Biological characteristics of the aquilaria crassna
More than 10 years ago, Aquilaria crassna tree was known as a money-making tree. People in many localities flocked to plant Aquilaria crassna trees to transplant agarwood, embracing the dream of collecting billions. But that dream is difficult to come true because not everyone understands the biological properties of the tree to take care of it properly. In this article, Tram Tue will share with you important knowledge about the Aquilaria crassna tree - a valuable product of Vietnam that is highly appreciated in the international market, but is in danger of extinction when it is exploited. overexploitation.
What is Aquilaria crassna?
The scientific name is Aquilaria crassna Pierre ex Lecomte, belonging to the kingdom Plantae, order Malvales, family Thymelaeaceae, genus Aquilaria, species of large tree class Magnoliopsida. Aquilaria Crassna tree has many names depending on the locality such as: Agarwood tree, gourd tree, hair tree. Some ancient documents are written as gourd tree. This is one of the endemic plants, having great economic value with the main purpose of exploiting agarwood and agarwood - extremely rare aromatic essential oils, formed from the resin of the Aquilaria crassna. Agarwood is a special material used in religion, cosmetic technology, medicine, and handicrafts.

The material forest of Tram Tue's Aquilaria crassna tree
With high economic value and increasing demand in the world in general and Vietnam in particular, natural agarwood is increasingly depleted. The populations of scorpions are being severely reduced due to overexploitation and indiscriminate human exploitation. Since the 1980s, A. malaccensis has been included in the Red List of the International Union for Conservation of Nature and Natural Resources (IUCN) as a critically endangered species (IUCN, 1994). Vietnam is known as an exporter of high-quality agarwood, most of which are derived from A. crassna (Pierre) species. Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora - Washington Convention on International Trade in Endangerd Species of Wild Fauna and Flora - CITES have ability to be extinct.
A lot of measures have been taken to protect the species. In 1995, the Rainforest project was implemented with agarwood species to increase the area of planting land and sustainably use agarwood. Aquilaria crassna seed project was implemented in 1997 in Ha Tinh province on the trial of exploiting agarwood. Currently, the natural species of Do Bau is being strictly protected and studied to be widely planted throughout the country.
Classification of Aquilaria crassna trees
The genus Aquilaria includes 24 different species, however, only 17 species are capable of producing agarwood, including: A. banaensis, A. bancava, A. baillonii, A. beccariana, A. borneesis, A. crassna, A. cummingiana , A. filaria, A. gollocha, A. grandiflora, A. hirta, A. khasiana, A. microcarpa, A. rostrata, A. rugosa, A. sinensis or A. chinesis. In which, A. rugosa species was studied by Dr. Le Cong Kiet and Dr. Paul Kessler from the Netherlands found in the Central Highlands in 2005. This is the 4th species in Vietnam and the 25th in the world.
The genus Agarwood is found widely throughout Asia but is distributed mainly in the tropics from India to Southeast Asia and southern China. In our country, 6 species of agarwood have been discovered in our country that are capable of producing agarwood in the trunk, which are: A. crassna (dó bau, dó tia, dó white), A. baillonii (dó brick), A. rugosa (dó dó). wrinkled fruit), A. malaccensis (Malay doo), A. sinensis (Chinese do), A. banaensis (do ba na). Dó trees are scatteredly distributed in tropical evergreen forests and primeval moist forests in the provinces of Tuyen Quang, Thanh Hoa, Nghe An, and Ha Tinh. Especially from Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Thua Thien Hue, Khanh Hoa, Quang Nam, Da Nang, Quang Ngai, Binh Dinh, Ninh Thuan, Binh Thuan to the Central Highlands, An Giang, Kien Giang and Phu Quoc island.
Among the species capable of producing agarwood, A. crassna is the most commonly grown species due to its ability to produce the best agarwood and agarwood in the world.
Growth characteristics of the Aquilaria crassna tree
Trunk
Aquilaria crassna is a large tree, about 30-40 m high, the most common is from 15-25 m, the diameter of the trunk reaches 60-80cm, the trunk is straight. Sometimes there are troughs, the outer bark is smooth, gray-brown, the flesh is white with a lot of fiber (cellulose), longitudinal cracks are rolling, easy to peel and strip back from the base up, separate from the body. Wood flesh is light yellow, soft wood has a density of 0.395. Branches slender, curled, yellow-gray or light brown, covered with soft or smooth hairs, sparsely crowned.
Leaf
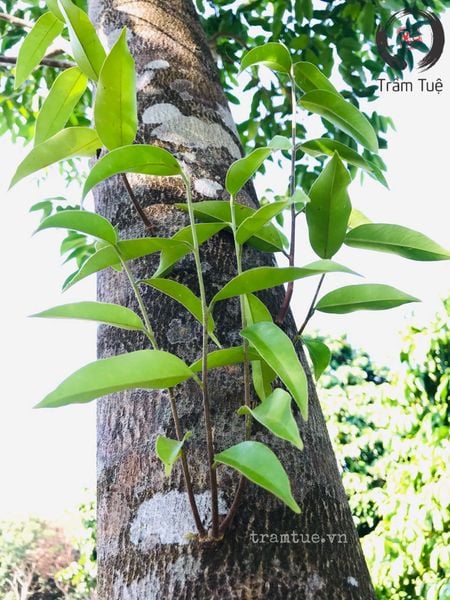
Leaves simple, alternate, oval, ovate, or spear-shaped, pointed at the base and narrow at the tip. The thin leaf blade is 8-15 cm long, 4-6 cm wide. The upper surface of the leaf blade is glossy, dark green, the lower surface is paler with fine hairs. Petiole 4-5 mm long, also hairy. Lateral tendons 15 - 18 pairs, erratic changes.

Aquilaria crassna leaves are raw materials for processing Agarwood tea.
Flower
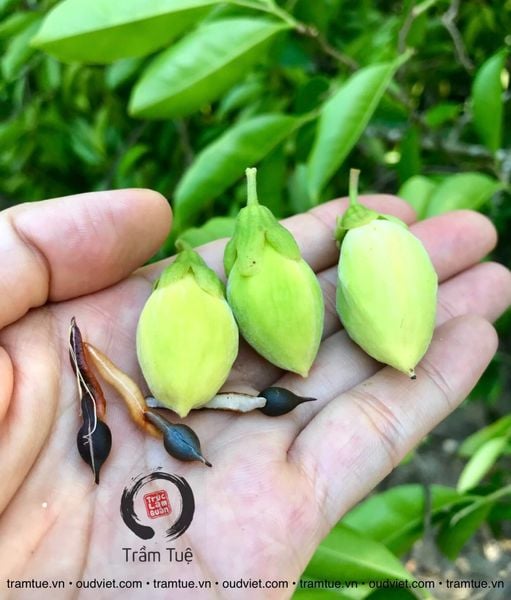
Flowers hermaphroditic, self-canopy or clustered flowers grow in the leaf axils or at the tips of branches. Flowers are small, greenish-yellow, ash-white or yellow-gray. Inflorescence peduncle, 2-3 cm long. Calyx in the lower part, bell-shaped (trumpet) with feathers on the mouth.

The flowers are greenish-yellow, pale white or yellow-gray.
Fruit
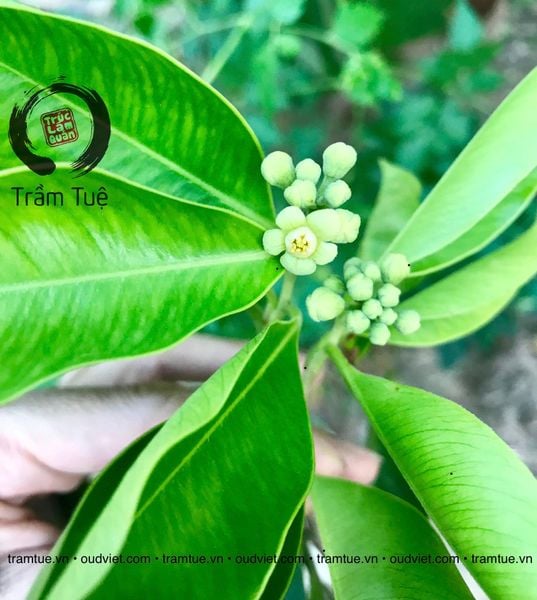
The capsule resembles an inverted ovoid or slightly flattened pear shape, 4 cm long, 2.5 -3 cm wide, 2 cm thick. The outside has soft, sparse, short hairs; The inner surface is almost smooth. Petal-shaped appendages, gourd base with nectar glands. The pods open into 2 spongy pieces, when ripe, separate themselves, usually each fruit has only 1-2 seeds. Flowering season in July, August. Fruit ripens in September, October.
Seed
There are 2 parts, the main part is at the top of the cone, the extension is at the bottom. The seeds are brown when ripe, the outer shell turns to hard wood, and the inside is soft and contains a lot of oil. One feature to note is that the seeds have a very short life (short-lived) and cannot be stored for a long time. In nature, when the seeds ripen and fall to the ground, if they meet the right humidity conditions, they will germinate immediately. If seeds are stored for more than 1 week, the germination rate will decrease by 80% or not at all.
It grows scatteredly in tropical moist evergreen forests, primary or secondary, on mountain slopes or on flat land at an altitude of 50-1000m, sometimes up to 1200m above sea level. In our country, gourd is often distributed scatteredly on the slopes of the mountain with small slopes, well drained. In the biome of do Bau, large trees are often encountered: Tau, sulphur, mahogany... Sometimes we also meet Do Bau trees growing in secondary forests with true holy species, silver-backed pomelos, pomelos, jackfruit.

Aquilaria Crassna (A. crassna) prefers typical feralit soils, mountain feralit weathered from bedrock, schist or granite. Topsoil medium or thin, slightly moist, acidic or near neutral (pH 4-6).

Aquilaria crassna is almost inverted ovate or pear-shaped, 4 cm long, 2.5 - 3 cm in diameter, with soft, short hairs, long gills, when cracked into 2 pieces, usually only 1-2 seeds each.
Economic and ecological value of Aquilaria crassna
The most important economic value of Aquilaria crassna tree is to exploit agarwood. Since ancient times, agarwood has been considered a very rare product. Today, agarwood is still a non-timber forest product with great international trade value. Around the world, agarwood is used to distill Agarwood essential oil - an important directional substance in the industry for the production of high-class cosmetics. Agarwood essential oil has special value, is used in the processing technology of high-grade aromatic substances and perfumes. Agarwood is a product of material culture, beliefs and spirituality of the Vietnamese people, which has existed from ancient times to the present day.
According to the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora, the volume of agarwood trade on the world market in the period 1995 - 1997 was about 1350 tons. The selling price of agarwood is calculated by kg depending on the quality. The selling price of agarwood in the Dubai market (Saudi Arabia) in 1993 ranged from US$27/kg (lowest grade) to US$10,000/kg (good grade). According to estimates of the Union of Science for the Production of Essential Oils - Flavors - Cosmetics of Vietnam, in the years from 1980 to 1990, the volume of agarwood of all kinds was exploited and exported from our country about 300 tons.

Aquilaria crassna tree creates agarwood.
In which, there are 2000 kg of Agarwood grades 1 - 4 worth about 1.5 million USD and 300,000 kg of Agarwood grades 5 - 9 worth about 4.5 million USD. Especially, 200g of grade 1 - 3 male period is worth USD 0.5 million and up to 2,800 kg of type 4 - 8 male period is worth USD 2.52 million. With high economic value, agarwood has brought promising promises to the forestry industry when 1 hectare of Aquilaria Crassna, creating agarwood can make a value of 1.5 - 1.8 billion VND/ 10 years. The average value generated is 150 - 180 million/ha/year, of which the profit is from 50 - 60%.
Distribution of Aquilaria crassna
In the world
In nature, the genus Aquilaria is distributed throughout Asia from the Middle - Near East, South Asia, China to Southeast Asian countries.
In the Central - Near East region, Do Bau tree grows a lot on the rugged mountains of Southern Arabia. In China, the trees are concentrated in some southern provinces, mainly Guangdong and Hainan, but the quality is not high (Tho Tram). There are 3 main species in this area: A. grandiflora Bth, A. sinensis Merr, A. yunnanensis S.C. Huang. In South Asia, there are many species in India, mainly A. khasiana H. Hallier.
Southeast Asia includes the following countries:
- Malaysia: there are 4 species: A. beccariana van Tiegh, A. microcarpa Baill, A. hirta Ridl and A. rostrata Ridl.
- Thailand: mainly A. subintegra Ding Hou.
- Indonesia: concentrated mainly on Sumatra island, there are 4 species: A. beccariana van Tiegh, A. hirta Ridl, A. microcarpa Baill, A. moszkowskii Gilg.
- Philippines: includes the following species: A. cumingiana (Decne) Ridl, A. filaria (Oken) Merr, A. apiculata Merr, A. acuminate (Merr.) Quis.
- Singapore: Primarily A. hirta Ridl.
Cambodia: Aquilaria crassna often grows scattered in coastal forests, there are 2 main species: A. crassna Pierre ex Lecomte, A. baillonii Pierre ex Lecomte.
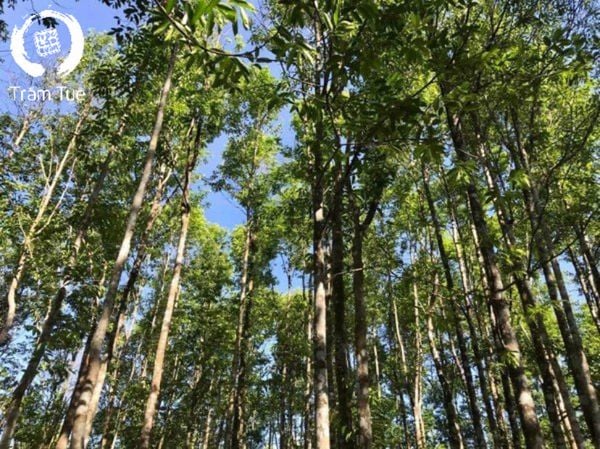

In Vietnam
Based on the specimens collected and stored from the notice of agarwood sources and investigation documents, the tree is distributed along the Truong Son mountain range throughout the length of the country.
- North: Hoang Lien Son, Vinh Phu, Hoa Binh, Ha Tay, Quang Ninh, Bac Ha, Cao Bang, Lang Son, Ha Bac.
- Central region: Thanh Hoa, Nghe An, Ha Tinh, Quang Binh, Quang Tri, Thua Thien Hue, Quang Nam, Da Nang, Quang Ngai, Binh Dinh, Phu Yen, Khanh Hoa (Dien Khanh). Central Highlands: in Gia Lai, Kon Tum, and Dak Lak provinces, agarwood-bearing areas are known as An Khe, A Yunpa, Dakto, Mang Yang, Sa Thay, Dakley and are abundant in Kon Plong with relatively thick density.
- South: Binh Thuan, Lam Dong, Binh Phuoc, Dong Nai, Tay Ninh, An Giang, Kien Giang, Phu Quoc island. In Lam Dong province, people also find agarwood in Don Duong, Di Linh, Bao Loc. In Thuan Hai province, agarwood is also encountered in the forests of Tanh Linh, Duc Linh, Ninh Son (Tay Phuoc, Phuoc Dai, Phuoc Thang, Ma Nhieu high mountain forest, Tra Co commune), Ninh Hai (Phuoc Chien, Phuoc Phuoc). Resistance). So far, it is known that gourd grows a lot on Phu Quoc island and recently found quite large agarwood roots with regenerated trees from seeds in the Bay Nui forest area, An Giang province.

Trees look like Aquilaria crassna.

Through the above article, Tram Tue hopes to have provided everyone with useful information about Aquilaria crassna tree. From there, cherish an extremely rare plant that nature has bestowed on us. You can refer to the section: Story of Agarwood to read in-depth articles and authentic images recorded by us at the company's raw material areas.