. Fresh-water biology. Freshwater biology. 266 176 (i7S) 177 (170) 178 (179) 179 (178) j8o (169) 181 (186) 182 (i8s) 183 (184) 184 (183) FRESH-WATER BIOLOGY Elongate, spindle-shaped; chromatophores two, ribbon-shaped; eye-spot obscure. , Chlorangium Stein. Representative species. Chlorangium stentorinum Ehrenberg 1838. Flagella terminal, subequal. Attached during the sedentary stage by a short, thick pedicel, singly or in groups up to ten or twelve zooids. Length 24 ju. Pond water, often attached to various Entomostraca. Fig. 443. Chlorangium stentorinum. X 37s. (After Stein.) Cuticle separate
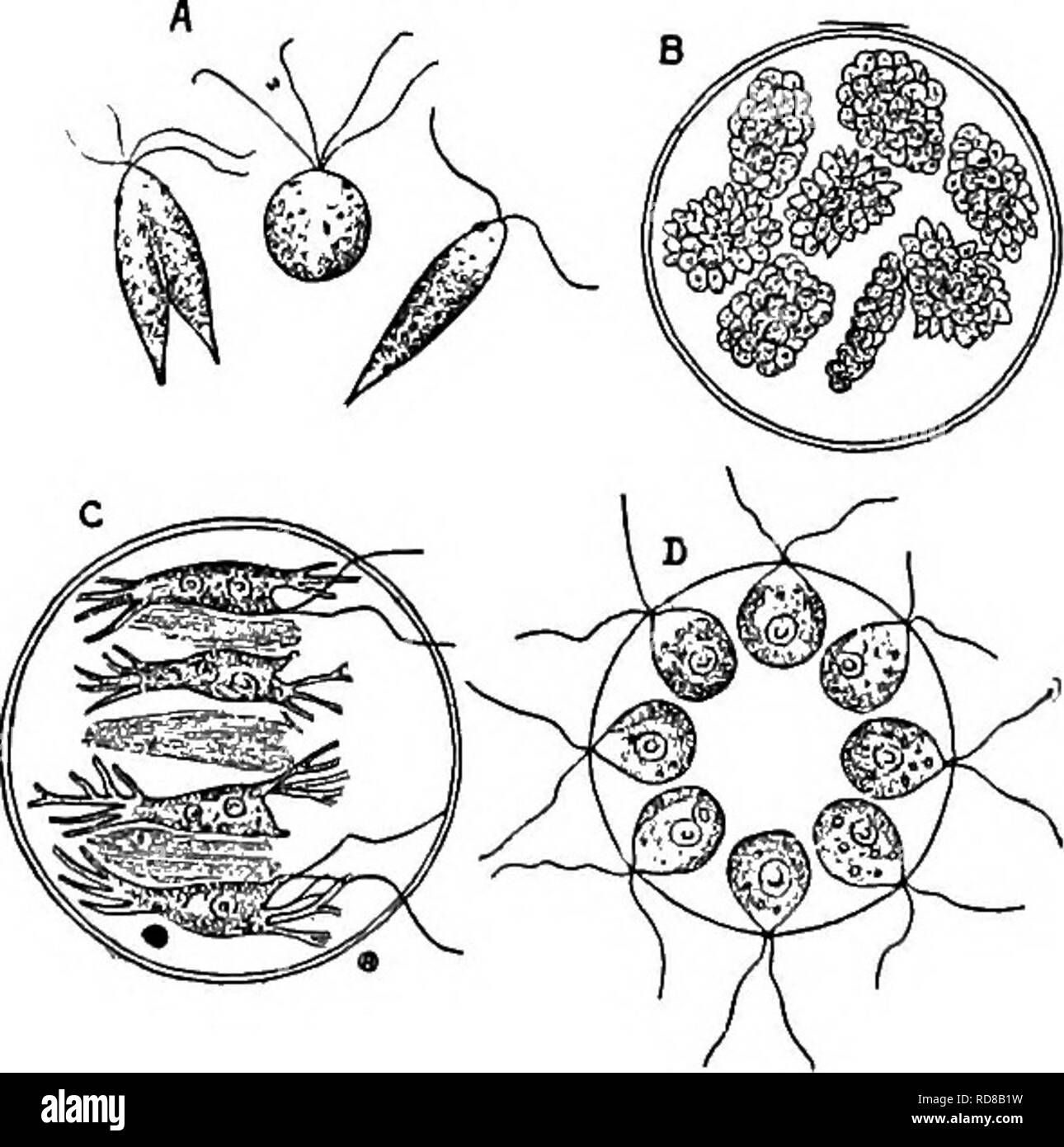
Image details
Contributor:
The Book Worm / Alamy Stock PhotoImage ID:
RD8B1WFile size:
7.1 MB (302.7 KB Compressed download)Releases:
Model - no | Property - noDo I need a release?Dimensions:
1575 x 1586 px | 26.7 x 26.9 cm | 10.5 x 10.6 inches | 150dpiMore information:
This image is a public domain image, which means either that copyright has expired in the image or the copyright holder has waived their copyright. Alamy charges you a fee for access to the high resolution copy of the image.
This image could have imperfections as it’s either historical or reportage.
. Fresh-water biology. Freshwater biology. 266 176 (i7S) 177 (170) 178 (179) 179 (178) j8o (169) 181 (186) 182 (i8s) 183 (184) 184 (183) FRESH-WATER BIOLOGY Elongate, spindle-shaped; chromatophores two, ribbon-shaped; eye-spot obscure. , Chlorangium Stein. Representative species. Chlorangium stentorinum Ehrenberg 1838. Flagella terminal, subequal. Attached during the sedentary stage by a short, thick pedicel, singly or in groups up to ten or twelve zooids. Length 24 ju. Pond water, often attached to various Entomostraca. Fig. 443. Chlorangium stentorinum. X 37s. (After Stein.) Cuticle separated from body mass. .178 Cuticle smooth. Raemotococcus Agardh. Cuticle rough. Coccomonas Stein. Forming colonies. 181 Colonies plate-like with flagella upon one face only. . 182 Colonies in a four-sided plate with envelop closely adherent. Cells four or sixteen. , Gonium Miiller . 183 Four cells. Sixteen cells. Gonium sociale Dujardin 1838. Gonium pectorale Miiller 1773. In this species each of the sixteen cells of the colony produces a daughter colony of sixteen cells. As the daughter colonies develop, a secondary shifting of the cells takes place resulting in individuals of the adult colonies lying in one plane. Fig. 444. Gonium pectorale. X 350. (After Stein.) 185 (182) Colonies in a rounded plate with envelop swollen, oval, or spherical. Stephanosphaera Cohn. Representative species. . Stephanosphaera pluvialis Cohn 1853. Cells four or eight, ovoid or spindle-shaped, with numerous processes.' This form represents a transition from a rosette arrangement of cells to a spherical aggregate, the units being arranged in a rosette but surrounded by a common gelati- nous envelop.. Fig. 445. Stephanosphaera pluvialis. .4, copula- tion of gametes; B, spore formation; C, cells with protoplasmic processes; Z), colony of eight cells. A X 132s; B, C, DX 425- (After Hieronymus.) 186 (181) Colonies spherical, ellipsoidal, or flattened, with flagella not confined to one face 187 187 (190) Coloni