Professional Documents
Culture Documents
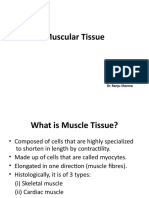
Muscle Tissue
Uploaded by
Jennie Watanabe0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
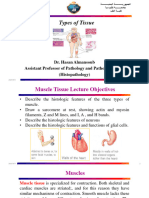
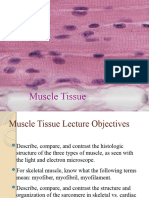
15 views1 pageThis document discusses the three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is composed of elongated, cylindrical cells with peripheral nuclei. Cardiac muscle has long, branched cells with one or two central nuclei. Smooth muscle contains spindle-shaped cells with a single central nucleus. The key distinguishing characteristics between the three muscle types are their striation, cell shape, number of nuclei, filament ratio, and motor control.
Original Description:
Original Title
muscle tissue
Copyright
© © All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
Share this document
Did you find this document useful?
Is this content inappropriate?
Report this DocumentThis document discusses the three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is composed of elongated, cylindrical cells with peripheral nuclei. Cardiac muscle has long, branched cells with one or two central nuclei. Smooth muscle contains spindle-shaped cells with a single central nucleus. The key distinguishing characteristics between the three muscle types are their striation, cell shape, number of nuclei, filament ratio, and motor control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
0 ratings0% found this document useful (0 votes)
15 views1 pageMuscle Tissue
Uploaded by
Jennie WatanabeThis document discusses the three main types of muscle tissue: skeletal, cardiac, and smooth muscle. Skeletal muscle is composed of elongated, cylindrical cells with peripheral nuclei. Cardiac muscle has long, branched cells with one or two central nuclei. Smooth muscle contains spindle-shaped cells with a single central nucleus. The key distinguishing characteristics between the three muscle types are their striation, cell shape, number of nuclei, filament ratio, and motor control.
Copyright:
© All Rights Reserved
Available Formats
Download as DOCX, PDF, TXT or read online from Scribd
You are on page 1of 1
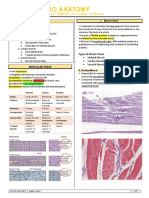
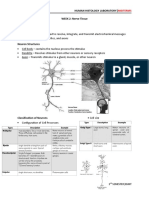
HUMAN HISTOLOGY LABORATORY|MIDTERMS
Muscle Tissue
General Features Types of Muscle Tissue
Terminology: Skeletal
Cardiac
prefixes sarco and myo
Smooth
Specialization for Contraction:
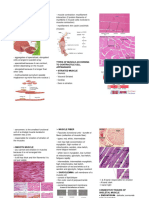
Skeletal Muscle
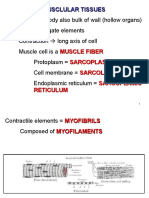
Myofilaments: thin filaments containing
Mature muscle fibers are elongated,
actin and thick filaments containing
unbranched, cylindrical, and
myosin.
multinucleated cells.
Mesodermal Origin flattened, peripheral nuclei
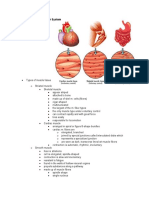
Nearly all muscle cells arises from Cardiac Muscle
mesoderm. Smooth muscle cells of the
Cardiac muscle fibers are long, branched
iris arise from ectoderm.
cells with one or two ovoid central
Cell Shape nuclei.
The length of the muscle cells is greater Smooth Muscle
than its width. Muscle cells are
Mature smooth muscle fibers, are
therefore often calls muscle fibers or
spindle-shaped cells with a single
myofibers.
central ovoid nucleus.
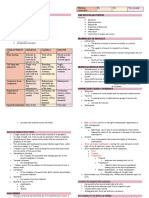
Distinguishing Characteristics of Muscle Types
Features Skeletal Cardiac Smooth
Striation Striated Striated Non-striated
Cells Thick, long, cylindric, Branched, cylindric Small, spindle shaped
unbranched
Nuclei per cell Many: peripheral One or two; central One; central
Filament ratio Six thin/ one thick Six thin/ one thick Twelve thin/ one thick
Motor-end plates Present Absent Absent
Motor control Voluntary Involuntary Involuntary
2ND SEMESTER|BSMT
You might also like
- BIOL 240 Lab Report 1Document11 pagesBIOL 240 Lab Report 1Ben CharlesNo ratings yet
- Introduction To StainingDocument15 pagesIntroduction To Stainingitzel rendonNo ratings yet
- Skeletal Muscle Tissue & Muscle OrganizationDocument90 pagesSkeletal Muscle Tissue & Muscle Organizationtiiandi100% (3)
- Cytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleolus Nucleus Organ Tissue Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast ChromosomeDocument17 pagesCytoplasm Mitochondrion Nucleolus Nucleus Organ Tissue Vacuole Cell Membrane Cell Wall Chlorophyll Chloroplast Chromosomeardusias100% (1)
- A. Prof. DR Ruzanna PHD, DM, MD, MSCDocument19 pagesA. Prof. DR Ruzanna PHD, DM, MD, MSCHassoun hassounNo ratings yet
- Histology of Muscle: Lecturer Anatomy DepartmentDocument19 pagesHistology of Muscle: Lecturer Anatomy DepartmentSUMAN GHOSHNo ratings yet
- Muscles and Muscle Tissue: Functional Anatomy, Excitation-Contraction CouplingDocument46 pagesMuscles and Muscle Tissue: Functional Anatomy, Excitation-Contraction CouplingRevanth VejjuNo ratings yet
- Eme 1Document20 pagesEme 1Tara LingatingNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument37 pagesMuscular Tissueمؤمل عدنان الشمخيNo ratings yet
- AHS 131 Lecture 4 MusclesDocument60 pagesAHS 131 Lecture 4 MusclesBikash MainaliNo ratings yet
- Muscle and Nerve HistoPHysioDocument91 pagesMuscle and Nerve HistoPHysioashley nicholeNo ratings yet
- Histo MusDocument33 pagesHisto MusBeyhNo ratings yet
- Muscles:: How They Work Why Skeletal and Smooth Muscle Are Suited To Different RolesDocument27 pagesMuscles:: How They Work Why Skeletal and Smooth Muscle Are Suited To Different Rolestalkameow123No ratings yet
- 6.0 Muscular SystemDocument76 pages6.0 Muscular System[R2A] Khadijah AzlanNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYDocument10 pagesChapter 7 ANATOMY AND PHYSIOLOGYAngela Mae MeriñoNo ratings yet
- Histology 6Document20 pagesHistology 6mkomyu088No ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument17 pagesAnimal TissuesLuis WashingtonNo ratings yet
- Muscular TissueDocument22 pagesMuscular TissueZidane LassaadNo ratings yet
- Week 3 - Muscles LabDocument19 pagesWeek 3 - Muscles LabMarx AsuncionNo ratings yet
- Microscopic Structure of Muscles DR - Dilrukshi ThavinDocument26 pagesMicroscopic Structure of Muscles DR - Dilrukshi ThavinOmar Ali AyoubkhanNo ratings yet
- Histology 6 MuscleDocument88 pagesHistology 6 MuscleAbdul RahmanNo ratings yet
- Week 7: Muscular System Histology and PhysiologyDocument101 pagesWeek 7: Muscular System Histology and PhysiologyHuffy PotterNo ratings yet
- Histology Study Material - Muscle TissuesDocument2 pagesHistology Study Material - Muscle TissuesYumeeeeeyNo ratings yet
- ANAPHY LAB W5.5 ReviewerDocument5 pagesANAPHY LAB W5.5 Reviewerangelmalang41No ratings yet
- 04 Muscle 2022Document39 pages04 Muscle 2022AlkadafeNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissues - PakaiDocument54 pagesMuscle Tissues - PakaiAisyah RaihanNo ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue - HistologyDocument35 pagesMuscle Tissue - HistologyjabirNo ratings yet
- ANAPHYSIO LEC (Midterms)Document14 pagesANAPHYSIO LEC (Midterms)KIM EUNHANo ratings yet
- 3c. Muscle 22893Document15 pages3c. Muscle 22893Musharaf RehmanNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument8 pagesMuscle TissueMiyuki MeyNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument7 pagesMuscular SystemHenry BuñagNo ratings yet
- Midterm Reviewer - Google DocsDocument61 pagesMidterm Reviewer - Google Docscpagente01No ratings yet
- Anatomy and Physiology of MuscleDocument51 pagesAnatomy and Physiology of Musclenandhini raguNo ratings yet
- 7 - MuscularDocument18 pages7 - MuscularMenna GomaaNo ratings yet
- Types of MusclesDocument8 pagesTypes of MusclesJoan Vito CruzNo ratings yet
- MuscularDocument61 pagesMuscularFranz DiazNo ratings yet
- Muscletissue 2. CardiacDocument8 pagesMuscletissue 2. CardiacAloha I. SarolNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument33 pagesMuscle TissueFady FadyNo ratings yet
- 6 - Muscle Tissue DR - Vera 2021-2Document45 pages6 - Muscle Tissue DR - Vera 2021-2Wilmarilys Ramos MartellNo ratings yet
- Muscle Cell ComparisonDocument1 pageMuscle Cell ComparisonRaihanur KiranNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument30 pagesMuscle TissueAhwaar Chaudary100% (1)
- Muscle TissueDocument20 pagesMuscle TissueDheeraj MenezesNo ratings yet
- Topic 5 Genhisto NotesDocument6 pagesTopic 5 Genhisto NotesShiina MashiroNo ratings yet
- Lesson 5 Muscular SystemDocument8 pagesLesson 5 Muscular SystemRodrigo SeriozaNo ratings yet
- Unit 3-Part 1-Skeletal Muscle Anatomy, Sarcomeres, and EC Coupling-SDocument32 pagesUnit 3-Part 1-Skeletal Muscle Anatomy, Sarcomeres, and EC Coupling-Sgdhanoa55No ratings yet
- Muscle Tissue - Wo AudioDocument33 pagesMuscle Tissue - Wo Audiozahra nabilaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System EducDocument9 pagesMuscular System EducRam AugustNo ratings yet
- Histo 1.9 Muscle TissueDocument7 pagesHisto 1.9 Muscle TissueMonesa Christy VillanuevaNo ratings yet
- Muscular System - Part 1 (BSN - 1F)Document5 pagesMuscular System - Part 1 (BSN - 1F)yulo.jhoselleanne.bsnNo ratings yet
- 3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015Document34 pages3b. Muscle Tissues-Lecture Last - 2015yigermalamanuel32No ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument16 pagesMuscular Systemjgabiran02No ratings yet
- Histology of Heart and Vessels - CVSF2023 - StudentDocument44 pagesHistology of Heart and Vessels - CVSF2023 - StudentJose PerezNo ratings yet
- Muscular SystemDocument13 pagesMuscular SystemavilajrjimuelNo ratings yet
- Chapter 4 AnaphysioDocument11 pagesChapter 4 AnaphysioAlanna Mae LinazaNo ratings yet
- 10th Week - Cardiac Muscle HistologyDocument15 pages10th Week - Cardiac Muscle Histologyნია გელაშვილიNo ratings yet
- Animal TissuesDocument4 pagesAnimal TissuesbendipatkoNo ratings yet
- Muscular Tissue: Sekolah Tinggi Teknologi Industri Farmasi BogorDocument12 pagesMuscular Tissue: Sekolah Tinggi Teknologi Industri Farmasi Bogorrizal bohalNo ratings yet
- Anaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemDocument4 pagesAnaphy Reviewer Muscular SystemJoyce Kathreen Ebio LopezNo ratings yet
- 5 MuscleDocument3 pages5 MuscleNicolePorsueloNo ratings yet
- Musculoskeletal System: Sugito Wonodirekso, MS, DR Department of Histology FmuiDocument54 pagesMusculoskeletal System: Sugito Wonodirekso, MS, DR Department of Histology FmuiJeanyfer Claudia FetrisNo ratings yet
- Muscle TissueDocument33 pagesMuscle Tissues vNo ratings yet
- Dasar-Dasar HsitologiDocument25 pagesDasar-Dasar HsitologiAkhdan NajlaNo ratings yet
- HISTO LAB - WEEK 2 Nerve TissueDocument3 pagesHISTO LAB - WEEK 2 Nerve TissueJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- HISTO LAB Week 1 Bone and CartilageDocument4 pagesHISTO LAB Week 1 Bone and CartilageJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Circulatory SystemDocument3 pagesCirculatory SystemJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Peripheral BloodDocument4 pagesPeripheral BloodJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Unit 1-The Reproductive System The Ovarian CycleDocument4 pagesUnit 1-The Reproductive System The Ovarian CycleJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Chapter 7 - Preventing Pregnancy Common Ways of Preventing PregnancyDocument3 pagesChapter 7 - Preventing Pregnancy Common Ways of Preventing PregnancyJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Self-Defense Law of Self DefenseDocument2 pagesSelf-Defense Law of Self DefenseJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- The Male Reproductive Organs IncludeDocument2 pagesThe Male Reproductive Organs IncludeJennie WatanabeNo ratings yet
- Plant & Animal Cells W FunctionsDocument2 pagesPlant & Animal Cells W FunctionsHananel ValerieNo ratings yet
- HistologyDocument57 pagesHistologyAnonymous 9xheGVRM1100% (2)
- Bone Marrow ExaminationDocument1 pageBone Marrow ExaminationCloudy GemsNo ratings yet
- Proses Deparafinasi Sediaan Jaringan Ginjal Dengan Dan Tanpa Pemanasan Menggunakan Mineral Oil Pada Pewarnaan HeDocument8 pagesProses Deparafinasi Sediaan Jaringan Ginjal Dengan Dan Tanpa Pemanasan Menggunakan Mineral Oil Pada Pewarnaan HerizkyNo ratings yet
- Central Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellDocument6 pagesCentral Mindanao University Department of Biology: "The CellNEIL MARTINEZNo ratings yet
- Answer Key To Short Answer Questions For "Look Out Below: A Case Study On Bone Tissue Structure and Repair"Document3 pagesAnswer Key To Short Answer Questions For "Look Out Below: A Case Study On Bone Tissue Structure and Repair"PRINCESS YVONNE ARELLANONo ratings yet
- Procedure of Gram StainDocument5 pagesProcedure of Gram StainMAHDI TV ASIANo ratings yet
- Answers: Pengenalan Kepada Biologi Dan Peraturan MakmalDocument58 pagesAnswers: Pengenalan Kepada Biologi Dan Peraturan Makmal牛油果AvocadoNo ratings yet
- Charlie Muller CellTypesSEDocument10 pagesCharlie Muller CellTypesSECharles MullerNo ratings yet
- Jawapan: Pengenalan Kepada Biologi Dan Peraturan MakmalDocument52 pagesJawapan: Pengenalan Kepada Biologi Dan Peraturan MakmalNurasyikin SaidinNo ratings yet
- Fundamentals of Crop PhysiologyDocument19 pagesFundamentals of Crop PhysiologyRsNo ratings yet
- Blood GroupsDocument28 pagesBlood GroupsKamran ZaheerNo ratings yet
- Artikel 3Document7 pagesArtikel 3Ratih ArmaNo ratings yet
- Bone Healing, Regeneration and Repair: On BiomolecoulerDocument26 pagesBone Healing, Regeneration and Repair: On BiomolecoulerSarah Nabella PutriNo ratings yet
- Defining The Practice of Medical TechnologyDocument47 pagesDefining The Practice of Medical TechnologyCharles Ian OliquinoNo ratings yet
- Dog Blood TypesDocument10 pagesDog Blood Typespuscas16ramona7105100% (2)
- XII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyDocument1 pageXII - CBSE - Worksheet - Anatomy of Flowering Plants - Answer KeyKishor KumarNo ratings yet
- Histo - Course HeroDocument16 pagesHisto - Course HeroNatalie EnriquezNo ratings yet
- Trans 1 - Cells As A Unit of Health and DiseaseDocument12 pagesTrans 1 - Cells As A Unit of Health and DiseaseCedrick BunaganNo ratings yet
- Artifacts in HistopathologyDocument8 pagesArtifacts in Histopathologysyed ahmedNo ratings yet
- Topic - Composition of BloodDocument18 pagesTopic - Composition of BloodChhavi SainiNo ratings yet
- Class 9th MCQsDocument8 pagesClass 9th MCQsAmit PratapNo ratings yet
- Anatomy-and-Pathophysiology-of-Anemia LEVEL 2Document8 pagesAnatomy-and-Pathophysiology-of-Anemia LEVEL 2Briana Louise HernandezNo ratings yet
- A Cell Is Like A CompanyDocument1 pageA Cell Is Like A CompanyFRANZ JOSEPH PINEDA HENo ratings yet
- Axonal Degeneration: Nerve RegenerationDocument1 pageAxonal Degeneration: Nerve RegenerationYogi drNo ratings yet
- Tissue BiomechanicsDocument76 pagesTissue BiomechanicsSanket RoutNo ratings yet
- Module 1. Topic 1. IntroductionDocument11 pagesModule 1. Topic 1. IntroductionMusawwira KulidtodNo ratings yet