J Environ Prot Ecol 6:195–206. https://doi.org/10.4236/gep.2018.69015
Liu J, Diamond J (2005) China’s environment in a globalizing world. Nature 435:1179–1186. https://doi.org/10.1038/4351179a
Lu F, Hu H, Sun W, Zhu J, Liu G, Zhou W, Zhang Q, Shi P, Liu X, Wu X (2018) Effects of national ecological restoration projects on carbon sequestration in China from 2001 to 2010. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:4039–4044. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1700294115
Luo ZB, Li K, Gai Y, Göbel C, Wildhagen H, Jiang XN, Feußner I, Rennenberg H, Polle A (2011) The ectomycorrhizal fungus (Paxillus involutus) modulates leaf physiology of poplar towards improved salt tolerance. Environ Exp Bot 72:304–311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envexpbot.2011.04.008
Martin M (2011) Cutadapt removes adapter sequences from high-throughput sequencing reads. EMBnet J 17:10. https://doi.org/10.14806/ej.17.1.200
Martínez-Valderrama J, Ibáñez J, Barrio GD, Sanjuán ME, Alcalá FJ, Martínez-Vicente S, Ruiz A, Puigdefábregas J (2016) Present and future of desertification in Spain: implementation of a surveillance system to prevent land degradation. Sci Total Environ 563-564:169–178. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.04.065
Matsuoka S, Mori AS, Kawaguchi E, Hobara S, Osono T (2016) Disentangling the relative importance of host tree community abiotic environment and spatial factors on ectomycorrhizal fungal assemblages along an elevation gradient. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 92:fiw044. https://doi.org/10.1093/femsec/fiw044
Mcgroddy ME, Daufresne T, Hedin LO (2004) Scaling of C:N:P stoichiometry in forests worldwide: implications of terrestrial redfield-type ratios. Ecology 85:2390–2401. https://doi.org/10.1890/03-0351
Mishra M, Pradhan M, Sukla L, Mishra B (2011) Microbial beneficiation of salem iron ore using Penicillium purpurogenum. Metall Mater Trans B 42:13–19. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9444-7
Munoz-Rojas M, Erickson TE, Martini D, Dixon KW, Merritt DJ (2016) Soil physicochemical and microbiological indicators of short medium and long term post-fire recovery in semi-arid eco-systems. Ecol Indic 63:14–12. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolind.2015.11.038
Neff JC, Asner GP (2001) Dissolved organic carbon in terrestrial ecosystems: synthesis and a model. Ecosystems 4:29–48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s100210000058
Nguyen NH, Song Z, Bates ST, Branco S, Tedersoo L, Menke J, Schilling JS, Kennedy PG (2016) FUNGuild: an open annotation tool for parsing fungal community datasets by ecological guild. Fungal Ecol 20:241–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.funeco.2015.06.006
Nunez-Mir GC, Iannone BV, Curtis K, Fei S (2015) Evaluating the evolution of forest restoration research in a changing world: a “big literature” review. New For 46:669–682. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11056-015-9503-7
Ohlson HM (2010) Tree influence on soil microbial community structure. Soil Biol Biochem 42:1934–1943. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2010.07.002
Pennisi E (2004) The secret life of fungi. Science 304:1620–1622. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.304.5677.1620
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP (2009) FastTree: computing large minimum evolution trees with profiles instead of a distance matrix. Mol Biol Evol 26:1641–1650. https://doi.org/10.1093/molbev/msp077
Qiu K, Xie Y, Xu D, Pott R (2018) Ecosystem functions including soil organic carbon total nitrogen and available potassium are crucial for vegetation recovery. Sci Rep 8:7607. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-25875-x
Raji BA, Uyovbisere EO, Momodu AB (2004) Impact of sand dune stabilization structures on soil and yield of millet in the semi-arid region of NW Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 99:181–196. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-004-4018-2
Ramette A (2007) Multivariate analyses in microbial ecology. FEMS Microbiol Ecol 62:142–160. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1574-6941.2007.00375.x
Schimel DS (2010) Drylands in the Earth system. Science 327:418–419. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1184946
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D (2011) Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol 12:R60. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-6-r60
Shoumik BAA, Khan MZ (2023) Spatio-temporal dynamics of soil organic carbon and total nitrogen: evidenced from 2000 to 2020 in a mixed ecosystem. Environ Earth Sci 82:84. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-023-10756-y
Si P, Liu E, He W, Sun Z, Dong W, Yan C, Zhang Y (2017) Effect of no-tillage with straw mulch and conventional tillage on soil organic carbon pools in Northern China. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64:398–408. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1359410
Silva A, Babujia LC, Franchini JC, Ralisch R, Hungria M, Guimarãesb EM (2014) Soil structure and its influence on microbial biomass in different soil and crop management systems. Soil Tillage Res 142:42–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.still.2014.04.006
Song L, Tian P, Zhang J, Jin G (2017) Effects of three years of simulated nitrogen deposition on soil nitrogen dynamics and greenhouse gas emissions in a Korean pine plantation of Northeast China. Sci Total Environ 609:1303–1311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.08.017
Song L, Zhu J, Li M, Yu Z (2014) Water utilization of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in a sparse wood grassland in the semiarid sandy region of Northeast China. Trees Struct Funct 28:971–982. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00468-014-1010-5
Song L, Zhu J, Li M, Zhang J, Zheng X, Wang K (2018) Canopy transpiration of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica in a sparse wood grassland in the semiarid sandy region of Northeast China. Agric For Meteorol 250:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agrformet.2017.12.260
Sousa NR, Ramos MA, Marques A, Castro P (2012) The effect of ectomycorrhizal fungi forming symbiosis with Pinus pinaster seedlings exposed to cadmium. Sci Total Environ 414:63–67. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2011.10.053
Souza E, Antoniolli Z, Machado R, Eckhardt D, Schirmer G (2012) Effect of ectomycorrhizal fungi isolates inoculation in eucalyptus grandis hill ex maiden seedlings development. Ciencia Florestal 22:251–261. https://doi.org/10.5902/198050985732
Sun T, Fu J, Chai F (2012) Study on characteristics and risk indicators of agricultural drought in northwestern Liaoning Province, China. Appl Mech Mater 212–213:739–743. https://doi.org/10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMM.212-213.739
Sun Y, Zhu J, Yan Q, Hu Z, Zheng X (2016) Changes in vegetation carbon stocks between 1978 and 2007 in central Loess Plateau China. Environ Earth Sci 75:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-015-5199-4
Sutton PC, Anderson SJ, Costanza R, Kubiszewski I (2016) The ecological economics of land degradation: impacts on ecosystem service values. Ecol Econ 129:182–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecolecon.2016.06.016
Tafazoli M, Hojjati SM, Jalilvand H, Lamersdorf N (2019) Simulated nitrogen deposition reduces the concentration of soil base cations in Acer velutinum Bioss. Plantation north of Iran. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 19:440–449. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00048-5
Tedersoo L, Smith ME (2017) Ectomycorrhizal fungal lineages: detection of four new groups and notes on consistent recognition of ectomycorrhizal taxa in high-throughput sequencing studies. In: Tedersoo L (ed) Biogeography of mycorrhizal symbiosis, vol 230. Springer International Publishing, Cham, Switzerland, pp 125–142
Tian H, Kah M, Kariman K (2019) Are nanoparticles a threat to mycorrhizal and rhizobial symbioses? A critical review. Front Microbiol 10:1660. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2019.01660
Tripathi SK, Sumida A, Shibata H, Ono K, Uemura S, Kodama Y, Hara T (2006) Leaf litterfall and decomposition of different above- and belowground parts of birch (Betula ermanii) trees and dwarf bamboo (Sasa kurilensis) shrubs in a young secondary forest in Northern Japan. Biol Fertil Soils 43:237–246. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00374-006-0100-y
Ushio M, Kitayama K, Balser TC (2010) Tree species effects on soil enzyme activities through effects on soil physicochemical and microbial properties in a tropical montane forest on Mt. Kinabalu Borneo. Pedobiologia 53:227–233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pedobi.2009.12.003
Vohník M, Sadowsky JJ, Kohout P, Lhotakova Z, Nestby R, Kolařík M (2012) Novel root-fungus symbiosis in ericaceae: sheathed ericoid mycorrhiza formed by a hitherto undescribed basidiomycete with affinities to Trechisporales. PloS One 7:e39524. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039524
Wang H, Zhou H (2003) A simulation study on the eco-environmental effects of 3N shelterbelt in North China. Global Planet Change 37:231–246. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-8181(02)00208-4
Wang J, Li M, Zhang T, Sui X, Ma W, Ni HW (2018a) Assessment of microbial diversity of Deyeuxia angustifolia wetland through phospholipid fatty acids (PLFA) in Sanjiang Plain. Int J Agric Biol 20:1463–1470. https://doi.org/10.17957/IJAB/15.0700
Wang JS, Sun J, Xia JY, He NP, Li M, Niu S (2018b) Soil and vegetation carbon turnover times from tropical to boreal forests. Funct Ecol 32:71–82. https://doi.org/10.1111/1365-2435.12914
Wang L, Yu X, Xue Z, Huo L, Jiang M, Lu X, Zou Y (2019) Distribution characteristics of iron, carbon, nitrogen and phosphorus in the surface soils of different land use types near Xingkai lake. J Soil Sediment 19:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11368-018-2044-x
Wang X, Huang H, Gong P, Biging GS, Xin Q, Chen Y, Yang J, Liu C (2016) Quantifying multi-decadal change of planted forest cover using airborne LiDAR and Landsat imagery. Remote Sens 8:62. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs8010062
Wei J, Peršoh D, Agerer R (2010) Four ectomycorrhizae of Pyronemataceae (pezizomycetes) on Chinese pine (Pinus tabulaeformis): morpho-anatomical and molecular-phylogenetic analyses. Mycol Prog 9:267–280. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11557-009-0637-x
Xue Z, Zhou Z, An S (2020) Changes in the soil microbial communities of different soil aggregations after vegetation restoration in a semiarid grassland, China. Soil Ecol Lett 3:6–21. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42832-020-0055-1
Yang K, Zhu J, Xu S, Zhang X (2018a) Conversion from temperate secondary forests into plantations (Larix spp.): impact on belowground carbon and nutrient pools in Northeastern China. Land Degrad Dev 29:4129–4139. https://doi.org/10.1002/ldr.3169
Yang TT, Musa A, Zhang YS, Wu JB, Wang AZ, Guan DX, Minasny B (2018b) Characteristics of soil moisture under different vegetation coverage in Horqin Sandy Land Northern China. PloS One 13:e0198805. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0198805
Yang Y, Fujihara M, Li B, Yuan X, Hara K, Da L, Tomita M, Zhao Y (2014) Structure and diversity of remnant natural evergreen broad-leaved forests at three sites affected by urbanization in Chongqing metropolis, Southwest China. Landsc Ecol Eng 10:137–149. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11355-011-0160-5
Yelle DJ, Ralph J, Lu F, Hammel KE (2010) Evidence for cleavage of lignin by a brown rot basidiomycete. Environ Microbiol 10:1844–1849. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1462-2920.2008.01605.x
Yoshimura C, Gessner MO, Furumai TH (2008) Chemical properties microbial respiration and decomposition of coarse and fine particulate organic matter. J N Am Benthol Soc 27:664–673. https://doi.org/10.1899/07-106.1
Zhang H, Tang M, Chen H, Zheng C (2010) Effects of inoculation with ectomycorrhizal fungi on microbial biomass and bacterial functional diversity in the rhizosphere of Pinus tabulaeformis seedlings. Eur J Soil Biol 46:55–61. https://doi.org/10.3724/SP.J.1005.2008.01083
Zhao Y, Liu B, Zhang W, Hu C, An S (2010) Effects of plant and influent C:N:P ratio on microbial diversity in pilot-scale con-structed wetlands. Ecol Eng 36:441–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.11.011
Zheng X, Zhu JJ, Xing Z (2016) Assessment of the effects of shelterbelts on crop yields at the regional scale in Northeast China. Agr Syst 143:49–60. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agsy.2015.12.008
Zheng X, Zhu JJ, Yan QL, Song LN (2012) Effects of land use changes on the groundwater table and the decline of Pinus sylvestris var. mongolica plantations in southern Horqin Sandy Land Northeast China. Agric Water Manag 109:94–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.agwat.2012.02.010
Zuo X, Zhao H, Zhao X, Guo Y, Li Y, Luo Y (2008) Plant distribution at the mobile dune scale and its relevance to soil properties and topographic features. Environ Geol 54:1111–1120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00254-007-1104-0
Zuo X, Zhao X, Zhao H, Zhang T, Guo Y, Li Y, Huang Y (2009) Spatial heterogeneity of soil properties and vegetation-soil relationships following vegetation restoration of mobile dunes in Horqin Sandy Land Northern China. Plant Soil 318:153–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-008-9826-7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Ding, C., Zhang, W. et al. Community Characteristics of Soil Ectomycorrhizal Fungi under Different Forests in the Sandy Areas of Northeastern China. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 23, 2273–2286 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01178-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-023-01178-7