Quick Facts
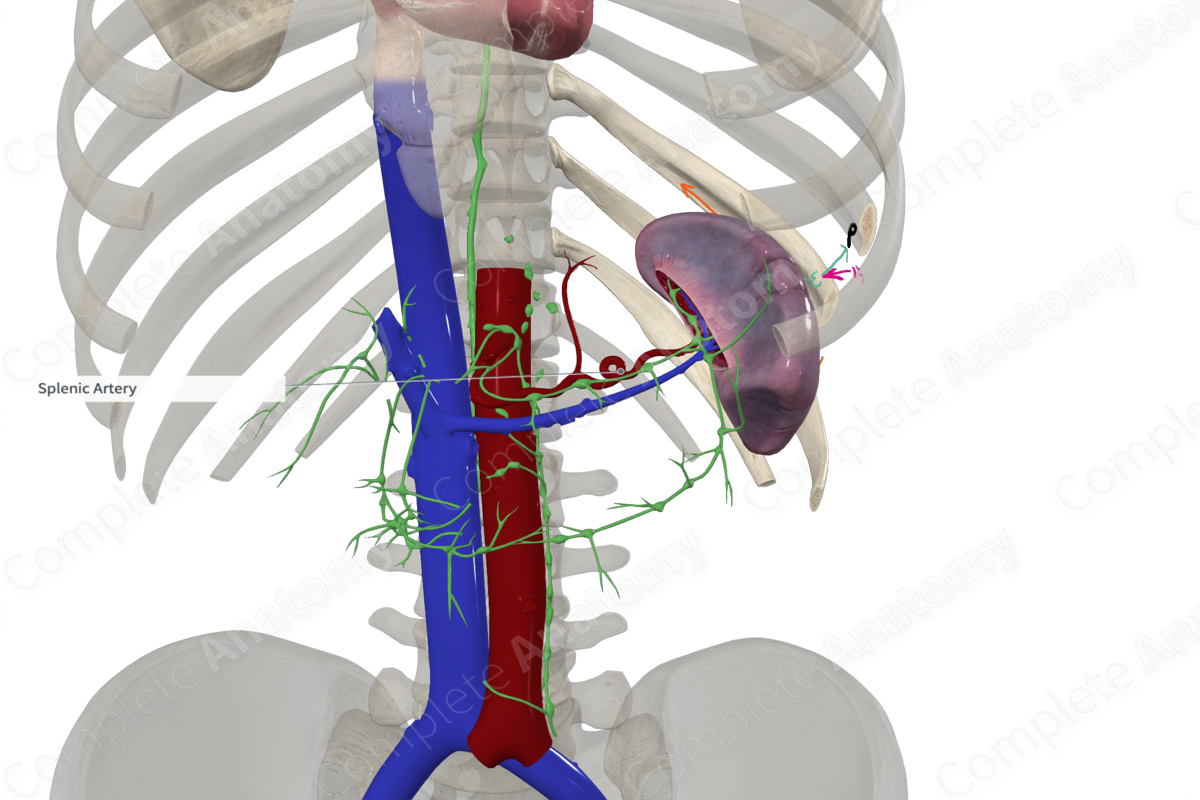
Origin: The celiac trunk.
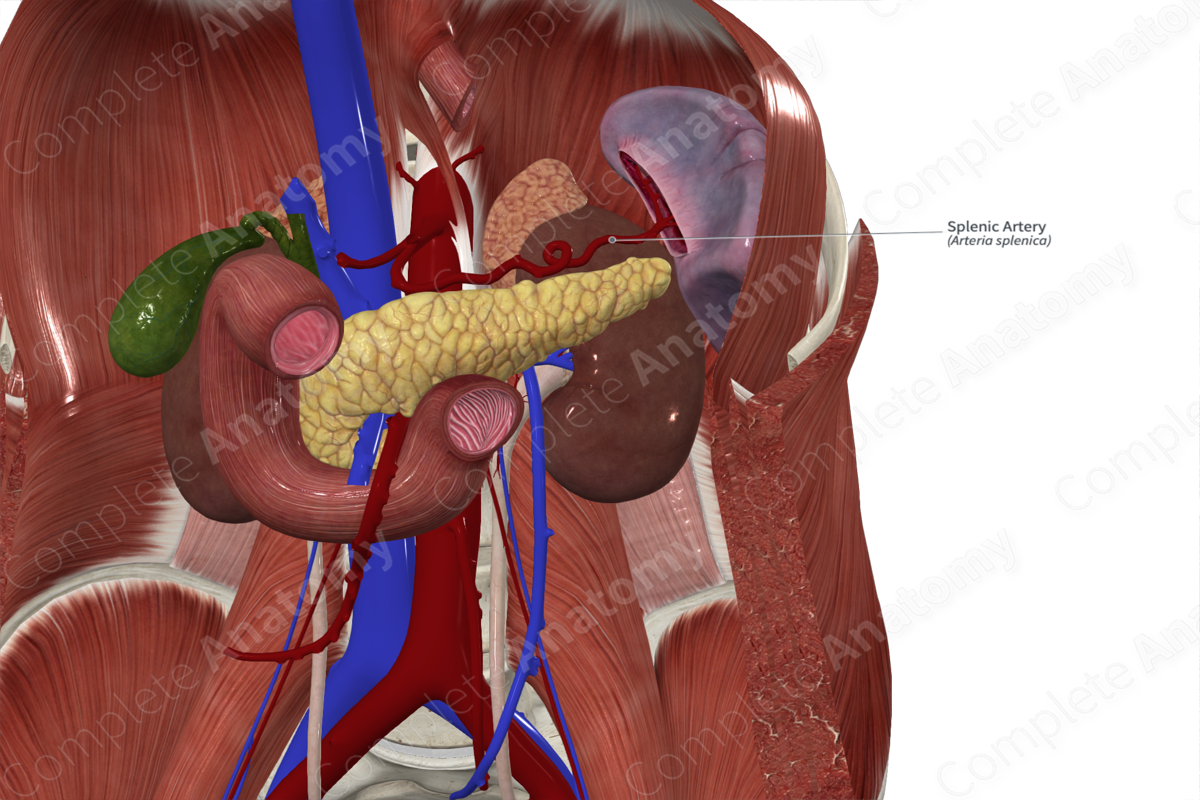
Course: Laterally towards the spleen, posterior to the pancreas.
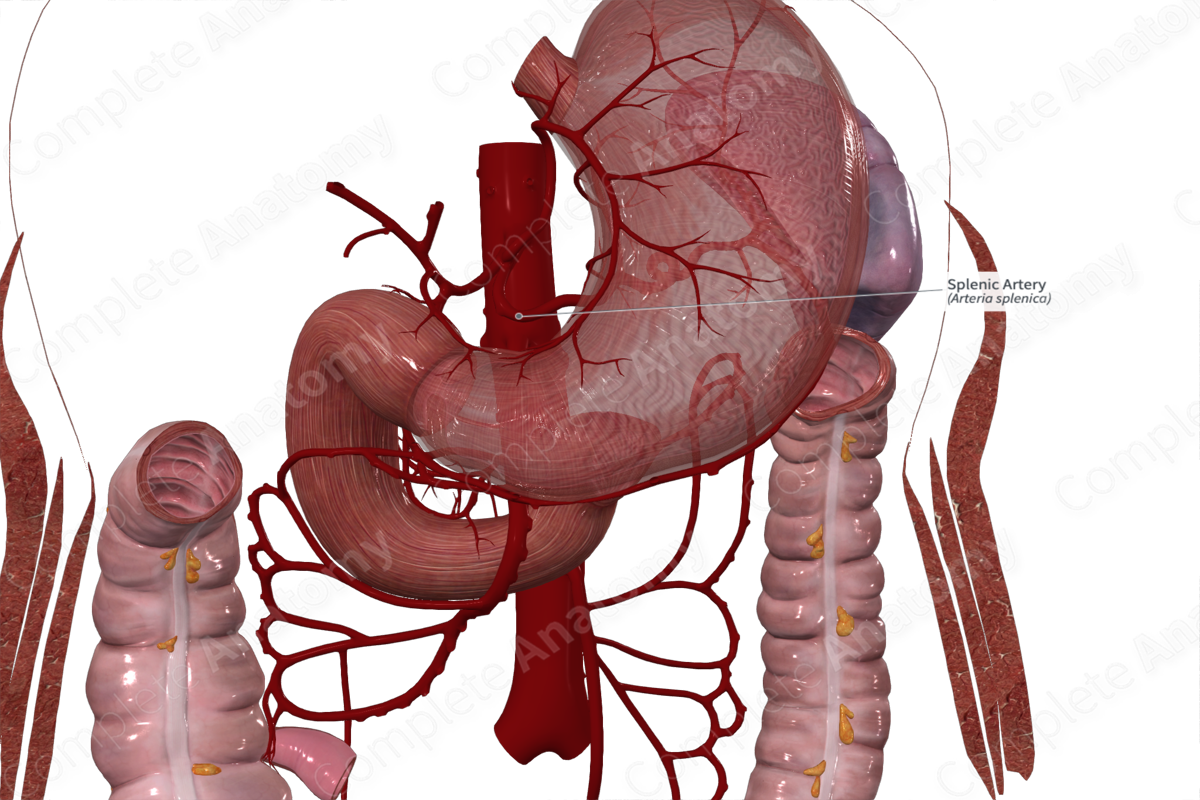
Branches: Left gastroomental, short gastric branches, posterior gastric, dorsal pancreatic, and greater pancreatic arteries.
Supplied Structures: Spleen, stomach, greater omentum, and pancreas.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
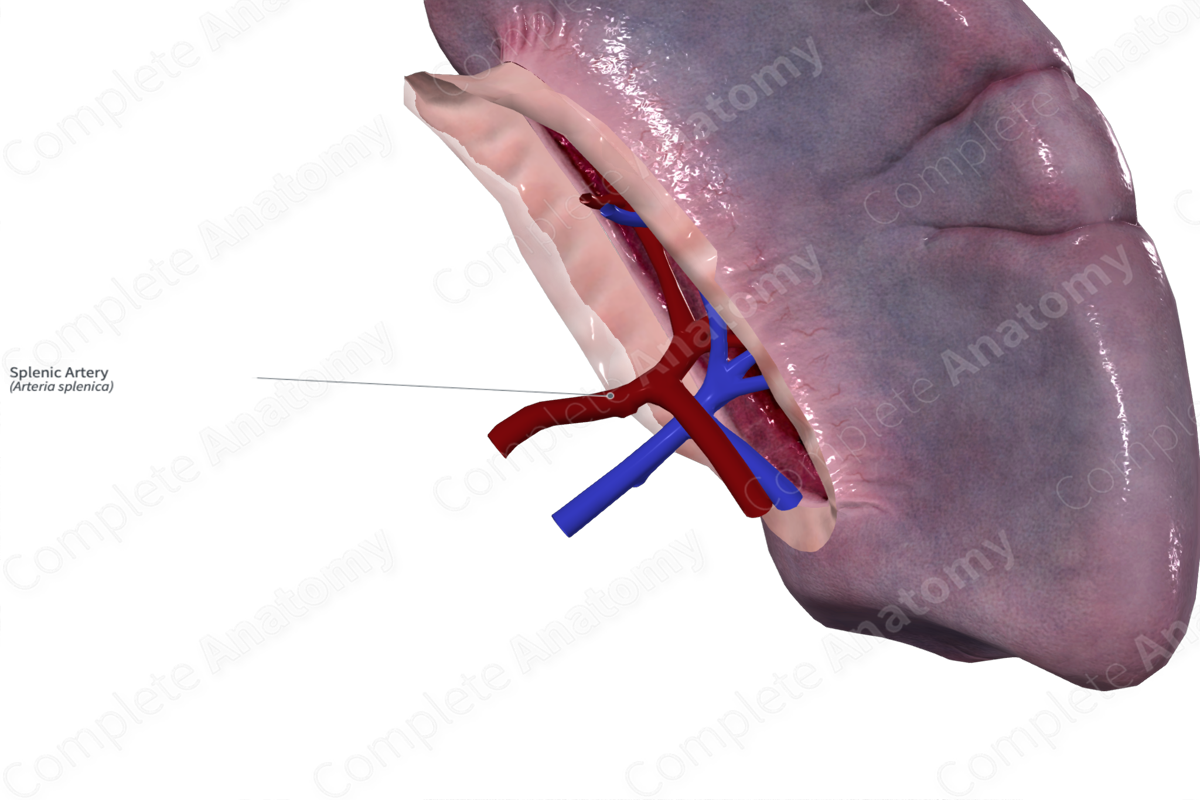
The splenic artery is the largest branch of the celiac trunk.
Course
The splenic artery has a very distinctive tortuous appearance and ranges in length from 8 to 32 cm. It first travels anteroinferiorly towards the pancreas. It then courses laterally, posterior to the upper portion of the body and tail of the pancreas. It passes anterior to the left kidney and left suprarenal gland before it enters the hilum of the spleen.
Branches
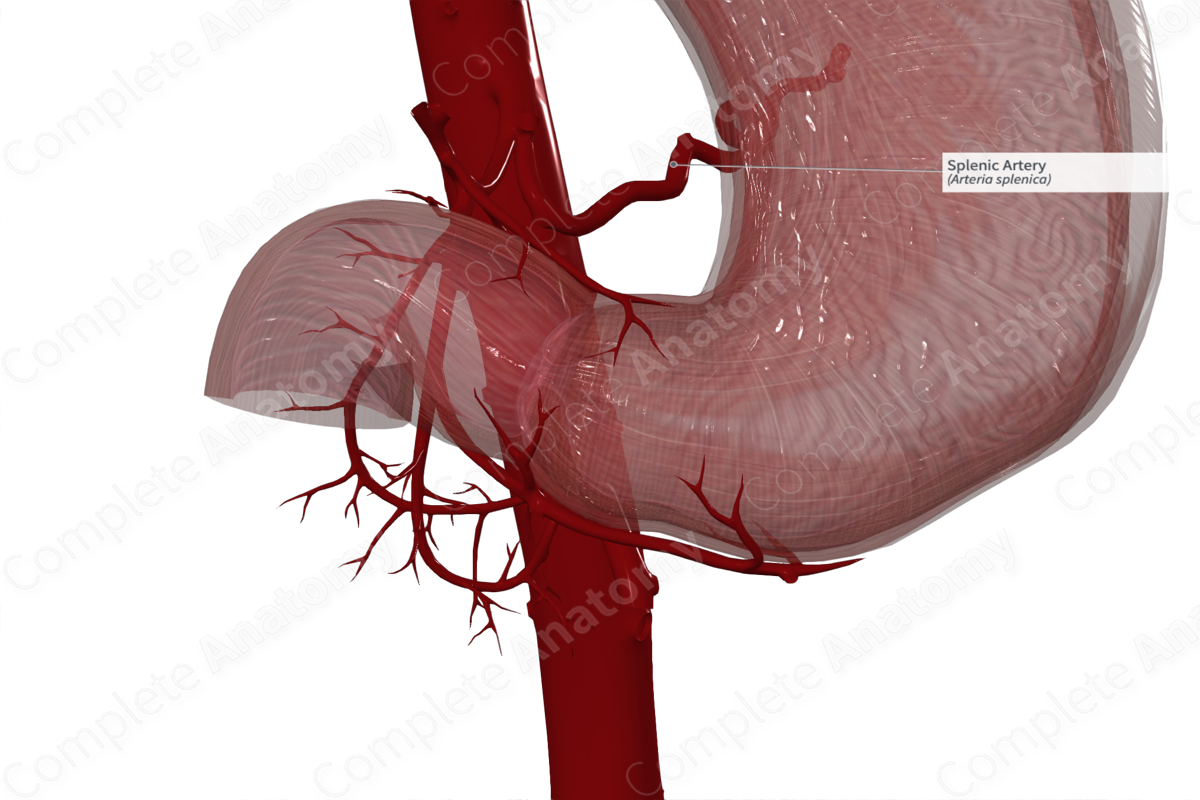
As it travels towards the hilum of the spleen, the splenic artery gives off pancreatic branches (dorsal pancreatic artery, greater pancreatic artery, and the artery to the tail of the pancreas) and gastric branches (5–7 short gastric arteries and the left gastroomental artery). Additionally, in approximately 25.5% of cases a posterior gastric artery arises from the splenic artery (and arises from the left gastric artery in 41.8% of individuals) (Loukas et al., 2007).
As the splenic artery reaches the splenic hilum, it divides into two or three branches that supply the spleen.
Supplied Structures
The pancreatic branches supply the body and tail of the pancreas. The short gastric branches, the posterior gastric artery and the left gastroomental artery supplies the stomach and the greater omentum. The terminal branches of the splenic arteries supply the spleen.
References
Loukas, M., Wartmann, C. T., Louis, R. G., Tubbs, R. S., Ona, M., Curry, B., Jordan, R. and Colborn, G. L. (2007) 'The clinical anatomy of the posterior gastric artery revisited', Surg Radiol Anat, 29(5), pp. 361-6.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Artery

When the artery is occluded blood is forced through the collateral vessels, drastically increasing fluid shear stress and triggering an inflammatory response which drives vessel remodeling.